Hyperparathyroidism in cats is a disease associated with a metabolic disorder (metabolic process), when calcium is washed out of bone tissue and enters the bloodstream. In accordance with the physiological norm, 99% of its volume is contained in the structures of the skeleton and tooth enamel, and the remaining 1% is present in the form of ions in the blood. With hyperparathyroidism, the balance is disrupted, which causes pathological changes in the body. Read more about the symptoms and treatment of this disease in our article.
Hyperparathyroidism in cats: symptoms and treatment
Hormones affecting calcium balance
The optimal amount of minerals in the blood, including calcium, is ensured by the action of hormones. One of these is parathyroid hormone, which is synthesized by the parathyroid organ. Under its influence, the calcium needed by the body is borrowed from the bones, and the kidneys begin to work to maximize the retention of these ions.
Mineral imbalance is followed by deterioration in well-being
The thyroid gland produces calcitonin, a specific hormone that has the opposite effect, thereby maintaining a healthy mineral balance. An incorrect balance can have detrimental consequences for your pet's health.
Description example
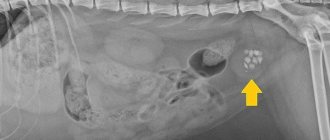
Descriptive part: In the wings of the ilium and in the ischial bones on both sides, single homogeneous focal formations are identified, hyperintense by T2, T2stir, hypointense by T1 VI, relatively homogeneous structure, with clear, somewhat uneven contours, with signs of lytic destruction of the cortical layer of the inner surface of the left wing ilium, with the presence of a minimal soft tissue component in this area, ranging in size from ..x..x.. cm to ..x..x.. cm.
CONCLUSION: MR picture of the same type of focal changes in the ilium and ischium on both sides with signs of destruction of the cortical layer of the wing of the left ilium (may correspond to Brown tumors, as a manifestation of primary hyperparathyroidism).
What happens in the body when there is calcium deficiency?
Calcium deficiency leads to a decrease in its volume in the blood, which, in turn, stimulates the active production of parathyroid hormone. It promotes the active removal of the mineral from natural storage (i.e. skeletal bones) and its transfer into the blood to maintain its normal composition.
Phosphorus oversaturation occurs in cats that often eat fish.
In this case, the bones are destroyed without having time to recover. They become weak and fragile. When an animal's diet is oversaturated with phosphorus, the problem worsens, since this trace element (if there is too much of it) interferes with the normal absorption of calcium from the intestines.
Clinical manifestations
Hyperparathyroidism can be asymptomatic and diagnosed accidentally during examination. With hyperparathyroidism, the patient simultaneously develops symptoms of damage to various organs and systems - stomach ulcers, osteoporosis, urolithiasis, cholelithiasis, etc.
Early manifestations of hyperparathyroidism include rapid fatigue during exertion, muscle weakness, headache, difficulty walking (especially when climbing or covering long distances), and a waddling gait is characteristic. Most patients report memory impairment, emotional imbalance, anxiety, and depression. Older people may experience severe mental disorders. With long-term hyperparathyroidism, the skin becomes an earthy gray color.
At the late stage of bone hyperparathyroidism, softening, curvature, pathological fractures (during normal movements, in bed) of the bones occur, and scattered pain occurs in the bones of the arms and legs, and the spine. As a result of osteoporosis, the jaws become loose and healthy teeth fall out. Due to skeletal deformation, the patient may become shorter. Pathological fractures are not painful, but heal very slowly, often with deformities of the limbs and the formation of false joints. Periarticular calcifications are found on the arms and legs. A large adenoma can be palpated on the neck in the area of the parathyroid glands.
Visceropathic hyperparathyroidism is characterized by nonspecific symptoms and a gradual onset. With the development of hyperparathyroidism, nausea, stomach pain, vomiting, flatulence occur, appetite is impaired, and weight decreases sharply. Patients are found to have peptic ulcers with bleeding of various locations, prone to frequent exacerbations, relapses, as well as signs of damage to the gallbladder and pancreas. Polyuria develops, urine density decreases, and unquenchable thirst appears. In the later stages, nephrocalcinosis is detected, symptoms of renal failure develop, progressing over time, and uremia.
Hypercalciuria and hypercalcemia, the development of calcification and vascular sclerosis, leads to impaired nutrition of tissues and organs. A high concentration of Ca in the blood contributes to damage to the heart vessels and increased blood pressure, causing angina attacks. With calcification of the conjunctiva and cornea of the eyes, red eye syndrome is observed.
Table 1.
Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism.
Diet for a cat with hyperparathyroidism
The range of well-known food brands always includes products intended for animals with health problems.
