Caring for your pet’s health is expressed not only in proper care and feeding. It is important to prevent your cat from becoming infected with dangerous infectious diseases, primarily rabies. This is a fatal disease that can only be recognized at a stage when treatment is no longer useful. Moreover, a cat with rabies will become dangerous to others, and rabies is no less dangerous for people. If a person bitten by an infected animal shows symptoms of this disease, then this is already 100% fatal, the only question is time. Therefore, rabies vaccination is the only way to protect against this disease.
What is rabies in cats
Feline rabies (hydrophobia, hydrophobia) is an acute viral infection caused by a specific neurotropic virus of the rhabdovirus family, the genus Lyssaviruses. The disease manifests itself as serious irreversible disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, since the main target of the rhabdovirus is the brain.
Under favorable conditions, the pathogen retains its virulence (ability to infect) for a long time. Do not be afraid of low, sub-zero temperatures and, for example, this infection persists in the corpses of those killed for 12-24 months. Not resistant to high temperatures. Kills instantly when boiled.
Important! Outbreaks of rabies are recorded everywhere, mainly in the spring-summer period and autumn. Hydrophobia is deadly for animals and humans.
The reservoir of infection in the natural environment is predators, wild birds, and rodents. Infection of pets occurs during a bite, when the saliva of an infected animal or latent carrier gets into open wounds, scratches, damage to the epidermis, as well as mucous membranes.
The duration of the incubation period in cats ranges from several days to 2-5 months and depends on:
- virulence, the amount of virus, the speed of its movement along the nerve pathways;
- age, weight, size of the cat;
- state of the immune system, resistance;
- localization of the bite site, its depth.
The deeper and closer the bite site is to the head, the shorter the latent period. In small kittens, the incubation period is shorter than in adult pets and the initial symptoms of infection are more pronounced.
Important! If a cat is infected, but there are no signs of rabies, it is a latent carrier and can infect humans and other animals. The average incubation period is 2-3 weeks.
Viral infection affects all warm-blooded animals, cats of any age and breed. The risk group includes unvaccinated, weakened individuals, small kittens, cats that are kept in unfavorable conditions, are free-range, live in rural areas, near steppes, forests or in regions unfavorable for this infection.
What diseases are vaccinated against?
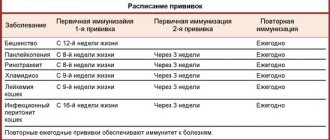
According to the vaccination calendar, cats are recommended to be vaccinated according to age against several of the most dangerous diseases.
What diseases is it recommended to vaccinate your cat against?
- Rabies (rabies) is a deadly infectious disease that cannot be cured. Manifests itself with severe symptoms that occur 2-3 days after infection. Infected animals and rodents are carriers of the infection.
- Rhinotracheitis is a herpesvirus infectious disease that affects the respiratory and visual organs. Has an acute course. The carriers of the virus are sick cats. Mortality occurs in 20% of cases.
- Calcivirosis is a common infectious disease of cats, transmitted from other members of the genus who are carriers of the insidious virus. The risk of death is more than 80%.
- Viral peritonitis is an infectious disease caused by coronavirus. Infection occurs through airborne droplets after contact with a carrier of the infection. The risk of death is very high (more than 90% of cats die).
- Panleukopenia is an acute viral disease also known as feline distemper. Sick or already ill cats serve as spreaders of infection. Difficult to treat. Causes critical symptoms. The risk of death is 90%.
- Chlamydia is a contagious feline disease of an infectious nature with a severe and long-term course. The main carriers of infection are birds and rodents. The disease affects the genitourinary, respiratory, visual and digestive systems. There are risks of infecting people.
- Microsporia is a skin disease also known as ringworm. Carriers of infection are sick animals. A cat with microsporia often infects its owner. The most popular drugs for vaccinating cats against various infections: Nobivak, Quadrikat, Multifel-4, Microderm, Leukotsel, Felovax-4, etc. The drug will be selected by the attending veterinarian.
Forms, stages of rabies
Rabies has several stages of development and occurs in cats in different forms, each of which has its own symptoms.
Forms of rabies in cats:
- Easy. The duration of the incubation period is from three to five days to 1-3 months. The animal's behavior changes. Cats become overly affectionate, annoying, and require increased attention from their owners. Attacks of affection are replaced by a state of panic. The pet is afraid of noise, sharp sounds, bright light, reacts inadequately to stimuli, and hides in secluded places. Foamy salivation, difficulty swallowing, disturbances in heart rhythm, breathing, and muscle spasms are noted.
- Violent. The most commonly diagnosed form of hydrophobia in cats. The pet shows aggression, disobedience, does not cooperate, refuses food due to spasms of the laryngeal muscles, and loses weight. The fur is tousled, dull, and falls out in clumps. The pupil does not react to light. The lower jaw droops. Saliva flows from the mouth. Anxiety gives way to complete apathy. The temperature is normal or elevated at the beginning of the development of infection or within the normal range. Paralysis of muscle structures develops, and the pet suffers from epileptic seizures. The cat dies from exhaustion, severe intoxication, and respiratory failure.
