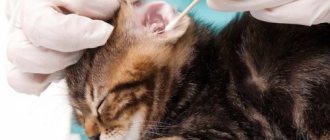
Scratching in cats is not considered a big problem, but only until the wounds are bloody or cover a large area. The speed of development of events is also frightening, since most often the cat itches a little, and after 10–12 hours bleeding wounds appear on the pet’s skin. Such a horrifying picture does not pose a serious danger as long as the wounds are not infected. The cat is in pain, nervous, eating poorly, anxious, how can you figure out what to do?
Causes of itching in the head and neck area in cats
Cats scratch their necks until they hurt for a variety of reasons. This behavior is provoked by external factors, ectoparasites and a number of diseases of varying degrees of danger. The largest number of cases are due to allergies and insect parasites. A smaller percentage of the probability is associated with viral, autoimmune and other diseases.
Ectoparasitosis
Otodectes cynotis, or ear scabies, is caused by mites. They settle in the ears or ear canal and cause severe itching in the cat. As a result, she regularly shakes her head and scratches her ears until they hurt. It is transmitted by contact and affects mainly young animals.
Notoedrosis or pruritic scabies develops against the background of Notoedres cati tick bites. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the scalp, hair loss and severe itching. An infected cat constantly scratches its head until sores appear.
Important! Notoedres cati itches spread from cats to other animals and even humans. For some time they cause pseudo-scabies and then go away, since there are no favorable conditions for life.
Cheyletiellosis, or wandering scabies, is caused by Cheyletiella mites. The fact that a cat has these parasites is indicated by severe itching and fine dandruff. The disease often spreads to humans and causes an itchy rash.
Demodectic mange or ironworm is the result of exposure to mites of the genus Demodex. They develop their vital activity in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. As a result, bald patches of skin and sores appear on the cats’ faces. The areas most commonly affected are the areas around the eyes and mouth, as well as the front legs.
Fleas are a common cause of scratching on the neck and other parts of the body. They parasitize primarily on cats and dogs. They can also temporarily transfer to humans. When infected with them, a large number of black crumbs appear under the fur of pets. These flea droppings are especially noticeable in the lumbar and back areas.
The animals themselves itch very much to the point of soreness, as they experience severe itching at the bite sites.
Allergies
A common reason why a cat scratches itself until it hurts is allergies. It implies an abnormal reaction of the body to a stimulus. When first hit, protective cells create an antidote and “remember” the allergen. And if it penetrates again, a violent reaction occurs in the body. It leads to inflammation, itching and other symptoms.
Allergies cause several diseases in cats:
- atopic dermatitis;
- flea dermatitis;
- food allergies;
- contact dermatitis.
Flea dermatitis
Flea dermatitis is a common reason why a cat scratches itself until it hurts. When one flea bites, it releases a special anticoagulant into the cat's skin. This substance prevents blood clotting. The pet becomes sensitized to it. And the body reacts to the bites of other fleas in the form of inflammatory processes, rashes and papules.
The affected areas are very itchy. The cat begins to behave restlessly and reacts nervously to touch. This type of dermatitis occurs in two forms: chronic and latent. In the first case, alopecia (foci of baldness) and nodules with flea feces develop on the body. The second is characterized by the appearance of papules with a red rim.
The cat begins to tear them apart until they hurt. Often secondary infection is associated with wounds.
Atopic dermatitis
The disease is typical for young animals aged 1 to 3 years. The main reason for its appearance is the uncontrolled selection of cats. As a result, animals develop allergies to dust and pollen. In this case, it is almost impossible to identify the allergen.
Important! Atopic dermatitis has no cure; cats will regularly scratch their skin until it hurts. The action of therapy is aimed at suppressing symptoms.
Dermatitis in cats manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- the appearance of dandruff on the withers and back;
- hair loss;
- labored breathing;
- discharge from the eyes and nose;
- cough;
- profuse salivation.
Contact dermatitis
This allergy is similar in symptoms to atopic dermatitis. It often manifests itself when the pet comes into contact with household chemicals, toilet filler, the hair of other animals, and flea products. Contact allergies are manifested by severe itching, flaking of the skin and a small rash. Often a cat itches until it hurts. And this increases the risk of secondary infections.
Food allergies
Allergens can accumulate in the body of animals. With their regular consumption, health problems begin. Food allergies are characterized by:
- the appearance of a rash on the cat’s neck and head;
- hair loss;
- the appearance of dandruff;
- inflammation of the eyelids;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth.
Important! Symptoms of food allergies in cats are often accompanied by vomiting and indigestion.
