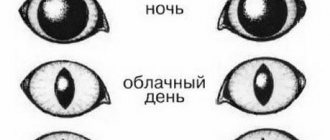
Cats can see well in the twilight, but this ability comes with a price.
Have you ever tripped over your striped pet at night and received a puzzled look from him that said, “How could you not notice me?” If yes, then you are aware that you are significantly inferior to your pet in the ability to see in the dark. In fact, its light sensitivity threshold is seven times lower than yours. However, to form images, a cat, like a person, needs light. A cat's vision is unable to distinguish objects in complete darkness. In addition, there is a downside to being able to make do with low light.
Eye structure
Cats have always been considered excellent night hunters. The anatomy and physiology of the visual organs was formed in the course of evolutionary development. It is important for cats to track prey and navigate in the dark. That is why the anatomical structure of the cats’ visual organs is designed in such a way that they are able to distinguish objects in low light conditions.
The structure of a cat's eye consists of three main parts. And each part has its own functional features:
- The outer fibrous part is the outer fibrous membrane, called the sclera, and has a convex shape, reminiscent of a ball. It occupies ¾ of the back surface of the eye, and another ¼ is occupied by the cornea - this is a transparent thin cellular layer that transmits beams of light into the eye organ;
- Vascular part. Located in the middle part of the cat's eye. This is a collection of blood vessels and capillaries through which oxygen and nutrients are transported to all eye tissues. In the place where the sclera and cornea connect, there is the ciliary body. It is controlled by the ciliary muscle, which holds the lens of the eyeball in a certain position. This muscle can tense and relax depending on the cat's attention and the location of the object. Under the influence of such muscle movement, the lens changes its shape. This process is called accommodation. The iris is located on the front of the choroid, and divides the front of the cat's eye into two chambers - anterior and posterior. At the center of the iris is the pupil. It changes its shape depending on the light flux - it narrows in bright daylight, expands in dim light;
- Inner part or retina. Consists of photoreceptors that transform light signals into electrochemical ones. It also transmits the received information to the nervous system. In the retina of the eye there is an optical disk or, as it is also called, a “blind spot” - this is an opening through which blood vessels and the optic nerve exit. Compared to other parts of the retina, the optical disc does not have photoreceptors. In turn, photoreceptors are divided into rods and cones. In four-legged pets, the rods are considered the most developed, since their main function is increased sensitivity to minimal streams of light at night. The function of cones is to recognize the color and clarity of images during the daytime.
Why do cats' eyes glow?
Why cats' eyes emit a green or yellow glow in the dark is the second question, the answer to which man could not find an answer for a long time.
Because of this amazing ability, cats were attributed magical otherworldly properties. It was believed that they could talk to spirits and play with brownies.
In fact, the answer is simple - the eyes do not glow, but reflect the light entering them. The structure of the cat's eye has a back wall of crystals - the tapetum. Such a mirror wall is present in the structure of the eyes of all predators that hunt in the dark.
It reflects the sun's rays onto the photoreceptors, thereby causing the cat's eyes to glow. No mysticism - a common physical phenomenon called photoluminescence! The reflected light has a wavelength corresponding to the green part of the spectrum. That's why a cat's eyes glow in the dark with green and yellow light. There will be no source of external light - the glow will disappear.
Cat and human vision. What are the differences?
Some people believe that cats see perfectly in complete darkness, but this is not true. Fluffy pets, like people, see nothing in the complete absence of light. But with minimal lighting they are able to recognize objects in the dark much better.
In humans, the ratio of rods to cones is 4 to 1. And in a cat, the number of rods is 25 times greater than the number of cones. This causes cats to prefer a nocturnal lifestyle.
In the daytime, cats are able to clearly distinguish objects at a distance of up to 20 m, and humans up to 40 m. In addition, cats have difficulty seeing objects at close range and identify them mainly based on their olfactory senses.
Do cats see colors?
For a long time it was believed that cats see the world in black and white. And only in the middle of the 20th century were scientists able to refute this statement. It has been scientifically proven that cats see 6 colors, including:
- grey;
- blue;
- blue;
- green;
- white;
- black.
Cats can also distinguish between purple and yellow. True, they see shades of the latter only on a green background. And purple is often confused with blue.