- Atypical. This form of hydrophobia is rare. The first symptoms, which are similar to manifestations of gastroenteritis (vomiting, diarrhea, high fever, loss of appetite, exhaustion, discharge from the eyes and nose) may appear 3-7 months after infection. In this condition, the cat's condition is changeable. Symptoms subside for a while, after which they appear again. The pet dies.
The first symptoms that allow you to understand that a cat is infected with the rabies virus are inappropriate behavior. If you suspect an infection, take the cat to a veterinary hospital until it is examined and an accurate diagnosis is made.
Pre-exposure (pre-exposure) immunization
- Indicated for persons at high risk associated with their profession (laboratory workers directly working with the rabies virus, veterinarians).
- Travelers who may be at risk of exposure to the virus.
- Persons living in areas where rabies is endemic and where the availability of anti-rabies biological products is limited.
It should also be remembered that for any injuries that damage the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, animal bites, burns, frostbite, etc. emergency prophylaxis of tetanus is carried out.
Rules for rabies vaccination of cats
Considering that rabies is an incurable infection and that a person can catch the infection from their pet, we recommend not to neglect preventive vaccinations, the schedule of which is established by the veterinarian. Pet owners should know the basic rules for vaccinating cats against rabies.
Rules for vaccinating cats against rabies:
- Clinically healthy cats are allowed to be vaccinated, so before immunization, the veterinarian examines the animals at the clinic.
- The cat must be prepared for immunization.
- If there are contraindications to immunization, the vaccination is postponed to a favorable period. If serious complications and post-vaccination reactions develop after the administration of the vaccine, the veterinarian should choose a different drug for the next vaccination.
- Cats living in regions unfavorable for rabies must be vaccinated.
- For vaccination, mono-polyvalent vaccines of domestic and foreign production are used.
After vaccination, the veterinarian puts stamps and signatures on the veterinary passport, certificate, and indicates which veterinary drug was used for immunization.
Post-vaccination period
Usually the vaccine is administered intramuscularly, less often - subcutaneously. The standard dose volume is 1 ml. If the preparation is carried out correctly, the animal’s well-being remains normal. It is possible that the cat’s activity may be suppressed for 2-3 days, but this is not critical, and the animal’s condition will improve on its own.
A lump may form at the injection site if the drug was administered subcutaneously. It resolves on its own within a week. After intramuscular injection, swelling does not form.
Negative consequences after vaccination are possible, but only if the animal is not properly prepared and the procedure is carried out without taking into account contraindications. Serious complications are allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock), which cannot be foreseen if a particular drug is used for the first time. Therefore, after the injection, the animal must remain in the clinic under the supervision of a doctor for 20 minutes.
Rabies is a serious and dangerous disease for both the pet and its owner. Therefore, it is necessary to vaccinate your pet, regardless of whether it is walking outside or not. To save time and reduce stress in the animal, it is worth using multicomponent vaccines - they will provide immunity against several diseases, and you will not have to visit the veterinarian often.
Pros and cons of vaccination
Many cat breeders mistakenly believe that rabies vaccination or other vaccines are harmful to the pet’s health and often neglect the vaccination schedule established by the veterinarian. In general, this is a misconception. Modern veterinary medications rarely cause side symptoms or side effects, of course, if the pet is properly prepared for vaccination and the veterinarian carries out the immunization according to all the rules.
Important! Post-vaccination complications are possible when introducing expired vaccines, in case of individual sensitivity of the animal’s body, and also if the vaccine was administered during the incubation period of the disease.
Preventive vaccinations today are one of the effective ways to protect our little brothers from viral and bacterial diseases. Rabies is an incurable infection. After the administration of the rabies vaccine, after 21-23 days, specific immunity to this disease is formed for a period of one to three years.
In addition, if the pet is not vaccinated against rabies and other infections, it is prohibited to take it out of the country or transport it on public transport. You cannot attend exhibitions or events with the participation of pets.
Numerous studies in the field of veterinary medicine have proven the fact that vaccinations somewhat reduce the immune potential of animals. In some ways this is true, but still, modern vaccines contain minimal doses of antigen that trigger the body's immune response.
Important! Even if the cat does not leave the house, in any case it must be vaccinated.
Validity period and frequency of revaccination
Interestingly, the validity period and frequency of revaccination differ significantly from each other. We have already written that many of the modern vaccines can contribute to the formation of three years of immunity at once, but revaccination is still mandatory once a year.
We have already written above why this frequency of repeated vaccinations is connected: too many factors act on the cat’s body, and therefore it is impossible to predict for how long it will remain resistant to rabies.
Age for first vaccination
Kittens are vaccinated against rabies for the first time at the age of 10-12 weeks. The most commonly used vaccine is a polyvaccine. If a monovaccine is administered, the rabies vaccine is given simultaneously with the administration of vaccines against other infections. Cats are vaccinated against rabies for the second time at the age of 10-11 months.