A common cause of food allergies is feeding cats salted, fried, smoked and other prohibited foods from the table. Mixed feeding with industrial feed and natural products also contributes to its appearance.
Treating scratches at home
If a cat scratches itself until it bleeds, the first step is to treat the wound so that it does not get infected. Regular human ointments are suitable for this.
To avoid further scratching of the skin, the cat should trim its claws and cover the problem area with something (for example, put a special collar or vest on the animal).
If a doctor has diagnosed lichen, the sick animal must be isolated from healthy ones. The fur next to the affected area is shaved off. The affected area is treated with ointments.
If an animal is taking any anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive drugs, they should be stopped for a while so that the body has the strength to cope with the fungus.
The room in which the cat lives, as well as all objects with which it comes into contact, must be disinfected. Treatment of lichen can take quite a long time, but if its initial stages are detected, the animal will fully recover.
A special diet will help overcome food allergies. A product that causes a negative reaction should be excluded from the diet. You can also purchase commercial food for cats prone to allergies.
Atopic dermatitis can also cause itching. This is also an allergic reaction of the cat’s body, but it is impossible to isolate the exact allergen and completely eliminate it. Atopic dermatitis cannot be cured, but with the help of medications, all negative manifestations of allergies can be eliminated.
If a cat is suffering from a bacterial infection, the first step is to use various ointments. If an animal develops ulcers, the doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics.
If the disease becomes chronic, the veterinarian takes microbiological tests. This is necessary to prescribe the most effective treatment for this type of bacteria.
When do you need veterinary help?
Often, scratching is almost harmless and does not cause the animal much discomfort. The owner may not even immediately notice that something is wrong with the pet. Problems begin when bacteria get into the wound. In this case, an abscess may form on the skin. In some cases, without timely treatment, the area of scratching may increase.
We recommend the article: What can cause a cat's paw to swell?
If an animal scratches a small wound once, there is no need to sound the alarm. Perhaps the cat just overdid it. The wound should be treated and the pet should be monitored.
In what cases should you take your pet to the veterinarian:
- The cat scratches the same place for a long time until it bleeds.
- The area of scratching increases.
- The wound oozes pus or does not heal.
- Scabs form on the affected area of the skin.
- The cat's hair falls out and bald patches form.
- The animal is constantly itching.
Scratching is often one of the symptoms indicating that the animal is unhealthy. In this case, you should pay attention to the general condition of the cat. You should contact your veterinarian if the following symptoms accompany itching:
- Decreased activity or excessive agitation.
- Increased body temperature.
- Lack of appetite.
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
Skin infections
Scratched cat sores on the neck and head in some cases occur due to infectious diseases. Cats with access to the outdoors are especially susceptible to them. When a bacterial infection of the skin occurs, one of two forms develops:
- Dry. Dry crusts, dandruff and scabs form on your cat's neck.
- Wet. It is characterized by the appearance of blisters and ulcers with liquid contents inside.
Animals with sensitive skin are predisposed to eczema. It develops through prolonged contact with flea collars, harnesses, after insect bites and skin parasites.
Important! Diabetes mellitus, neuropathy and hormonal changes contribute to the appearance of eczema.
A rash and blisters appear on the pet's body. Severe itching leads to the cat scratching its neck until it bleeds, and sores appear that do not go away for a long time. To eliminate eczema, antibacterial therapy, various ointments and powders are prescribed.
Viral dermatoses
Cat scratching on the skin is also characteristic of viral dermatoses. The herpes virus affects the eyes and respiratory tract of the animal, often manifesting itself as skin lesions. They are often localized in the area of the nose and eyes, less often on the paws and stomach.
Feline herpes is characterized by:
- bloody stains;
- small rash;
- swelling of the skin;
- small scabs on the neck, sores on the head.
Skin changes appear 1.5 weeks after the disappearance of conjunctivitis and other characteristic symptoms.
Cowpox or poxvirus is a rare disease. It can enter the cat's body through the bites of small rodents. It manifests itself as skin lesions in the form of nodules and small ulcers. With good immunity, it goes away on its own. In weakened animals there is a risk of developing a severe form.
Autoimmune dermatoses
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by an abnormal reaction of the immune system to its own tissues and cells. Skin manifestations on the body of cats are characteristic of several diseases:
- Common pemphigus. It is characterized by the development of ulcers in cats around the mouth and in its cavity itself. Involves long and difficult treatment. It often ends critically for animals.
- Erythematous pemphigus. Crusts, ulcers, blisters, sores and other lesions are concentrated in the area of the animal’s nose and bridge of the nose. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by a change in skin color.
