How can one get poisoned?
Poison from rats and mice is a serious toxic substance that can lead to the death of the animal. The poison is used to get rid of rodents; it is placed in places where unpleasant individuals accumulate. There are many reasons and factors that provoke poisoning. How does animal poisoning occur?
Factors:
- The main cause of overdose in felines is the consumption of poisoned rodents. The poison does not have time to leave the body of the rat or mouse and ends up in the stomach of the cat.
- The substance is often given a pleasant odor to attract mice and rats. However, the cat itself can often eat the poison and become poisoned.
Compounds that interfere with blood clotting are often added to drugs for rodents. Mice die from internal bleeding. In cats, rat poison destroys vitamin K and causes problems in the circulatory system.
Manufacturers are trying to produce products with a dosage at which the animal does not die immediately, and it remains possible to provide first aid to it.
Symptoms:
Anticoagulant rodenticide poisoning may not appear immediately (signs usually develop on the first to fifth day), and the cat feels fine until its vitamin K resources run out.
The symptoms of rat poison poisoning are the same regardless of whether the cat ate the poisoned mouse or the bait.
These are: lethargy, refusal to eat, high temperature, internal and external bleeding: bloody vomiting, bloody diarrhea, hematomas, anemia of the mucous membranes, shortness of breath, tachycardia, neurological problems, convulsions.
In the case of rodenticides such as strychnine, bromethalin, zinc phosphide, symptoms may appear almost immediately after poisoning - lethargy, vomiting, anorexia, convulsions, hypertonicity of the extremities.
In case of poisoning with zoocoumarin, symptoms are observed for 4-7 days, with diphenacin - 2-4 weeks.
What are the symptoms and causes?
How does poisoning occur in cats? The owner is advised to pay attention to certain signs and symptoms and behavior of the pet.
Signs:
- Apathy, lethargy, indifference to everything;
- Cough;
- Lack of appetite;
- Enlarged belly;
- Bleeding from the nose, anus;
- Presence of blood in the urine;
- Intestinal dysfunction, frequent diarrhea;
- Nausea, urge to vomit;
- Vessels in the eyeballs burst, the whites turn red, and in severe cases, complete blindness is possible;
- Bruises that occur for no reason;
- Swollen joints;
We recommend: How salmonellosis manifests itself in dogs - first symptoms and treatment methods
When poisoned, a cat loses playfulness and refuses food and treats. Signs of intoxication can manifest themselves abruptly; the main thing is not to panic, but to quickly provide assistance to the injured animal.
Other dangers for cats
Vitamin D is also often used to get rid of rodents, but it is dangerous for cats
The cat also runs the risk of being poisoned by substances no less dangerous than anticoagulants intended for deratization. Ordinary vitamin D3 is used to get rid of rodents, and its excess leads to a sharp increase in the level of calcium and phosphorus in the animal’s blood and, as a result, kidney failure is determined.
Signs of poisoning are frequent urination, swelling, frailty - if you do not come to the veterinarian in time for an appointment, the cat may die.
Less commonly, indoor pest control is carried out using potassium cyanide. Despite the danger of this substance for humans, this poison does not always harm cats - the dosage for a small animal will not kill the cat. However, if he has eaten an excessive amount of toxin, the pet will develop convulsions and weakness, and worsening gait.
Properly selected adsorbents and timely veterinary care will help save the health of the animal.
At risk are cats and cats that go for walks outside and interact with wild rodents, and have the habit of picking up food scraps from the ground and eating them.
Treating a cat at home
How to save a cat?
Is it possible to treat poisoning at home? If signs of intoxication with rat poison are detected, first aid must be provided to the pet. Correct actions will help cleanse the body of toxic products in case of poisoning. It is definitely recommended to call your veterinarian and explain the situation.
What to do:
- It is strictly forbidden to give your cat anything to drink. If the pet has swallowed a large amount of poison, then the water will lead to severe internal bleeding.
- In case of poisoning, it is imperative to do a gastric lavage and try to induce vomiting in order to rid the body of the remnants of rat poison.
- After cleansing, the cat is given sorbents. Activated carbon is considered the simplest and most effective remedy. The affected pet is given one tablet per kilogram of weight.
- On the recommendation of a doctor, the animal is given a cleansing enema. This will help speed up the release of the toxin from the body.