The age for the first rabies vaccination will be determined by your veterinarian. In some cases, if the cat is unwell, there are other contraindications, the rabies vaccine is administered to cats after the change of milk teeth, at about 8-10 months. But in any case, the pet must be vaccinated against this infection for up to a year.
Preparing for vaccination
The animal must be properly prepared for vaccination and revaccination. Preparing for vaccination involves following certain rules:
- Protect your pet from stress, drafts, overheating, hypothermia, and other negative factors that weaken the body.
- If a rabies vaccine is being administered to a pet for the first time, owners should limit the cat's contact with other animals that may be potential virus carriers. If your cat walks outside, do not let him go for walks until he is vaccinated. This will avoid possible infection from other animals.
- Keep your house and apartment clean, and also pay attention to your pet’s hygiene.
- Before vaccination, two weeks before vaccination, the cat is driven away from worms with complex anthelmintics and treated with insecticidal and acaricidal agents against ectoparasites.
Two to three days before vaccination, monitor your pet’s condition, measure its temperature twice a day, recording the readings in a notebook.
If vaccination is scheduled for the morning, do not feed your pet, but do not limit it to water. If the cat is vaccinated in the afternoon, you can give light food (half a serving) in the morning. Before vaccination, a comprehensive examination of the animal is carried out.
What to do after vaccination
After vaccination, the cat is kept in quarantine for 20-23 days, avoiding contact with other animals. During this period, immunity against viral infection is developed. Protect your pets from stress (moving, changing residence), hypothermia, overheating, and other factors. Provide optimal living conditions and a high-quality diet.
After vaccination, any surgical operations can be performed no earlier than 3-4 weeks later. An exception is medical measures that are required to save the life of an animal.
After vaccination, in the first 3-6 days, a cat may develop post-vaccination complications, especially in kittens and young animals. Therefore, carefully monitor the condition of your furry pet.
A one-time refusal to feed, diarrhea, vomiting, the appearance of a lump at the injection site, lethargy, drowsiness is a completely normal reaction of the body to the vaccine. As a rule, such symptoms go away on their own and the cat’s condition returns to normal on the second or third day.
If serious complications develop, with a progressive deterioration in health, immediately contact a veterinarian, call him at home or take the cat to the clinic.
Types of rabies vaccines
Several types of vaccines are used in veterinary medicine. All of them are multicomponent, that is, after one vaccination the animal receives immunity from several diseases. The price of the vaccine depends on its type. The following drugs are common today:
- Nobivac Rabies. A multicomponent vaccine that protects against rabies, rhinotracheitis, panleukopenia (distemper), and calcivirosis. The first vaccination is given no earlier than 8 weeks of age. Stable immunity is formed after revaccination, which is carried out after 3 weeks. One dose costs about 370 rubles.
- Quadricate. Complex vaccine against rabies, panleukopenia, respiratory diseases. The drug does not contain live strains, so it is easier to tolerate and completely safe. Vaccination is carried out at 4 months, revaccination is carried out annually. One dose costs about 600 rubles.
- Defensor 3. Provides lasting immunity against rabies. It is administered once, to kittens from 3 months of age. Revaccination needs to be done every 3 years. The cost of one dose is about 100 rubles.
- Rabisin. Used to prevent rabies in many animals. Cats are administered twice - the first time from 3 months of age, the second time a year later. The cost of one dose is about 200 rubles.
It is difficult to say which vaccine is the best. All of them are high quality, tested. The choice of drug is based on the individual characteristics of the pet, the capabilities of its owner, and the desired effect.
Contraindications
As already noted, only clinically healthy animals are vaccinated. If there are contraindications, vaccination is postponed to another time.
The following are not vaccinated against rabies:
- kittens that are under 2-2.5 months old;
- if the pet's weight is less than 500 g;
- pregnant, lactating females;
- during the recovery, rehabilitation, postoperative period;
- weakened, exhausted, sick animals;
- kittens during the period of change of milk teeth.
Older cats should be vaccinated against hydrophobia with caution.
The most popular types of drugs
All vaccines are divided into two types: live (attenuated) and inactivated. “Non-live” ones consist of “dead” viral bodies, and live types of injections consist of weakened strains. Vaccination against rabies of the “light” form is accompanied by a strong immune reaction caused by the fact that your pet is ill with a milder manifestation of the virus.
Vaccination is often free of charge - the owner can vaccinate the kitten at a veterinary hospital or at an on-site veterinary center where a domestic type of injection is used. The procedure is carried out in a veterinary clinic - the drugs require specialized storage with a special temperature regime and careful monitoring of the expiration date. Most drugs are imported analogues of the domestic vaccine "Rabican", widely used in private veterinary clinics:
- Quadrocket. An imported medicine that is effective against a number of infections.
- Felovax. It gained popularity due to its minimal side effects.
- Purevax RCP. Affects parvovirus, calicivirus and rhinotracheitis.
- Nobivak. Analogue of "Rabican". It has a targeted effect on a complex of infections.