One of the most deadly injuries is a concussion in a cat. Head injury is accompanied by impaired coordination of movement, increased drowsiness, loss of memory or consciousness. It is important for the owner to be able to provide first aid, since injury is dangerous due to complications in the form of hemorrhagic stroke, loss of vision, cerebral edema, paralysis, and malignant tumors. You should urgently take your pet to a veterinary clinic, where the doctor will diagnose and prescribe treatment, which will determine the prognosis.
According to the observation of veterinary surgeon I. Smirnov, brain injuries in cats most often occur in the summer, when the animal falls out of the window due to the owner’s oversight.
Causes of brain damage
A concussion in cats is a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and is characterized by compression of areas of the organ and disruption of blood flow due to a strong collision with the skull. Damage can be closed, when the integrity of the skull is not violated, and open, which is characterized by crushing of the cranial bones and mechanical damage to the brain. Pathology occurs after a blow to the head under the following circumstances:
- falling from a great height;
- auto injury (when a cat was hit by a car);
- accidental trapping of an animal in the door wings;
- a heavy blunt object falling on the cat's head;
- Hitting your head on hard furniture or a wall while playing.
Treatment of the disease
After examining the patient and establishing an accurate diagnosis, the veterinarian prescribes treatment. Primary therapy is aimed at reducing cerebral edema in a cat; the drugs Hypothiazide and Indapamide, as well as diuretics such as Furosemide and Veroshpiron, are excellent for these purposes. The pet is also prescribed pharmaceuticals with a pronounced analgesic effect, for example, Analgin, and injections that can support the functioning of the cardiac system (caffeine).
Immediately after swelling and the most painful symptoms are removed, the doctor prescribes nootropic drugs (Piracetam, Glycine) for the cat, which improve metabolism in brain tissue and nourish nerve cells. In addition, the cat is prescribed mild sedatives, such as Fitex and Xylazine, as well as those based on medicinal herbs - motherwort, peppermint. The duration of medication is determined by how severe the cat's concussion was. On average, complete healing takes from 7 to 14 days.
Never try to treat an animal at home. Even experienced veterinarians cannot always understand all the nuances of a concussion without the use of X-rays or CT scans. Caring for an injured pet on your own without first consulting a doctor will probably only aggravate the current situation and lead the cat to irreversible disorders of the functioning of the brain.
Symptoms: how to recognize the problem?
If the pet has received moderate injuries, then it may become aggressive.
The most severe injury is considered to be a fracture of the base of the skull, when the cervical vertebrae connecting the spine and the skull are broken. In this condition, the animal loses consciousness and falls into a coma, after which death occurs. In a kitten, traumatic brain injury occurs faster and is more severe due to the fragility of the skull bones and the high risk of swelling. Symptoms of a concussion in cats depend on the severity of the injury, they are shown in the table:
| Degree | Signs |
| Lightweight | Minor loss of motor coordination |
| Vomit | |
| The animal lies down a lot and refuses to play. | |
| Average | Brief loss of consciousness |
| Loss of orientation in space | |
| Memory loss (the cat does not recognize the owner) | |
| Attacks of aggression or apathy | |
| Convulsions | |
| The cat is looking for a dark corner | |
| Headache (the cat tries to rest against a hard object and does not move) | |
| Heart rhythm disturbance | |
| Heavy | Dilated pupils, lack of reaction to light |
| Frequent shallow breathing | |
| Decreased vision and hearing | |
| Severe cramps | |
| Paralysis | |
| Involuntary loss of urine and feces | |
| Breathing problems, wheezing | |
| Paleness of the mucous membranes of the mouth | |
| Bleeding from the ears or mouth | |
| Loss of consciousness, coma or death |
Other diseases Is it necessary to somehow treat cones and hematomas of Vetna cats?
