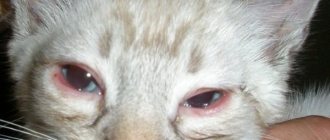
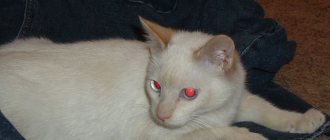
If the Sphynx's eyes fester, this may be a symptom of conjunctivitis, blepharitis, or entropion. In addition to suppuration, the inflammatory process is accompanied by photophobia, unnatural squinting of the eye, and swelling. At the first symptoms, you should take your pet to a veterinarian, who will prescribe medications or perform surgery.
Veterinarians warn that purulent eye diseases in most cases lead to panophthalmitis, so treatment of inflammation should begin quickly.
How and why does suppuration develop in sphinxes?
Inflammation of the connective membrane
The eyeball of the sphinx is covered by the conjunctiva, a tissue that produces tear and mucous fluid to moisturize the eye. Hairless cats have almost no eyelashes, so their visual organs are not sufficiently protected. Damage to the membrane promotes the introduction of pathogenic microflora into the eye structures, which provokes an inflammatory process. Causes:
- fights with relatives;
- incorrectly performed or lack of eye toilet;
- use of contaminated hygiene products;
- allergies, in which the animal scratches its eyes and causes microtrauma;
- entry of a foreign body into the visual organ.
Conjunctivitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- profuse lacrimation;
- eye hyperemia;
- swelling;
- soreness;
- the appearance of purulent discharge;
- the formation of crusts, due to which the eyelids stick together.
Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids)
A visual decrease in the palpebral fissure and the appearance of purulent crusts may be signs of the development of blepharitis.
It is characterized by a violation of the integrity of the ocular skin folds, through which pyogenic microorganisms - staphylococci or streptococci, as well as fungi - penetrate. Often the disease is accompanied by severe itching, which causes the Sphynx to scratch the eye and contribute to the spread of infection. The disease can be acute or chronic. Causes:
- injuries;
- skin rashes due to helminths;
- eczema due to improper bathing and skin care regimen;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- lack of vitamins and microelements.
Blepharitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- edema;
- severe itching;
- redness;
- compaction and thickening of the eyelids;
- visual reduction of the palpebral fissure;
- the appearance of purulent crusts.
Turn of the century
If the sphinx's eye ligaments are weakened, the eyelid turns inward, creating friction against the cornea and injuring it. Entropion can be congenital, when the disease manifests itself in a kitten, or acquired, occurring due to injury or inflammatory processes. It is distinguished by its serious severity, since representatives of the breed have deep-set eyeballs. Signs:
In the case of an inversion of the eyelid, the pet experiences lacrimation and swelling of the organs of vision.
- painful reaction to light;
- lacrimation;
- local increase in temperature;
- swelling;
- squinting or blepharospasm;
- mucous discharge, which later becomes purulent;
- strong pain.
Panophthalmitis
The disease occurs in advanced cases when the infection spreads to all tissues of the eye and melts them. The main reason is late contact with the veterinarian and the owner’s attempt to cure the pet’s purulent process on his own. Symptoms:
- protrusion of the eyeball (exophthalmos);
- profuse suppuration;
- loss of vision;
- clouding of all transparent structures;
- puffiness and swelling of the eyelids.
Eye diseases
Conjunctivitis (eyes festering)
In most cases, it occurs as a result of injury (from another animal, less often from sharp objects in everyday life), vitamin deficiencies and previous infectious diseases.
When infection penetrates through damage to the conjunctiva, the inflammatory process begins. Discharged pus indicates purulent conjunctivitis (in advanced cases), but in most cases, cats do not have purulent conjunctivitis, but catarrhal conjunctivitis (the discharge is not purulent, but transparent).
Catarrhal conjunctivitis is manifested by serous (transparent) discharge, lacrimation, redness and swelling of the conjunctiva of the eye; when trying to touch, the animal resists because it feels pain.
With a purulent process, the symptoms become more pronounced, the conjunctiva becomes covered with a white coating, and the discharge becomes purulent.
During treatment, anesthetic drops (novocaine solution) are used, the crusts around the eyes are soaked using a bandage soaked in warm boiled water or a 0.05% chlorhexidine solution, and then carefully removed. Eye ointments with antibiotics (for example, tetracycline) are placed in the conjunctival sac, and eye drops (chloramphenicol, sodium sulfacyl, also known as albucid) are instilled.
For purulent conjunctivitis, treatment is more complex: the veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics orally and intramuscularly (injections).
Keratitis (inflammation of the cornea)
This disease in cats also occurs mainly after injuries, as well as other infections, and metabolic disorders. The inflammatory process is localized in the anterior transparent part of the cornea of the eye.
Outwardly, this can be manifested by obvious painful sensations (the animal can rub its sore eye with its paw), lacrimation, fear of direct sunlight, the eyelid is constantly squinted or completely closed, there is no appetite, the cat is passive.
