- Posted by Olesya Vakhraneva
- Date: March 14, 2019
Sometimes the owner becomes curious about what the cat actually sees and how he perceives the world and people around him. And this curiosity is justified - the vision of cats and humans is very different.
- 2 What kind of vision does a cat have
2.1 Color perception - 2.2 Vision in the dark
2.2.1 Why do cats' eyes glow in the dark?
- 6.1 Video: a cat communicates with its reflection
Features of the anatomy of cat's eyes
The structure of a cat's eye has some characteristic differences from the anatomy of the human eye:
- the size of a cat's eye is larger than that of a person, if we consider them relative to the size of the body;
- the cat's eyes are buried deeper in the skull, therefore, better protected;
- the cat's eye is equipped with a third eyelid that cleanses, moisturizes and additionally protects its surface;
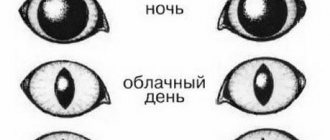
- the elongated shape of the pupil allows you to regulate the intensity of the light flux falling on the retina: in bright light, the cat’s pupils take a shape close to a vertical line;
In bright light, the pupil constricts as much as possible
- behind the retina there is a peculiar reflective element - a layer of tapetum lucidum cells, which enhances twilight vision;
- the presence of panoramic vision - retinal receptors (rods and cones) in cats are distributed evenly over the entire surface of the retina; Humans have a central type of vision, most of their receptors are concentrated in the area of the macula, also located on the retina, which narrows their field of vision compared to a cat’s, but gives a noticeable advantage in visual acuity.
The central type of human vision provides a noticeable advantage in acuity compared to the panoramic vision of a cat
Discovery five: THEIR EYES GLOW IN THE DARK!
The whole secret of this miracle is in the so-called tapetum - a layer of the eye shell that captures light and directs it to the retina. That's why a cat's gaze seems so mysterious and even magical! Interestingly, you can calculate the color of the eyes by the color of the glow: blue pupils usually glow red, and yellow pupils glow green.
And now is the time to do...
What kind of vision does a cat have?
A cat's vision is characterized by the following parameters:
- range - the main focus of the cat’s vision is at a distance of 2–6 m, it is at this distance that the cat can estimate the location of an object with an accuracy of a centimeter, which is very important for the accuracy of the jump when hunting from an ambush; When preparing to jump, cats often make slight nodding movements with their heads, additionally focusing on their target to improve accuracy; at a distance exceeding 20 m, the cat sees objects blurry, and she also sees very poorly what is located closer than 50 cm from her - at this distance she uses smell and touch;
The cat explores what is close by using smell and touch.
- viewing sector - a cat’s viewing angle exceeds that of a human and is more than 200° (for a human it is 180°);
- three-dimensionality - the cat sees three-dimensional objects and has binocular vision, in which both eyes are able to see the same object, the image of which is processed by the brain and converted into a three-dimensional picture;
- number of frames per second - researchers believe that a cat sees about 40 frames per second, a person is able to see 24 frames per second, and it is precisely this speed of perception that modern television is configured for, and a cat sees on TV only pictures one after another; in order for them to acquire mobility for a cat, a speed of 50 frames per second is required, i.e., the perception of moving objects by a cat is much faster than by a person; The cat distinguishes especially well between objects moving in the horizontal plane and somewhat more slowly in the vertical plane.
A cat perceives movement twice as well as a human
Color perception
Cats have color vision, but it is different from human vision. Daytime vision photoreceptors—cones—located in the retina are responsible for color perception. Cats do not have cones that perceive shades of red, so they do not perceive red, brown, burgundy, and orange shades. At the same time, cats perceive shades of blue and green, and about 25 shades of gray are distinguished.
Cats do not perceive shades of red due to the lack of corresponding receptors in the retina
Vision in the dark
Cats cannot see in complete darkness. Like humans, cats require lighting in order to see surrounding objects; To see clearly at dusk, a cat needs 10 times less light than a human.
A cat only needs a small light source to see in the dark.
Also, compared to humans, the cat’s retina contains a larger number of rods - receptors for twilight vision. The ratio of rods to cones in a cat is 25:1, while in humans it is 4:1.
Enhancing twilight vision is the tapetum layer, located behind the retina and reflecting incoming light back onto the retina. Thus, each quantum of light stimulates the retinal receptors twice, which allows the cat to clearly distinguish surrounding objects in conditions of poor lighting.
The twilight vision of a cat is much more effective than that of a human, and makes it possible to hunt at night
Why do cats' eyes glow in the dark?
Due to the presence of a tapetum layer, the cat's eyes reflect light and appear glowing in the dark. At the same time, the eyes of blue-eyed cats glow red in the dark, and green-eyed cats glow green.
Cat's eyes reflect light so they appear to glow
Differences with human vision
Of course, it's all about the brain. Unlike humans, cats have developed areas of the brain that are responsible for hearing and smell, so vision in cats is worse than these senses. In humans, most of the neurons are taken away by hand motor skills.
Unlike other creatures, a cat's vision is an auxiliary sense, and not the main one - hearing and smell are considered the main ones. Evolution put everything in its place due to the fact that the cat is considered an animal that hunts from an ambush. That is why she does not need a far-sighted gaze of several kilometers.
Dogs see better than cats, and this is also due to brain development. The structure of the limbs and their work in the cat family is much more complex, therefore, together with the development of areas responsible for hearing and smell, there is no room left for vision on the surface of the cerebral cortex in cats, and they see worse.