The cat's body is as fragile as the human body, so the phenomenon of bumps and hematomas on the animal's body also occurs. Not all owners know how to deal with this problem. Some say that our pets “lick” their injuries on their own, while others insist on the need for an immediate visit to an experienced veterinarian. In fact, this issue requires a more detailed discussion, so let's get down to this topic.
Cones - what causes them
You may notice a lump on your pet's body, and most often this is attributed to some kind of injury, especially when your pet has free access to the street. But are you sure that this bump is a swollen bruise? It is quite possible that the problem lies a little deeper than it seems. If the swollen area of skin does not change in any way within a week, then you should make a visit to the veterinarian, since cancerous tumors are as common in pets as in people. You should take this especially seriously and carefully if the swelling was found in an unusual place: the eye, ear, tips of the paws, tail, and so on. As a rule, these places are treated with ordinary bruises at the site of the injury, and the occurrence of swelling there is extremely rare. For prevention, it is necessary to constantly examine your pet’s body. This is done very simply: • Place the pet in a position that is comfortable for him, and examine the surface of the body. Do not forget to remove the fur and easily feel the areas that have a visibly swollen appearance or an unusual skin color. • After this, place the cat on its back to examine the abdominal area. Palpation is carried out in exactly the same way. • The final stage is to examine the ears, head, eyes and tail. Here you need to be more careful.
Bruises and abrasions
Bruises and abrasions are quite common for our furry friends, since cats are very active animals, and they can get so busy that they don’t even notice the injury. This applies not only to street animals, but also to domestic ones. For example, domestic cats can easily hit the corner of the bed, fall from a height, or awkwardly slip on laminate or parquet flooring, skidding into a wall. If you realize that your cat has hurt himself, there is no need to panic, since all this swelling and hematoma in cats goes away on their own. In the course of everyday life, animals experience almost no pain from them. Particularly caring owners will immediately want to anoint the pet’s injured area with some ointment, but this is not necessary. There is no need to press on the painful part of the body again. It is also not recommended to massage this area too much, so as not to cause additional discomfort to the cat. Just wait a while and the disease will go away on its own.
Preventing injuries - is it possible?
We all remember from childhood what bruises, contusions, abrasions and bumps are. Our parents constantly told us to be more careful so as not to injure ourselves more, but did it really work? I still had to smear my knees with brilliant green and also apply plantain. The same applies to cats, animals that are particularly energetic and playful. Your pet will not be able to sit in one place all its life, so do not limit its will, play and walk outside. This way life becomes much more interesting and eventful, and possible bruises and bumps will go away on their own. To reduce the risk of injury, it is enough to create a special place for games at home. When walking with an animal (if the cat is used to the street), do not let it out of the harness, and also do not let it play with stray cats and other animals. Toys should not be too hard or heavy. Also make sure that there are no heavy things in your home that are placed untidy on shelves or other high places.
How to provide first aid?
It is strictly forbidden to independently reduce or remove bone fragments in the event of an open injury.
In the room where the pet is, you need to close the curtains so that it is not disturbed by bright lighting.
If a cat hits its head, you need to act quickly, as the prognosis depends on it. Algorithm of actions:
- Ensure peace and quiet, turn off bright lights or draw curtains.
- Apply cold to the head for 15-20 minutes, this will reduce the risk of developing a hematoma and prevent brain swelling.
- Place a thin cloth band between your teeth to prevent your tongue from sticking.
- If vomiting begins, you need to make sure that the animal does not choke. Remove the remaining vomit from the mouth with a finger wrapped in a bandage.
- In case of cardiac arrest, perform artificial respiration: Lay the cat on its side and sharply compress the chest 6 times in the direction of the neck.
- Exhale into the cat's nose.
- Repeat pressing (at least 80 rubles per minute) and exhalation, alternating cardiac massage with artificial respiration - 15 sec./10 sec.
Cat care
A cat that has suffered a concussion needs careful care and attention from the owner. The following recommendations will help ensure a quick recovery:
- The animal must be in a state of peace and quiet. Loud sounds and bright lights are contraindicated for him.