The consequences of keratitis can be complete or partial loss of vision, clouding of the cornea (the appearance of a so-called cataract), and other inflammatory processes.
The veterinarian prescribes treatment depending on the diagnosed cause of inflammation. The cat is placed in a dimly lit room.
Cataracts in Sphynxes and other cats
Cataract is a disease in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy. In its normal state, light rays pass through it and hit the retina. A clouded lens does not allow them to pass through completely or partially, and the quality of vision is greatly deteriorated.
Externally, the disease is manifested by a change in eye color to white or light gray.
The reasons for the development of cataracts in Sphynx cats can be different; not only past infectious diseases and injuries, but also the natural aging process of the animal’s body can play a role in this process.
To learn how to slow down the aging process of your cat, ensure a comfortable existence for her in her older age, and support her body, read the article “How to make a cat a long-liver.”
The only treatment for cataracts is surgical – transplantation of the clouded lens. There are also therapeutic methods - special drops are used, however, they only slow down the progression of the disease.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma in cats is also a serious disease characterized by periodic or constant increases in pressure inside the eye. The main danger is not only loss of vision, but also the risk of rupture and leakage of the eyeball.
Symptoms: the eyeball is tense and hard to the touch, reddened, the cornea is enlarged in size, the animal is afraid of light, and constantly rubs its eyes with its paws due to severe pain.
Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a veterinary ophthalmologist. Special drops (miotics) are prescribed that reduce intraocular pressure. Sometimes this is not enough and you have to resort to surgery.
How to treat a sphinx?
Drug therapy
Do not use tea bags for compresses. They are not sterile, their effectiveness is questionable and may worsen the condition.
If a disease is detected, you should contact a veterinarian, who, after examination, will prescribe treatment, for example, Beafar Ophtal.
All medications are prescribed by a veterinarian; self-medication leads to organ loss. If the Sphinx's eyes are watery, but there is no inflammation, a thorough toilet should be carried out daily using hygienic means, such as:
- "Dewdrop";
- "Green tea";
- "Beafar Ophthal";
- "Klin Ai";
- "Kleenie";
- "Teddy Pets" (wet wipes for eyes).
Veterinarians recommend treating purulent diseases with the following antibacterial drops:
- "Leopard";
- "Iris";
- "Diamond Eyes";
- "Tsiprolet";
- "Anandin";
- "Zoohealth."
Herbal compresses
If the sphinx's organ of vision becomes sour, it is recommended to make lotions to soak and remove the crusts. Suitable herbal decoctions include chamomile, string, St. John's wort, and sage. Preparation:
- Take 3-5 g of any herb and pour 200 ml of hot water.
- Leave for 20-30 minutes, cool.
- Filter so that no debris or sediment remains.
- Moisten a cotton pad, squeeze it a little and gently apply it to the eye. Rubbing or squeezing the organ is prohibited.
- Carry out the procedure until the crust is completely removed.
What and how to treat?
The first step when diagnosing bacterial conjunctivitis is to isolate an adult patient .
himself
must more carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene : do not touch his eyes with his hands, wash his face several times a day, use only his own clean towel.
During treatment, the patient must undergo a biomicroscopic examination ; it is also possible to take a sample from the conjunctiva of the eye (this is done through a smear).
Such diagnostic measures make it possible to identify the causative agent of the disease as accurately as possible.
After which treatment will be prescribed using one of these ointments:
- tetracycline;
- erythromycin;
- gentamicin.
Additionally, depending on the situation, the ophthalmologist will prescribe antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops .
How long is the treatment? As a rule, the disease is treated within 5-7 days, less often recovery occurs after 2-3 weeks. The timing depends on the type of bacteria, the therapy performed and the general condition of the body. Bacterial conjunctivitis is treated with tetracycline-based antibiotics.
What to do for prevention?
Whether a particular patient can wear contact lenses or whether glasses are recommended for him is decided by the ophthalmologist during an examination before the person buys his first lenses.
If there are no contraindications, pain can occur only for “technical reasons” (that is, due to problems with the products themselves).
And it is up to the patient to avoid pain during the use of such products if he follows the following recommendations:
How to eliminate pain after wearing?
First of all, you need to replace the optics if they are damaged, and also buy a new solution if it has expired.
Sometimes it happens that the lens is intact and there are no foreign bodies on it, but the pain is still felt.
This may mean that the lens is not seated correctly, and if you take it off and put it back on , the problem often goes away.
If pain occurs due to irritation of the cornea (this happens when it is hypersensitive), you can instill keratoprotective ophthalmic drops , moisturizing drops or anti-inflammatory drugs .
Keep in mind! Experts recommend these drugs:
- oxyal;
- ophtagel;
- ophtolic;
- inox;
- video;
- Visomitin;
- Visine;
- hydrocortisone or dexamethasone.
Such drugs should be used only in accordance with the instructions or according to the scheme drawn up by the ophthalmologist after examination.
But in any case, if the problem is not mechanical damage to the product, it is better to deal with the problem together with a doctor who will accurately identify the cause of the pain.