Table. Ready-made food for animals with kidney pathology
| Name | Characteristic |
ADVANCE Cat Renal (Spain) | Therapeutic diet for cats with kidney disease. Complete and balanced composition for animals with poorly functioning kidneys and calcium deficiency. Prevents the formation of stones. Features low phosphorus content and high quality proteins |
| Hill's Feline j/d (USA) | Composition for cats with bone and joint problems. Normalizes their functionality in 1 month. Contains the optimal amount of nutrients, as well as beneficial omega-3 fatty acids |
| Royal Canin Mobility for cats and cats (France) | A complete product with chondroprotectors that improves the mobility of animal joints after injuries and operations, as well as for diseases of the musculoskeletal system |
| Pro Plan Veterinary Diets Feline NF Renal Function dry (Italy) | Medicinal composition for adult and old cats and cats, regardless of breed, all breeds with chronic renal failure and its complications |
| Pro Plan NF ST/OX RENAL FUNCTION (Italy) | Ready-made food for cats containing a small amount of dietary phosphate. Inhibits the development of renal failure and significantly reduces the incidence of secondary hyperparathyroidism |
It is important to understand that:
- in the fight against hyperparathyroidism and its manifestations, diet has medicinal value, which means it must be selected individually;
The diet for hyperparathyroidism is developed with the participation of a veterinarian
- some formulations are intended for constant feeding, others should be given for a limited time and in strictly defined quantities;
- There are therapeutic foods that are sold by prescription. But, even if the product can be purchased freely, its use should be previously agreed with a veterinarian.
The needs for minerals and other important components are different between young and old cats. When choosing a ready-made diet for a sick animal, you should take into account its age.
Causes:
- Incorrect diet, poor in calcium and/or rich in phosphorus.
! The disease is typical for animals that eat only meat.
Meat is very rich in phosphorus, but contains little calcium. There is also a lot of phosphorus in fish. Most meat diets have a Ca:P ratio of 1:25 or higher. For example, in horse meat the Ca:P ratio is 1:10, in the heart and liver it is 1:50
| Name | Beef | Veal | Mutton |
| Calcium (g/kg) | 0,15 | 0,22 | 0,24 |
| Phosphorus (g/kg) | 12,10 | 12,00 | 11,45 |
- Breed predisposition. Cats have individual abilities to absorb and retain calcium. The most susceptible to the disease are Siamese, Scottish and British breeds, and Sphynxes.
- Poor absorption of calcium is also promoted by: gastrointestinal diseases, thyroid diseases, kidney failure, increased amounts of vitamins A and D, fluorine, magnesium and phytin in food.
- Growth rate. Fast growing animals are more sensitive to calcium deficiency.
Consequences of hyperparathyroidism
This pathology rarely goes away without a trace for the animal. Common consequences include:
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system if the spine is deformed. They are expressed by paralysis and paresis, difficulties with bowel movements, urinary incontinence;
Urinary incontinence can become chronic
- curvature of the limbs, making the animal’s movement uncomfortable and painful;
- deformations of the pelvic bones and chest, which negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive and genitourinary systems;
- dental problems;
Caries, pulpitis and even tooth loss are common in cats suffering from calcium deficiency.
- slow growth of the animal.
The earlier hyperparathyroidism is detected and the sooner treatment is started, the greater the cat’s chances of full recovery.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
When examining the urine of animals suffering from hyperparathyroidism, a slight decrease in calcium levels is noted. The amount of phosphorus in the blood and urine does not deviate from the norm. Changes indicating reduced skeletal mineralization are detected only in advanced stages of the disease.
X-rays are used to confirm or refute the diagnosis. The bones of sick animals in the photographs look transparent, have thinned walls, and low density. The boundaries between soft tissues and bones are erased, and already healed fractures can be detected.
X-rays help assess the degree of bone deformation. The prognosis for a successful recovery is made based on the condition of the spine, thoracic and pelvic bones.
Cats with neurological disorders are carefully examined for spinal injuries. The pictures may show cracks, curvatures, deformation of the vertebrae, and hernias.
If an X-ray examination reveals a full intestine or bladder, the animal is given immediate assistance.
To obtain high-quality x-rays, the pet must remain motionless for several minutes, which causes difficulties during this procedure. If, due to severe pain and anxiety, the cat does not want to lie still, you need to be patient and calm the animal. The effectiveness of further treatment largely depends on the quality of the images obtained and the accurate diagnosis.
Prevention
To protect your pet from hormonal pathology, which can lead to irreversible consequences, you must:
- take care of his proper nutrition, the best option for which would be the use of balanced ready-made feed;
The best option for a cured pet would be specialized premium food.