The most important color for cats is gray, so they can distinguish all its shades. This is explained by the fact that this is how rats, mice and some birds, which wild representatives of the cat family feed on, are colored this way.
Colors that are inaccessible to the eye of pets include pink, brown and red shades. Also, cats do not perceive colorful combinations.
Night and color vision
At night, with minimal lighting, cats are 15 times better than people at distinguishing objects. Of course, for a successful hunt, small predators also use other senses, such as hearing and smell. The human eye perceives all colors, but the cat's eye can only see:
- blue;
- yellow;
- gray and its shades.
Green, red, brown and orange are the same colors for a cat.
The main features of cat vision include:
- Changes in the pupil depending on illumination. This feature helps regulate the beams of light entering the retina.
- Behind the retina of the eye there is a layer of tapetum. It is a “mirror” and reflects light. Thus, a light beam hitting the retina of the eye penetrates the tapetum, is reflected and re-enters the retina. Thus, the eye cells receive a double stream of light, as a result of which the cat’s night vision is enhanced. And the glowing eyes of pets in the dark are also caused by the tapetum layer.
Ultraviolet perception (UV or black light)
In some ways, cats can see in the dark. A person is not susceptible to ultraviolet radiation (or, as it is also called, black light). Being in a room filled with UV rays, it will seem to him that the room is completely dark - the lens of the human eye will block these light streams. Most mammals, including cats, dogs and monkeys, are designed differently: their lenses allow ultraviolet radiation to pass through. Such a “superpower” could be useful for cats and other predators to track fluorescent traces of animal urine or to recognize camouflaged prey.
This is interesting
The retina of the human eye is able to perceive UV rays. If the lens is removed, as is done, for example, during cataract surgery, people will be able to see in ultraviolet light. After such a surgical procedure, the famous artist Monet began painting using ultraviolet pigments.
What else helps a cat navigate in the dark?
In order to “see” in the dark, representatives of the cat family use additional senses in addition to vision - something similar to echolocation, which helps bats navigate at night. The lack of eye muscles that can change the shape of the lens leads to the fact that the pet does not see nearby objects clearly enough. To form a complete picture of space, the cat resorts to the help of its whiskers, which pick up the slightest vibrations. This information is used to build a three-dimensional “map” of the surrounding reality. If, for example, the prey or favorite toy of your household is located within reach (that is, too close to have a clear image), it extends its whiskers, forming a kind of “web” to track movements.
Features of cat vision
The cat's organ of vision differs sharply from the human one in structure and ability to perceive space. They have large, round eyes with a convex lens. The viewing angle of space is 270 degrees.
A special feature of cats is stereoscopic vision. Each eye receives its own image of an object, which is then combined by the brain into one three-dimensional picture. As a result, the predator receives accurate information about the location of the prey and the distance to it.
Everything that the left eye sees goes to the right side of the brain and, conversely, the right eye transmits the picture to the left half
The genetic memory of a predator makes animals react to moving objects. Stationary animals are practically of no interest to them. Watching a moving object, the animal begins to actively move its head up and down: this is how the cat changes its viewing angle and focuses on the prey. This natural ability helps the predator calculate the distance to the prey down to the millimeter, which is why the cat’s jump is so accurate.
The special sensitivity of a cat's eyes is directly related to the structure of the pupil. It is located vertically and has increased elasticity. In bright light, it narrows, limiting rays from reaching the retina. Lack of lighting causes the pupil to dilate greatly, allowing more light to enter.
The sensitivity of a cat's eye is 6–8 times greater than that of a human. The reason for this is a special layer behind the retina called tapetum. It is a shell of vessels that look like mother of pearl.
How they see our world
To see our world through the eyes of a cat, you need to look at a faded, blurry photograph. Nature has provided for the ability of predators to clearly see moving prey without paying attention to small details. A cat's eyes do not provide a complete picture of the world, so their vision is supplemented by other senses.
Cats see immediately with their eyes, nose and vibrissae - sensitive organs located on the face and tail. It is much more important for them to touch and smell an object than to just see it.
Do they see the image on TV and their reflection in the mirror?
Scientists are divided on the perception of images on a TV screen. Some argue that animals see flickering and movement of objects. To confirm this, many owners testify that their pets love watching animals on the screen, and after switching the channel they immediately lose interest in the TV.