After all procedures have been completed, you need to take your pet to a veterinary clinic. Further treatment of poisoning is selected by a specialist based on the cat’s condition.
Conclusion
Poisoning with rat poison is very dangerous for a cat: if the animal survives, which does not always happen, the consequences of intoxication can affect its health for years. It’s easier to prevent the cat from getting poisoned. To do this, you need to be especially careful when using drugs to kill rodents in your backyard or country house. And residents of city apartments should take warnings about deratization being carried out in their area very seriously: do not let their cat outside on these days and, just in case, keep on hand everything necessary to provide first aid to your pet. If the cat is still poisoned, it is necessary to take him to the clinic as soon as possible to make a diagnosis and begin treatment.
When to go to the hospital
If a cat is poisoned by rat poison, then contacting a medical facility is mandatory. The veterinarian will examine the animal and carry out the necessary diagnostics. After receiving the examination results, suitable treatment is selected. However, first of all, an antidote must be administered. For rat poison, this is vitamin K1, sometimes it is replaced with the drug Vikasol.
In the first stages of poisoning, the antidote is administered in large volumes by injection. After the cat’s condition has stabilized, the medicine can be given in tablets. Additional medications are required to normalize the animal’s condition.
Ten days later, an additional examination is carried out to determine the level of platelets in the blood. If the indicator is close to normal, treatment can be completed. If treatment of poisoning is started on time, the prognosis is favorable.
After poisoning, you need to carefully monitor the animal's diet. The diet includes dietary products with low fat content; it is recommended to avoid industrial feed for a while. You can’t force feed your cat, as the appetite will gradually be restored.
We recommend: Can you give your dog activated charcoal and what is the dosage?
Consequences for a cat who eats a poisoned mouse
Substances intended for baiting mice take a long time to be eliminated from the body of cats and almost always have consequences for the health of their four-legged friend. If a cat has eaten a poisoned mouse, then after intoxication the following may be observed:
- chronic cystitis, weak bladder,
- infertility, the appearance of stillborn kittens in the litter,
- chronic jaundice due to liver damage,
- hearing loss, vision loss,
- paralysis and cramps of the limbs,
- severe allergies,
- coma.
Other types of poisonous agents
Rat poison contains different components, the reaction and symptoms will also differ. What else can poison a cat?
Vitamin D3
A similar compound is often included in anti-rodent drugs. When a cat consumes poison, the level of phosphorus and calcium in the blood increases. The result of such an excess is kidney failure.
The furry pet has a frequent urge to urinate, swelling, apathy, and a reluctance to play and eat. In the absence of prompt treatment, the consequences will be negative - possible disability or death.
Potassium cyanide
The substance poses a serious danger to any living organism.
When ingested, the poison provokes the development of cerebral edema. Unfortunately, potassium cyanide causes symptoms similar to intoxication with compounds that affect blood clotting. However, vitamin K will be powerless in this case. When a cat is poisoned with this substance, there is a lack of coordination, weakness, and convulsive manifestations are possible.
The first symptoms appear a couple of hours after consuming an impressive dosage of a toxic substance. If a cat has eaten a small amount of poison, then signs will appear after three days. Therefore, any change in the pet’s habits requires careful attention.
Phosphide
This substance differs in action from the previous ones. The degree of its danger increases with the increase in food eaten by the animal. Phosphide reacts with hydrochloric acid, so the more of it, the more severe the poisoning will be. The cat begins to vomit, have severe diarrhea, cough, and have difficulty breathing.
You will like the article: “ What to do if your dog is poisoned by rat poison? ".
If signs are detected, the pet needs help as quickly as possible, otherwise the likelihood of death is high. During this period, the animal should not be given any food, as this will accelerate negative reactions in the body. Before the doctor arrives, the animal undergoes gastric lavage. However, this must be done in the fresh air, so as not to get poisoned by the resulting toxic gas.
We recommend: What to do if your dog is poisoned by rat poison?
The poisons described do not have an antidote, so it is important to provide timely assistance to the injured animal and begin treatment.
Where can a cat find poison?
Poisoning by zoocoumarins in cats is the most common reason for visiting a veterinarian with severe symptoms of intoxication. You need to know what zoocides are and how they affect the body of a pet. This is important in order to promptly identify the onset of the pathological process and seek help from a specialist.