Does a cat see paranormal phenomena?
In some cases, observing attacks of unprovoked excitement in a cat, the owner is inclined to associate them with the influence of paranormal factors. It is often said that cats see the spirits of the dead or play with brownies. But as a rule, the cat simply hears sounds or smells that are inaccessible to human perception, and reacts to them.
The cat picks up sounds that are inaccessible to the human ear, but they are not at all supernatural
Many phenomena, for example, electromagnetic fields, ultrasonic waves, radiation, are imperceptible to the human senses, but perhaps the cat perceives them and reacts accordingly.
First discovery: EVERYTHING IS COLORFUL!
Look, it's not as boring here as some might think!
For a long time, for some reason, everyone believed that cats see only shades of gray. But recent research proves that our purrs can distinguish many colors perfectly! They are just not as bright as our vision reproduces them.
Photographs taken by American photographer Nikolai Lamm will help us understand the difference. After consultations with zoologists, he, with the help of an editor, reproduced the visual features of a domestic cat in photographs.
The top photo shows a landscape seen through a person’s eyes, and the second one shows his pet. Significant difference, isn't it?
Now look at the edges of these pictures. We can immediately make a second discovery - it turns out...
What does a cat see in the mirror?
The cat in the mirror clearly sees its image, but does not identify itself with it. Moreover, a flat and odorless moving image can frighten a cat. Sometimes cats mistake their image in the mirror for the presence of another animal in the room and try to play with it.
Sometimes cats perceive a reflection as another animal
Video: a cat communicates with its reflection
Discovery three: CATS ARE POORLY DISTINGUISHING DISTANT OBJECTS!
Everything that is at a distance of 6 meters or more from them becomes blurry, as if in fog. This is approximately how these animals see the panorama of the city:
This small drawback is compensated by a delicate sense of smell and acute hearing. And besides, a domestic cat doesn’t live in the jungle to spot prey tens of meters from its place of residence!
But…
Does your pet see something we don’t see?
Whiskered pets were often accused of conspiring with the forces of evil, attributing magical abilities to them. But over time, most of the superstitions were explained by felinologists.
Differences from human vision and perception
Having figured out what kind of vision cats have, it is easy to identify its main differences from humans. Possible superpowers are confirmed by a wider viewing angle, faster perception speed and clearer visibility in low light.
Most owners have noticed more than once how their pets stare at one point for a very long time or suddenly jump up and start running around the room. At such moments, their pupils dilate and their fur stands on end. This behavior makes you very uncomfortable and even a little scary.
Vision problems: how to notice them
Cats suffer from various vision disorders quite often. The owner should be wary if the animal hides its eyes from bright light or often rubs its face with its paws. Signs of inflammation are frequent blinking of the pet, pus in the corners of the eyes, clouding of the whites, swelling of the eyelids. Any of these signs is a reason to immediately consult a veterinarian.
Kittens that are blind at an early age have much longer whiskers than their kittens. This is how nature compensates for the lack of visual perception of the world
Some eye diseases can cause complete blindness in your pet. It is difficult to notice vision problems in cats in order to take timely measures, since they are able to navigate in space even with complete blindness. The following signs indicate that vision problems have begun and should be checked:
- the animal does not jump to its favorite places located at a height or, when jumping, misses and falls;
- when moving around the house, he comes across moved or new furniture, objects standing in unusual places;
- your pet’s pupils do not constrict in bright light;
- stops responding to favorite toys;
- when the pet looks at the owner, his gaze does not focus on him.
All these signs indicate a deterioration in the cat’s vision or the onset of blindness.
What to do if your cat begins to see poorly
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to restore a pet’s vision, but this is not a reason to abandon a sick animal. The owner should organize the space of the home in such a way that the animal feels comfortable. Your pet can live a full life if you do the following:
- do not change the location of bowls with food and water;
- do not let the animal out into the street unattended, take it for a walk on a leash;
- in a new room, accustom the cat to the location of objects, without frightening them and allowing them to find their own way;
- do not block the path with boxes, scattered toys and other objects.
Color range of perception
Many animals see the world in black and white. However, cat vision is endowed with a more diverse range of shades. However, their color vision is very different from humans. A cat does not clearly see all colors, but only their rich spectrum of shades. Features of color differences :
- According to the old theory, the animal can only distinguish 25 tones of gray. This was explained by the fact that the cat hunts for rodents more often. The color of their skin is painted in various shades of gray. It was believed that it was these that a cat could spill in poor lighting.
- Modern scientists have already proven that the color scheme of a cat's eye is very diverse. The animal is able to distinguish other shades besides gray - blue, green, yellow. However, in the cat version the shades are duller and lack brightness.
- Do cats cut colors? Animals see mainly the hay-yellow spectrum. It is very difficult to distinguish between red and green. Yellow and white, brown and red and orange are often confused. Cat breeds do not necessarily need a variety of colors to live. For them, it does not matter what color (and how saturated it is) the surrounding objects are painted.
© shutterstock
The cat sees people not only with ordinary vision, but also with internal vision, and the sense of smell also helps. There is an opinion that animals consider people simply larger relatives, whose responsibilities include the care and maintenance of their smaller brothers. However, due to the peculiarities of the organs of vision, when contact is too close or 6 meters away, the cat sees the owner very vaguely and is more oriented by smell.