Allergy
Allergy is a real “scourge” of our time. It can arise completely unexpectedly, and manifest itself both qualitatively and quantitatively. A qualitative allergy is usually called a specific permanent reaction of the body to a certain irritant (allergen). This allergy torments people for years, or even their entire lives. True, there are cases known, for example, during pregnancy, when due to serious hormonal changes, the body stops responding to the allergen. But should we expect a miracle if the condition negatively affects one’s well-being? In turn, a quantitative allergy can be temporary, arising due to an excess of a substance in the body.
Purulent discharge from the eyes due to allergies occurs due to inflammation of the conjunctiva, and the resulting disease is called allergic conjunctivitis. In addition to purulent discharge, the disease is usually accompanied by itching, inflammation, an unpleasant feeling of “sand” in the eyes, burning, and blurred vision.
First of all, with allergic conjunctivitis, it is necessary to eliminate not the effect, but the cause. Namely, start taking antihistamines without trying to deal with pus from the eyes. It is these drugs that suppress the production of a hormone that responds to the allergen. The next step is to try to get rid of the irritant. When the disease has a pronounced seasonality, for example, the allergy begins during the flowering of trees and grasses, it is unlikely that the irritant can be eliminated. In other cases, you need to protect yourself from anything that causes such a reaction.
To relieve inflammation from the eyes themselves, it is better to use a weak infusion of chamomile. Chamomile has a drying effect, in addition, it is able to relieve local inflammation and fight microbes. Lotions with its infusion are enough to do twice a day, morning and evening. To prepare the infusion, the flowers of the plant are brewed and cooled to 37°C. This procedure must be accompanied by taking anti-allergenic drugs. In this case, it is advisable that the allergy medication be prescribed by a doctor. After all, only a specialist, after conducting the necessary research, is able to determine the severity of the disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Infection
The infectious cause of purulent discharge from the eyes is much more serious, although in advanced forms of allergies the condition of the eyes is also cause for concern. The main infectious cause of pus discharge from the eyes is a bacterial infection. As a rule, this is bacterial conjunctivitis or barley.
Conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is a consequence of an infection that has entered the mucous membrane of the eye and caused severe inflammation. This condition is very serious and in some forms can cause the entire eyeball to become red and severely swollen. In addition to the discharge of pus, this disease, as with allergies, is accompanied by unpleasant sensations: itching in the eyes, burning, discomfort, blurred vision. The main thing to remember is that such symptoms are temporary and disappear immediately after the disease is cured. At the same time, it is worth knowing that a bacterial infection can only be treated with antibiotics.
In case of conjunctivitis, this antibiotic is prescribed locally. As a rule, these are drops or ointments for the eyes. One of the most effective ways to treat eyes with bacterial conjunctivitis is the use of tetracycline group drugs. However, trying to make a diagnosis yourself, much less prescribe antibiotics, is very dangerous. Therefore, first, be sure to consult a doctor. Only a specialist can correctly assess the situation, give the correct conclusion, and prescribe the medication you need.
You can also relieve purulent manifestations of conjunctivitis with infusion of chamomile or string. And, of course, it is very important not to scratch your eyes, even with severe itching. In addition, it is worth paying attention to the correct removal of drying pus. Usually this happens after sleep. The pus is removed with a swab dipped in warm black tea brewed. It gently washes away the unpleasant “nitrous” and does not harm the eyes.
Barley
This is another fairly common infectious disease that manifests itself as suppuration of the eye. With barley, the abscess matures gradually, and pus is released towards the end of the disease, also after sleep. Barley is treated with local remedies; complications that can develop when a new infection is introduced with dirty hands pose a particular danger. That is why doing anything with barley is strictly prohibited. The maximum is eye drops or ointment. As in previous cases, a drug for the treatment of barley must be prescribed by a doctor. In the absence of an associated infection, in most cases, barley goes away on its own.
Folk remedies
For bacterial conjunctivitis, it is permissible to be treated using traditional medicine .
Important! But such a course, which should be carried out in parallel with the main course, must be agreed with the attending physician, since patients may have contraindications to some components and ingredients.
In addition, some products may be incompatible with medications prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
Here are some common and safe prescriptions :
- Several small dried aloe leaves are crushed and poured with boiling water in the ratio of “1 teaspoon of plant to two glasses of boiling water.” After the solution has cooled, you can use it to make compresses or wash your eyes . If there are no allergic reactions to aloe, freshly squeezed aloe juice . But in this case, it must be diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1:10, and if the symptoms of the disease intensify or in case of irritation of the organs of vision treated with this product, its use is canceled.
- One hundred grams of dried and crushed marshmallow roots are poured into a glass of cold boiled water and left for six hours. After this time, the infusion is filtered, and the finished product can be washed with the eyes two to three times a day.
- A teaspoon of dried and crushed rose petals is poured into a glass of boiling water and left for half an hour. The solution is also used for rinsing.
Treatment with folk remedies should not replace drug therapy: such methods are only suitable for relieving the symptoms of conjunctivitis in complex treatment.