In addition, it is important to know where the cat can find poison and try to prevent the possibility of toxic substances entering the cat's body in the future.
Chemicals developed to poison vertebrate pests have the scientific name zoocides. This is a general group of toxins, which include rodenticides, avicides and ichthyocides. All zoocides are dangerous for cats, but most often poisoning occurs with rodenticides.
This type of poison is used to prepare food baits that help kill rodents. Rodenticides have a pronounced pathogenic effect only after contact with the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. There are acute and delayed poisons. Thus, acute rodenticides are zinc phosphide and arsenic compounds.
Chronic rodenticides are anticoagulants that do not pose a particular danger to humans. Their effect is to block vitamin K, as well as the production of a specific substance - prothrombin. Against the background of these processes, blood clotting factors are disrupted and multiple hemorrhages occur.
Rodenticides that block the work of vitamin K were created against the backdrop of studies of intoxication in sheep when eating moldy clover. Coumarin of natural origin in the body of animals was converted into the toxic compound dicumarol. During the study, warfarin (zoocoumarin) was produced.
Rodenticides based on zoocoumarin decreased their effect on rodents over time. Therefore, there were new compounds that also had a negative effect on pets. Derivatives of indanedione.
With long-term use of warfarin-based rodenticides, animals have developed resistance, and new, more powerful drugs have been proposed, which sometimes affect pets. Derivatives of zoocoumarins have a pronounced toxic effect on the body of an animal (cat, dog, rodent), with a elimination period of about 14 hours.
The main reason for cat poisoning by zoocoumarins is the owner’s oversight. An animal is poisoned only by eating bait intended for baiting rodents or by eating the corpses of rats and mice.
Animal prevention measures
During the recovery period, the cat is given more attention, its nutrition and reaction to medications and foods are monitored. However, poisoning is easier to prevent than to treat. Preventive measures are quite simple.
Measures:
- When baiting rodents, do not allow the cat to visit these places.
- Make sure that the animal does not pick up anything from the ground.
- In villages and villages where there are a lot of mice, do not allow the cat to walk in places where they accumulate.
It is often difficult to keep track of the movements of a furry pet, so you need to pay attention to its behavior, always have a supply of activated carbon in the house and know the veterinarian’s number.
You will like the article: “ What to feed a cat (kitten) after poisoning .”
Any animal owner should know the symptoms and treatment for cat poisoning with rat poison. It is recommended to remember that such a substance is dangerous and can be fatal. Timely assistance and selected treatment will help save the cat’s life, and compliance with preventive measures will help avoid poisoning.
A cat was poisoned by rat poison: how to recognize the symptoms of poisoning and help the animal
Everyone knows that a cat is a freedom-loving animal that loves to walk on its own, if it is not limited in this freedom. The ability to walk outside without the supervision of an owner is one of the natural needs of mustachioed animals. However, sometimes such freedom of action is fraught with serious consequences. While hunting for rodents, a cat can catch a rat that has eaten poison and become poisoned itself. What should you do if your cat is poisoned by rat poison? How can you help an animal to save it from death?
How is poisoning by rat poison different from poisoning by other types of toxic substances?
An animal can be poisoned by rat poison in two ways:
- through a poisoned rodent. This happens when a cat catches a rat that has eaten poisoned bait. Poisoned rodents lose their agility and mobility, so catching them is not difficult for a cat;
- through eaten poison. How can a cat be attracted to rat poison? The fact is that modern rat poison is produced with special additives that attract not only rodents, but also cats.
"Note! Most poisons used to kill rats contain zoocoumarin. It impairs blood clotting and provokes internal bleeding, which is fatal.”
It is internal bleeding, coupled with a blood clotting disorder, that distinguishes poisoning by rat poison from poisoning by other types of poisons.
Another difference from poisoning with other substances is that the symptoms of poisoning do not appear immediately. They appear only after a few days, or even 2-3 weeks, when degenerative changes that cannot be treated have already begun in the body.
Symptoms of poisoning
Symptoms of a cat being poisoned by rat poison include:
- development of nosebleeds and bleeding from the gums;
- cough and shortness of breath, as well as bleeding from the trachea;
- bloody vomiting;
- tachycardia;
- convulsions;
- refusal of food;
- increase in temperature indicators;
- bloody urine;
- intestinal bleeding;
- the appearance of hematomas on the skin;
- apathy or lethargy;
- a swollen abdomen due to internal bleeding or degeneration of internal organs;
- enlargement of joints and inflammation in them.