- Pemphigus foliaceus. The main symptom is the appearance of large pustules on the skin near the mouth and ears. Associated signs in cats include elevated body temperature, refusal to eat, and apathy.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus. It affects all systems and organs of the animal. Wounds on the scalp manifest themselves through depigmentation of the skin, the development of a rash and the subsequent formation of ulcers.
Skin tumors
Skin neoplasms are in first place among oncological diseases in animals. By their nature, they are also divided into benign and malignant forms.
The first includes:
- Basalioma. The sore is a pigmented dome-shaped tumor. At the point where it appears, the animal loses its hair.
- Cutaneous histiocytoma. Characterized by a rapidly growing tumor under the skin. A rare pathology for cats.
Malignant skin tumors develop in two cases:
- Squamous cell carcinoma. The disease manifests itself in the nose, eyelids and ears. Metastases spread through the lymphatic system.
- Basal cell carcinoma. Develops from basal cells of the skin. Characterized by rapid growth and a high probability of metastasis.
Main symptoms
Some pathological conditions of the skin, which are accompanied by severe itching, are clinically manifested by redness of the skin at the site of the lesion, loss of elasticity and firmness, as well as scratching from the claws of the animal. Since a sick pet is trying to relieve itself of the discomfort that has arisen, it will constantly scratch and lick the itchy areas of the body.
In places of intense itching, wounds from scratching, areas of baldness, and infected scratches are identified. A cat that is bothered by itching must be shown to a veterinarian, who will conduct a series of studies to determine the nature of the underlying disease and prescribe adequate treatment.
History taking
Diagnostics will help you understand why your cat scratches its neck and what caused the sores. But before carrying it out, the veterinarian needs to collect an anamnesis.
Age and breed
A kitten up to one year old is susceptible to skin and subcutaneous parasites. Young animals suffer predominantly from allergic reactions. If an elderly cat scratches its neck until it bleeds and hurts, this may be due to autoimmune dermatoses.
The breed of the animal also leaves its mark. Persian cats are prone to dermatophytosis and dermatitis, while Sphynx cats are prone to allergies and neoplasms.
Lifestyle
A large number of animals in one area, access to the street, participation in cat shows and other factors increase the risk of infection with parasites and viral diseases.
Seasonality
Allergies to pollen, bee or mosquito bites have a pronounced seasonality. Flea dermatitis in cats manifests itself regardless of the time of year. But it is most common in August-September.
Routes of infection
The most common route of infection with cat scabies is contact. The microscopic tick can easily jump from one infected animal to another. Moreover, it is absolutely not necessary to contact sick relatives. A cat can become infected from a dog, from another cat, or from birds - domestic or wild. Pigeons are especially prone to scabies.
This can happen anywhere: during a walk, at a veterinarian’s appointment, at an exhibition, on public transport. Small kittens often become infected from their sick mother during the period of cohabitation and feeding.
The second common route of transmission of parasites is through animal care items. You can pick up a tick from someone else's comb, brush, or bedding. The third is housekeeping clothes and shoes. A person can bring ticks into the house on their clothes or shoes.
Who is at risk
Most often people become infected with scabies:
- Animals with weakened immune systems.
- Exhausted cats.
- Pets in shelters and stray cats.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostics will help determine why a cat scratches its neck until it hurts. The doctor prescribes one or more methods:
- Combing wool. A fine comb is used for this. The procedure allows you to see fleas, lice and skin mites on cats. Can be done independently at home.
- Trichogramma. Determines the presence of spores and eggs on the hair shaft.
- Examination of earwax under a microscope. It is carried out if otodectosis is suspected.
- Wood's lamp. Shows the glow of spores on the skin of an animal from certain types of fungus.
- Cytological examination. The veterinarian recommends this to detect yeast and bacterial infections.
- Allergy test. Prescribed for confirmed atopic allergies in cats.
- Skin scraping. Detects ticks, their larvae, and spores.
- Elimination diet. Prescribed by a veterinarian to determine the allergen for food allergies.
- Fungal culture. An effective method for dermatophytes.
Diagnostic procedures
If a cat tears its paw, tail, area under the eye, or on its back, the veterinarian conducts an external examination. Flea dermatitis can be identified when small black granules called flea excrement appear on the skin. For subcutaneous infection, scraping of the epidermis and scales is performed. Pyoderma scratching in a cat requires examination of the pus to determine the causative agent. Fungal infections are detected using a Wood's lamp. In addition, diagnostic methods are prescribed, such as:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- thyroid tomography;
- hormone testing;
- stool analysis for worm eggs.