Cats not only love to watch TV, but also sleep on it.
Others are sure that TV programs in the eyes of animals look like static pictures replacing each other. They explain this fact by the fact that cat's eyes perceive images at a speed of 40 frames per second. In this case, the TV is configured for human perception, that is, 24 frames. For an animal to see movement on the screen, the frame must be updated 50 times per second.
In the mirror, the cat sees itself normally, but begins to hiss and flatten its ears. This behavior indicates fear. The image without odor and auditory vibrations is incomprehensible and causes fear.
How cats see humans
Pets see people as they are. They adequately assess height, recognize movements and voice. But animals see a clear picture only at a distance of 0.5 to 5 meters. At a distance of 7–10 meters, the pet sees only a silhouette and can recognize the owner by smell and voice.
There is an opinion that, in addition to the physical body of a person, cats can see his biofield. This ability can explain different attitudes towards strangers. The animal approaches some without fear, allows itself to be petted, and even goes into your arms. He doesn't let some strangers come close to him. The animal evaluates a person's aura and accurately determines who may pose a danger to him.
The ability to see the aura is reflected in the cat’s ability to identify a sore spot on the owner’s body. The pet draws out the negative energy of the owner, thereby having a beneficial effect on his health.
If a cat living in a house is constantly sick and no treatment helps, the owners should think about their own health.
By the way a domestic predator looks at a person, you can understand what his mood is at the moment and guess his desires:
- peace and tranquility is expressed by squinting eyes and constricted pupils;
- fear is reflected in wide open eyes and maximally dilated pupils;
- when the pet intends to beg the owner for a treat, the gaze becomes intent, straight into the person’s eyes;
- if an animal, without looking away, looks at a person, periodically slowly closing its eyes, it expresses its love.
The tray should not be surrounded by pitch darkness
However, belief in miracles that are not true, but imaginary, forces some people to conduct strange experiments on their pets. Confident that their cat can see perfectly even in complete darkness, owners who are especially sensitive to the interior arrange a toilet for their pet in dark bedside tables or close the hole in the door of the corresponding room without windows with a blank opaque door, where they themselves enter only with light.
The truth is that cats can see in complete darkness no better than we can! No extra sticks or pupils dilated to the limit will help catch light that is not there! And you and I are sure - well, or almost sure - that there is no evil monster or ghost hiding in the darkness. A cat may well experience anxiety due to the fact that it is not able to fully control the space around itself - this is not superstition, but instinct.
Therefore, it is not surprising that the animal will find a safer place for its toilet, for example, in the owner’s sneaker in a brightly lit hallway or on the carpet in the middle of the living room. And who is to blame for this? Certainly not the cat, but human ignorance!
What is the connection with the other world?
Cats often observe objects that are not visible to humans. They suddenly jump up and start running around the room, knocking them over. At such moments, the animal’s pupils are dilated and its fur stands up. This behavior makes one believe that the cat sees the other world and its inhabitants. His gaze is accessible to what a person is unable to see.
When an animal looks into emptiness or, turning its head, examines an empty wall, there is no reason to worry. This is explained by the fact that even the quietest sounds that are alarming are accessible to a cat’s hearing. They do not come from the other world, but, quite possibly, from under the baseboard. The grandmothers’ assertion that at such moments the domestic predator communicates with the brownie is also from the realm of half-fairy tales.
Over the centuries, cats have been the source of scary stories thanks to their ability to see in the dark.
But the cat’s connection with a world unknown to man still exists. If your pet begins to behave restlessly, for no apparent reason, it is advisable to consecrate the home. Esotericists claim that a cat, having noticed an otherworldly body on its territory, tries to protect its owner from it. First, the animal freezes, trying to assess the “alien”’s intentions. If the cat thinks that the uninvited guest is dangerous for the owner, she tries to force him out with her own energy. When the danger is too strong and the cat cannot cope with it, it may even leave the house. It is not uncommon for cats to return as unexpectedly as they left. So the pet removes evil spirits from the home, and after getting rid of it outside the walls of the house, it returns.
Scientists do not see anything mystical in this behavior of cats and claim that any behavior of a cat is explained by its increased sensitivity to sounds and smells.
But no evidence has been presented to refute the ability of cats to see the inhabitants of the other world, so you can still believe in the supernatural power of a cat’s vision.