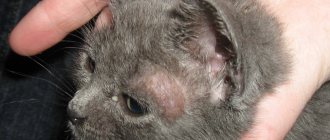
"Important information! The most characteristic symptom that a cat has been poisoned by rat poison is hemorrhages in the eyes, causing them to take on a bloody tint.”
Often, eye bleeding leads to blindness due to ruptured blood vessels in the eyeballs. This indicates a severe damage to the body by poison. In this case, it is extremely rare that the animal can be saved.
Diagnostic measures
What to do if your cat is poisoned by rat poison? First of all, take her to the veterinary clinic, where veterinarians will carry out diagnostics.
When the first signs of poisoning appear, the cat should be examined immediately. To do this, the veterinarian will examine the clinical picture, draw blood for the presence of anticoagulant substances in it, and conduct a urine test. In addition, he will question the owner in detail about how the animal became ill and how it behaved before going to the clinic. Based on the data obtained and test results, the doctor will make a diagnosis and provide treatment.
How to help your cat at home?
If the owner notices in time that the cat has been poisoned by rat poison and takes appropriate measures, he will be able to save the animal and avoid complications, which are often fatal. That is why you should act quickly and without panic.
First aid for poisoning
If the owner does not have the opportunity to contact a veterinarian, he will have to help the cat himself. But how to do that?
- Induce vomiting in the animal. Thus, it will be possible to quickly remove zoocoumarin from the body. However, this should only be done when the owner has seen the pet eat poison or a poisoned rat. But if a lot of time has passed since the poisoning, there is no need to induce vomiting, since the condition can only get worse.
- Pour adsorbent into the cat. This can be polysorb or activated carbon. They need to be diluted in water and pour 100 milliliters of the resulting mixture from a syringe into the cat’s cheek.
- To avoid dehydration and maintain water-salt balance, the animal should be given rehydron diluted in water. You need to drink the solution every hour, pouring in 10 milliliters of dissolved powder.
- To prevent the toxic substance from entering the bloodstream, you need to give the cat a product with an enveloping effect. This could be starch jelly or egg white.
"Note! The cat should be given liquid only after the vomiting has stopped, otherwise the water and the medicine will not stay in the body and will not have the desired effect.”
After 3-4 hours after eating poison or a poisoned rodent, the animal should be given Vaseline oil. It will help remove feces, and with them some of the poison. If the poison was recently eaten, it is easier to do an enema; it will have a faster effect and remove zoocoumarin from the body.
After providing first aid, the owner should take the pet to the clinic. It is especially important to see a doctor if your cat starts bleeding; in this case, the doctor will perform a blood transfusion, which will not only save the pet’s life, but also speed up recovery.
Treatment at the veterinary clinic
After making a diagnosis, the veterinarian will prescribe treatment and begin therapeutic measures. What treatment is prescribed if a cat is poisoned by rat poison? First of all, the doctor will give the animal an intravenous injection of Vikasol, which will improve blood clotting. Sometimes, if there is no other option, the cat is injected with vitamin K, but usually it is not used, since it is poorly absorbed by the animal’s body.
After the antidote, the pet will be given the necessary intravenous injections, which will be selected depending on the animal’s condition and a saline solution will be instilled. If the cat bleeds, it will be given a blood transfusion or plasma.
Maintenance therapy will also be carried out, after which the owner will be able to take the cat home.
"Important information! In the first time after the onset of intoxication, Vikasol is administered only intravenously, using loading doses of the drug. A shock dosage is used because most of the medicine neutralizes the poison anyway. After the cat’s condition returns to normal, the dosage of Vikasol is reduced and it is prescribed in tablet form.”
How to care for a cat at home?
On the first day after poisoning, the cat can only be given liquid in the form of rehydron or plain water. In addition, your pet can be given a decoction of chamomile, linden or nettle. From the second day she is allowed to eat dietary meat or fish, boiled vegetables, kefir and low-fat cottage cheese, and oatmeal with water. The animal can also be given specialized medicinal food for cats with gastrointestinal problems.
However, before purchasing it, you should consult a veterinarian. It will help you choose the most optimal food option for an organism weakened by poisoning.