- Feed your cat healthy food rich in vitamins and microelements.
- Until complete recovery, you should not let your pet go outside.
- Over the next 4-6 months, take your pet to the vet regularly.
There is little pleasure in brain injuries, and they are extremely dangerous for a furry fidget. Therefore, at the first sign of a concussion, the pet should be taken to a veterinary clinic as quickly as possible. It also happens that if the owner ignores even the slightest, seemingly insignificant bruises to the head of his pet, he remains disabled for life. Feel free to take care of your cat and take care of his health, and he will always be cheerful and energetic.
Diagnostic measures
First, the sick animal is examined externally by a doctor.
To identify a concussion in a cat, the doctor finds out the causes of the injury, listens to the owner’s complaints, conducts an external examination and prescribes diagnostic procedures, such as:
- neurological reflex test;
- ophthalmoscopy;
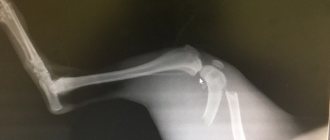
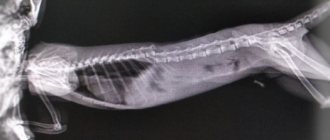
- radiography of the skull bones;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- blood pressure measurement;
- General and biochemical blood test.
Examination procedure
If we talk about a general examination, then it is necessary to measure the rectal temperature and see what color the animal’s mucous membranes are. You also need to determine how long it takes for the white spot to disappear after you press on the animal’s skin. You need to measure the pulse rate, see if there is external bleeding, vomiting, or other discharge. The integrity of the skin and the animal’s state of consciousness are also assessed.
When examining the chest, you need to calculate how often the animal breathes, to see what kind of breathing it has. You also need to visually inspect and feel the animal’s chest in order to check for various penetrating wounds and rib fractures. Both sides of the chest should move equally, and heartbeats should be felt. It is necessary to determine the areas in which the sound is duller and conduct auscultation. It is carried out in order to determine the heart rate, as well as various pathologies. It is also necessary to determine the noises that appear when the animal breathes.
When examining the head and neck, they should be examined for injuries. You especially need to pay attention to the skull, eyes, mouth and nose. It is necessary to check how well the animal moves its head and whether it has pain during these movements.
When examining the abdominal cavity, the presence of wounds is checked, and palpation is also performed. To determine pain or fluid. Other organs can also be identified. The organs are examined to determine whether there is fluid or air in them. Rectal examinations are also performed.
The spine and all limbs of the animal are carefully examined in order to determine the presence of injuries, as well as various deformities that can be seen visually. You also need to determine the temperature of the extremities. Palpation is needed to identify fractures or various displacements.
When testing an animal's nervous system, the animal's reflexes, how its limbs are positioned, and whether the animal is paralyzed are assessed. Muscle weakness and the ability to stand or walk are assessed.
Treatment: which methods are effective?
To avoid severe consequences, the following treatment methods are used for traumatic brain injury in cats:
- Taking medications: To prevent edema, diuretics are prescribed - “Hypothiazide”, “Urotropin”, “Furosemide”, “Veroshpiron”.
- To maintain the functioning of the heart, injections should be made with drugs such as “Caffeine benzoate sodium 20%”, camphor solution 20%.
- Antishock medications - Prednisolone, Travmatin, Dexamethasone.
- Metoclopramide and Cerucal are effective in suppressing the gag reflex.
Concussions and contusions of the spinal cord
When a spinal cord injury occurs, conduction along centrifugal and centripetal pathways in one part of the brain weakens or disappears. When the brain is damaged in the cervical thickening, paralysis of the motor pathways of all extremities of the body and internal organs occurs, but the work of the brain and the cyphergram continues to ensure breathing. Damage to the spinal cord between the medulla oblongata and the 4th-6th pairs of cervical nerves is fatal, as paralysis of the respiratory center immediately occurs.
