Worms are considered one of the most common types of parasitic worms that infect humans. Characterized by a wide variety of species and forms, helminths can provoke the development of many serious diseases.
A helminthic infestation is quite easy to detect due to the huge number of external manifestations of infection. On the other hand, the majority of symptoms caused by helminths are not specific, which, along with the high number of parasites in the body, can greatly complicate making a specific diagnosis. As a rule, the final differentiation of the disease occurs only based on the results of a special laboratory study. What are the signs of helminthic infestation in adults?
About roundworm infection
Roundworms cause a whole group of diseases.
Nematodes are a whole group of specific diseases caused by the same pathogen - roundworms.
Symptoms of such ailments can be very different, depending on the type of parasite that has entered the body. In general, all nematodes can be divided into two large categories:
- acute, characterized by a clear manifestation of symptoms from the very first days of the development of the disease;
- chronic, sluggish and passing, as a rule, almost asymptomatic.
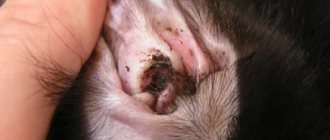
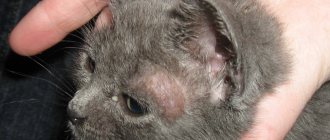
Types of worms in dogs and cats
In dogs, as in cats, there are three groups of worms:
- Nematodes (roundworms).
- Trematodes (flukes).
- Cestodes (tapeworms).
Nematodes are invasive diseases of dogs and cats, the causative agents of which are representatives of the class of roundworms (Nematoda), and are collectively called nematodes. This type of worm parasitizes not only the intestines, but also affects the heart, aorta, eyes, kidneys, bladder and subcutaneous tissue. The most common representatives of this group are roundworms, pinworms, whipworms, toxocaras, hookworms, trichinella, strongoloidiasis, heartworms.
Trematodes are helminth infections caused by representatives of the class of flukes or trematodes (Trematoda). A large number of trematode species are known in animals, each of which is characterized by structural features, life cycle, localization (habitat) and pathogenic effects on the host organism. Trematodes in dogs and cats most often parasitize the liver and intestines. The most common representatives of this group are fascioliasis and opisthorchiasis.
Cestodoses are diseases in dogs that are caused by representatives of the class of tapeworms or cestodes (Cestoidea). They are collectively called cestodiases. Sexually mature cestodes parasitize animals only in the intestines. The larval stages of causative agents of cestodiasis can parasitize a variety of organs and tissues in both animals and humans. The most common representatives of this group are dipylidia, diphyllobothriasis, alveococcosis, taeniasis, and echinococcosis.
Roundworms
The most common causative agent of nematodes in humans is roundworm. Typically, the first signs of infection with this worm appear in the second week, when the larvae of the parasite begin the migratory phase.
Most patients suffering from one type or another of ascariasis exhibit the same characteristic symptoms of this condition. Thus, with helminthic infestation of the lungs, patients usually complain of:
- temperature increase;
- paroxysmal asthmatic cough accompanied by chest pain;
- discharge from the lungs of a small amount of mucous sputum (sometimes streaked with blood).
Due to the ambiguity of symptoms, the described type of ascariasis is often confused with allergies, bronchitis, ARVI, asthma or even pneumonia. This kind of invasion is generally the last thing to be suspected, since the adult parasite does not take root in human lungs.
In other words, such a condition can arise only during the period of migration of roundworm larvae. As a result, only an x-ray showing a large number of infiltrates (that is, accumulations of eosinophils reacting to helminth toxins) in the patient’s lungs usually helps to establish an accurate diagnosis. With helminthic infestation of the intestines, the symptoms of the disease become more specific:
Types of worms in cats and cats
Worms in cats come in different sizes and shapes, and they feed and reproduce differently. They have long been classified into three categories: flukes, tapeworms, and roundworms. Let's study the enemy!
Peculiarities
Symptoms in a cat
This infection enters the cat if it drinks from a dirty source or eats crustaceans. Tapeworms destroy the lungs with cyst-like formations
- heat;
- refusal to eat;
- fever;
- wheezing and frequent cough.
The parasite can easily take up residence in both the cat’s body and the human body. In a cat, the size of a tapeworm rarely exceeds a length of 30 cm. The danger is expressed by damage to the intestinal walls. The parasite can be brought by fleas and lice eaters.
The pet is vomiting, losing weight, and is irritable. My stomach is constantly rumbling and I have diarrhea.