It also happens that a cat may not want to accept the food offered to it by its owner. This condition is considered normal for up to three days. However, if it lasts longer, it will be necessary to take the animal on intravenous drips, which will support the body until the animal begins to eat.
"Important information! Only a veterinarian should treat a cat poisoned by rat poison, otherwise the pet may die.”
Rehabilitation activities
Poisoning with zoocoumarin is considered the most severe and dangerous type of intoxication, and accordingly, it will take a long time for the animal to recover from it, especially if treatment was started at the bleeding stage.
"Reference! In some cases, the consequences of poisoning in a cat last a lifetime, so it is better to prevent this dangerous condition than to later think about how to help it in this case.”
If a cat is poisoned by rat poison, it may develop complications in the liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system. Often other complications arise after poisoning.
If the poisoning causes bleeding, the animal may suffocate from pulmonary hemorrhage or become completely blind as a result of damage to the vessels in the retina.
It is for this reason that in order for the cat to fully recover, you should carefully monitor its condition and note the slightest changes, which may be the consequences of poisoning with rat poison.
Conclusion
Poisoning with rat poison is extremely dangerous for a cat. And even if the animal survives the poisoning, it will likely develop serious complications. Therefore, it is easier for the owner to prevent his pet from getting poisoned. For this purpose, rodents should be poisoned with pet-safe poisons or mousetraps should be used. And if exterminators are engaged in poisoning rats, then it is necessary, during their work and for several days after that, to isolate the cat from visiting places where there may be poisoned rats. In addition, you need to make sure in advance that if your cat is poisoned by rat poison, she has something to provide first aid.
Well, and, of course, if a cat has been poisoned by rat poison, you should not hesitate to visit the veterinary clinic. After all, the life and health of the animal will depend on how promptly the veterinarian provides assistance to her.
Add a comment Cancel reply
Poisoning with acids (alkalis)
Intoxication with these chemicals is possible through inhalation of vapors, contact with the skin or in the stomach.
Poisoning by acid vapors is manifested by burns of the mucous membranes, bleeding, dry cough, bloody vomiting, pain in the mouth and chest.
Poisoning by household chemical vapors is accompanied by headache, cough, abdominal pain, nausea, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Redness of the eyes, burning, runny nose, headache, nausea - typical symptoms of poisoning with vapors of varnishes and paints and traditional companions of home repairs!
Thallium poisoning
Thallium is a highly toxic poison that enters the body through the skin, respiratory and digestive organs. Thallium poisoning is rare in everyday life; this poison is more often used for criminal purposes.
How many hours does it take for signs of poisoning to develop? Symptoms in adults occur within 3 hours and resemble an acute viral infection: runny nose, dry cough, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain. Among the late manifestations of intoxication: hair loss, memory impairment, paralysis.
Enterosgel and treatment of poisoning
The ability of carbon (coal) and silicon (clay) sorbents to absorb harmful substances has been known for a long time. Our ancestors intuitively understood that wounds heal better if they are sprinkled with ashes or covered with clay. Ashes and clay were used for stomach pain, fever and other illnesses.
However, the low absorbency and tablet forms of enterosorbents limited their medicinal properties until recently. The invention of Enterosgel, a new generation gel-like sorbent, at the end of the 20th century opened up additional opportunities for saving lives and treating patients with poisoning.
Enterosgel is especially effective for oral poisoning. Often, its timely use relieves all symptoms of food poisoning, since it absorbs and removes not only toxins, but also pathogenic bacteria, without disturbing the normal intestinal flora. Toxins do not have time to be absorbed into the blood, and bacteria do not have time to multiply and show aggression. Enterosgel removes from the gastrointestinal tract the products of secondary inflammation and intoxication that accompany poisoning with caustic substances.
No matter how the poison enters the body, it enters the intestinal lumen through the intestinal mucosa and is then reabsorbed. Therefore, Enterosgel is used for almost all types of acute poisoning.
Enterosgel is also used to prevent chronic poisoning in people employed in hazardous work.
First aid
- If a cat is poisoned by a mouse that dies from the poison, symptoms will not be visible soon.
- But directly eating the poison itself will affect the health of your pet very quickly.
- Hematomas will become visible on the body. Bruising on the gums and nosebleeds will be noticeable.