Symptoms.
In case of mild bruises, without damage to the substance of the splint, short-term paresis is noted; in severe cases, the presence of vertebral cracks, ruptures of the meninges and spinal roots, and complications of hemorrhages in the brain are recorded. In this case, there are signs of persistent spinal cord paralysis, decreased deep and superficial sensitivity of the tail and limbs, and prolapse of the rectum. Cats move only with the help of their front limbs, their hind limbs drag. The pelvic part of the body is lowered, the animal is characterized by a sitting position with elongated pelvic limbs. A hump forms at the site of injury.
Diagnosis.
Clinical signs of the disease appear in the animal within the first 5-6 days. With hemorrhage, movement disorders gradually decrease; with appropriate treatment, they completely disappear after 10-15 days. When the meninges are compressed, paraplegia slowly develops and symptoms of movement disorders appear, first on one limb, then on both, and disorders of urination and defecation occur. Preservation of the function of the thoracic limbs in case of pelvic paralysis is determined by a violation of the conductivity of the spinal cord in the anterior part of the lumbar region.
Injury to the sacral spinal cord is characterized by paralysis of the pelvic limbs, tail, sphincters of the rectum and bladder. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to take x-ray pictures of the injury site and two projections.
Treatment.
The cat is given complete rest, the bleeding is stopped, and cold is applied. Then sedatives and pain-relieving drugs are administered. In the future, thermal procedures and spinal massage are prescribed. Darsonvalization of the spine is very effective in combination with vitamin Bi2 and strychnine (0.1% solution) - 1 ml for paralysis of the pelvic limbs.
For cracks and fractures of the spine, surgery is performed if possible. It should be borne in mind that the treatment is long and requires patience from the doctor and the cat’s owners.
Cats are very dexterous animals, but they do not always manage to avoid falls and bruises. Head injuries and severe concussions in cats are common.
The cause of a concussion in outdoor cats can be a fall from a height, being hit by a car on the road, an awkward jump from a tree, or being hit by a person.
Domestic cats receive head injuries as a result of heavy objects falling on them or hitting a wall if the animal is frightened or does not have time to brake in time. A concussion is accompanied by cerebrovascular accident and sometimes hemorrhage. This process results in disruption (temporary or permanent) of normal brain activity and activity.
First of all, you need to call a veterinarian. An experienced doctor will provide immediate assistance to the animal.
What are the consequences?
One of the complications from injuries sustained in a pet may be partial paralysis.
Traumatic brain injury is a serious injury and, even if signs are identified promptly and treatment is started, the following complications may develop:
- Hemorrhagic stroke. It is characterized by rupture of a vessel and accumulation of blood in the space between the brain and the skull. May cause blurred vision, gait and memory impairment.
- Loss of vision. Occurs when the visual areas of the brain or nerve are injured.
- Brain swelling in a cat. The condition threatens the life of the animal, since the adult or kitten is subject to impaired oxygen exchange in the lungs and suffocation, which leads to death.
- Paralysis. Occurs when there is dysfunction of the areas of the brain responsible for the innervation of the limbs. May be partial or complete.
- Malignant neoplasms. Trauma can trigger a cell cycle failure, when cells begin to divide and grow abnormally quickly and form a tumor. The condition is dangerous due to the spread of metastases to vital organs, which leads to death.
How to help an animal with bleeding
If the animal has bleeding, it must be eliminated by any available method. For example, you can compress the vessels, but as first aid it is quite possible to use a soft pad or a pressure bandage. At the moment when the animal’s condition improves, you can turn to surgical intervention. The intervention will depend on the nature of the injury, as well as on the type of vessels that are affected. If the bleeding is arterial, then this condition is very dangerous. Venous bleeding is less dangerous, but more difficult to control over the long term. If there is a possibility of internal bleeding, then the blood is sucked out from the chest, as well as the abdominal cavity of the animal.