- Periodically show your cat to a veterinarian in order to have objective information about the state of its health, and, if necessary, also receive professional advice on diet and maintenance.
Prevention is the simplest and most inexpensive way to protect an animal from diseases and prolong its life. Owners of pets with hyperparathyroidism should take note of a balanced diet, which will help protect their pet from an excess of a particular substance in the body.
Natural cat diet
Treatment of the disease
The scheme of therapeutic intervention is largely determined by the stage to which the pathology has progressed. Veterinarians distinguish primary and secondary nutritional hyperparathyroidism, each of which has its own specific characteristics and requires a specific type of treatment.
Primary form
It is important to understand that when the first signs of the disease appear and its subsequent diagnosis, the cat will need a carefully prepared diet, including ready-made food. This measure is justified by the fact that they are created under the supervision of specialists, which means they contain all the microelements and vitamins a cat needs. In some cases, the pet is prescribed a diet made up exclusively of natural products. It should be noted right away that the owner should not try to compile it on his own; it is better to use the help of the attending physician.
This form of the disease is quite easy to get rid of through surgery. Its essence is for the veterinarian to remove the damaged lobes from the animal, and also to minimize the production of parathyroid hormone, thereby reducing the release of calcium into the blood and preventing the microelement from being sucked out of the bones. Owners should be prepared for the fact that the cat will spend the next week after the operation under the supervision of a doctor. He will monitor your pet's calcium levels in the bloodstream daily.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
It is divided into kidney and food varieties. Treatment for each of them is strictly individual and depends on many factors, such as weight, age and general condition of the pet. The beginning of therapy consists of restricting the cat's movement. To do this, it is placed in a special container for a period of no less than 3-4 weeks. In addition, a diet is developed that includes all the vitamins and minerals the patient needs.
The food variety is treated with pharmaceuticals. Such means for improving the condition of bones as Travmatin and Chondartron have proven themselves well. Additionally, the cat is prescribed courses of vitamins that promote the absorption of beneficial components from the food it absorbs. The disease is aggravated by chronic constipation, so the animal will need to take Vaseline oil to soften the stool.
The renal subtype of the disease is treated with the same methods, only with one condition - you need to reduce the level of phosphorus in the circulatory system and reduce its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Owners must understand that such a dangerous disease cannot be cured in two days, so they must be patient and carefully follow all the specialist’s recommendations.
Diseases of the endocrine system can negatively affect the quality of life of a mustachioed pet. You can protect yourself from them with the help of a properly composed menu for your pet and regular examinations by a veterinarian. At the first signs of hyperparathyroidism, you should take your pet for examination to a specialist. Ignoring the problem can lead to disability and death for the cat.
List of used literature and sources
- Brown tumors [Electronic resource] / Dr Hani Salam. – 2010. – Access mode: https://radiopaedia.org/cases/brown-tumours – Access to the source: 04/05/2018
- Dedov I.I. Primary hyperparathyroidism: clinical picture, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment methods [Electronic resource] / I.I. Dedov, G.A. Melnichenko, N.G. Mokrysheva, L.Ya. Rozhinskaya // Journal. Problems of endocrinology. – 2016. – T. 62, No. 6. – P. 40-77. – Access mode: https://www.mediasphera.ru/issues/problemy-endokrinologii/2016/6/1037596602016061040 (access date: 04/05/2018).
- Diagnosis of hyperparathyroidism on MRI and CT images of bones [Electronic resource] – Access mode: https://mritest.ru/article/Ortopedija/Metabolicheskie_naru/ Giperparatireoz – Access to the source: 04/05/2018
- Primary hyperparathyroidism [Electronic resource] / Dreval A.V. – 05/06/2015. – 427s. Access mode: https://www.rmj.ru/articles/endokrinologiya/Pervichnyy_giperparatireoz/ - Access to the source: 04/05/2018
Diagnostic procedures
If such an illness is suspected, the furry puppy should see a doctor as soon as possible.
The sooner owners detect hyperparathyroidism in kittens and contact a veterinary clinic, the higher the chances of a favorable outcome and prevention of many complications. The specialist must clarify the pet’s diet and conduct a visual inspection. To detect hypoparathyroidism, your veterinarian will order x-rays for cats. If the symptoms of the disease appear due to dysfunction of the endocrine system, then the kitten’s bones in the pictures are almost transparent, the spinal column is curved and several small fractures are observed. After diagnosis, the specialist will tell you how and how much to treat the cat. The selection of a therapeutic course is influenced not only by the degree of hyperparathyroidism, but also by the age of the kitten and its general condition.