- The body succumbs to spasms and convulsions. In case of poisoning with poisons and rodenticides, disorientation in space will appear, the animal’s head will shake and its paws will tangle.
- The cat will develop diarrhea and vomiting. Traces of blood will be visible in the vomit or stool.
- In case of poisoning with zinc phosphides, a rotten smell from the mouth and breathing problems will appear.
- Signs include refusal to feed, complete apathy, and even fear of people.
- Possible shortness of breath and tachycardia.
Even one of these signs should alert you, especially if there is information about rodent control measures, if there is even the slightest chance that the cat has eaten poison or a poisoned mouse.
If you observe any signs of intoxication in an animal, you must urgently take it to a veterinary clinic or call a doctor at home.
At the same time, if calling for help is difficult (for example, the locality is located far from a veterinary clinic), the owner must help the pet right at home.
What to do before the doctor arrives:
- If a poisoned mouse or poison for mice and rats was eaten by a cat right in front of the owner, it is worth inducing vomiting using a solution of hydrogen peroxide diluted in a ratio of 1 to 1 (one teaspoon diluted per 1 kg of body weight). You can also induce vomiting in an animal by placing a pinch of soda on the tongue. If the duration of the poisoning has not been established, it is not recommended to induce vomiting: this will only cause dehydration of the exhausted body;
- To bind a toxic substance in the stomach, the cat must be given an adsorbent: enterosgel, activated carbon, polysorb. The drug is diluted in 100 ml of water at room temperature and poured into the mouth using a syringe. Adsorbents are not used if the cat does not stop vomiting;
- To cleanse the intestines, the animal is given an enema of 30 ml of warm boiled water or saline solution.
After poisoning with zinc phosphide, you need to rinse the cat's stomach with a 0.5% solution of copper sulfate or a weak solution of soda.
To provide your cat with the most effective help, you need to know exactly what kind of poison the animal was poisoned with. To obtain this information, you need to do a special analysis in the laboratory. However, it is not always possible to immediately contact a veterinarian for help; in this case, you must act without delay on your own.
After this, you need to adhere to a consistent algorithm of actions that will help your pet recover. If you neglect the following rules and recommendations, this will lead to the death of the cat. Before giving the cat an absorbent, it is necessary to induce a gag reflex in the pet.
You can do this in the following ways:
- Mix equal parts hydrogen peroxide solution and plain water.
- Pour 4 ml of emetic root into the pet's mouth, which can be purchased at any pharmacy.
- Dissolve a couple of tablespoons of table salt in a glass of water.
- Sprinkle some baking soda on the tip of your tongue.
- Give the cat water to drink, then press on the root of the tongue.
It will be more convenient to give the cat the above solutions using a regular medical syringe.
It is very important to force a poisoned cat to drink a sorbent in the form of activated carbon after vomiting. This will help relieve intoxication and neutralize the poison.
Also, in addition to coal, Enterosgel can be used as an effective sorbent.
After the above procedures, you should do the following:
Two hours after the cat has taken the sorbents, it is necessary to give him vitamin K1, which will help neutralize the internal bleeding that has begun.
The dosage is calculated based on the level of poisoning and the intensity of bleeding. An hour after the above procedure, it is very important to cleanse your pet’s intestines. To do this, you can use laxatives: sodium sulfate solution 2% or castor oil. You can also do an enema to flush the intestines; this will be much more effective and safer for your pet.
35 ml of purified water or saline solution should be injected into the rectum.
It is very important to understand that your pet is currently experiencing the most difficult hours of his life. If your cat has been poisoned, treat him as carefully and gently as possible, do not expose him to stress
Alcohol poisoning
Symptoms most often occur in the morning. Many consider them a kind of “retribution” for a stormy evening. This condition is more often called a hangover rather than alcohol poisoning.
Symptoms depend on the concentration of ethyl alcohol in the blood. At the beginning of intoxication, this is euphoria and talkativeness, with an increase in alcohol concentration - impaired speech and coordination of movements. The liver begins the process of recycling alcohol into simpler substances, aldehyde, water, carbon dioxide. It is acetaldehyde that is “to blame” for morning ailments: headache, thirst, nausea, dry mouth, dizziness.
Be careful!
In order for alcohol poisoning to occur, an adult needs on average about 200 ml of 40% ethanol; alcohol poisoning in a child occurs when drinking 30 ml of 40% ethanol (vodka).