The parasite grows in the body up to 1.5 meters in an animal, and up to 12 meters in a person. You can become infected by eating raw fish, crustaceans and drinking river water.
- diarrhea;
- lack of appetite;
- vomit;
- weight loss.
The fluke has chosen the liver as its home and does not disdain the pancreas and gall bladder. To acquire such a neighbor, you can eat raw fish.
The vomit is colored in shades of yellow, there is no appetite, the animal is weakened. Diarrhea appears and the temperature may rise. Complex treatment is used here, due to the ineffectiveness of standard treatment.
The parasite reaches a length of 4-5 mm and does not pose a danger to the cat. For many years this neighborhood has been quite peaceful, but as soon as a person becomes infected, trouble will strike. It is difficult to make a diagnosis; the patient faces death due to metastases to various organs, and a liver tumor develops. The worm can enter the body as a result of eating a rodent.
The localization of five-centimeter helminths is the esophagus, gall bladder and liver. The source of infection is food, and cases of intrauterine infection are also known. The parasite is dangerous for kittens, as the rapid development of toxocara begins, which is fraught with ruptures in the small intestine.
No symptoms observed
The size of these guests of the cat’s body does not exceed 1 cm. Hookworms choose the intestines as their place of residence, and blood as their source of nutrition. Helminth eggs can enter the body with food, and the larvae can even penetrate the skin of a pet.
Appetite is reduced, the animal is lethargic and apathetic to everything. The stool is liquid and there is visible blood in it.
The cat is vomiting and coughing a lot.
These are the main parasitic creatures that can seriously complicate the life of a pet and its owner.
Pinworms
Pinworms - cause severe swelling in the anus.
In general, pinworm infection is characterized by the same specific symptoms as ascariasis. In addition, the patient may feel severe itching in the anus, noticeably increasing in the evening and at night.
The nervous system suffers especially greatly with this type of helminthic infestation: the patient becomes restless and irritable; suffers from sleep disorders.
Typically, all the described symptoms begin to appear at the moment when the parasite that has settled in the body fully matures and begins the active process of reproduction and laying eggs.
Young children are most often infected with pinworms. The disease caused by these parasites, enterobiasis, in some cases can manifest itself in the form of urinary incontinence or suspicious heavy vaginal discharge (in women) or a rash similar to hives that occurs in the genital area (in both sexes). This is due to the fact that, in attempts to lay eggs in the perianal area, worms can penetrate the urethra.
It is curious that pinworms never begin to reproduce directly in the intestines. That is why the fact of infection with these helminths is so difficult to establish using a standard stool analysis, while eggs or even adult individuals of other parasites can often be seen in the stool with the naked eye.
TOXASCARIDOSIS
Toxascaris leonine is a toxascarid, a round helmin of the class Nematoda, family Ascaridae (roundworms). Males are 4-8 cm in length, females are 6-10 cm. The body is light yellow in color, the oral end has three lips and lateral wings. The eggs are oval or round in shape, thick-walled, with a smooth surface.
Routes of infection
Helmin is ubiquitous. The infection rate in cats is approximately 20%.
- An animal on a street walk can become infected by licking city/village dust from its fur or paws (oral-fecal route of infection).
- Mousecatching cats are at risk because Toxocara uses rodents as possible intermediate hosts.
- When eating raw meat in a diet contaminated with helminth eggs.
- A person can bring eggs into an apartment on shoes, clothes, or bags.
- The larva passes through the placental barrier, and the kittens are born already infected
. Transmission through breast milk is also possible.
Life cycle
An infected animal releases toxascarid eggs into the external environment with feces, which are carried by a host of carriers (flies, cockroaches, lice, fleas, rodents, etc.). Once ingested, the egg hatches into a larva that burrows into the submucosal layer of the intestine. In this place she molts twice. This period can last up to one month. After this, the larva returns back to the intestinal lumen and develops into an adult sexually mature individual. The lifespan of toxascarids is 7-8 months. The fundamental difference from toxacorosis is the absence of a larva migrating through the bloodstream.
The definitive host for Toxascaris leonine is cats, dogs, and fur-bearing animals.
The paratenic host is rodents (the larva is encapsulated).
There are no reported cases of human toxascariasis infection in the literature.
Symptoms
The main symptoms are associated with the introduction of the larva into the submucosal layer of the intestine, which causes inflammation and the development of gastroenteritis. The animal's eating behavior changes, appetite decreases, digestive disorders (vomiting, diarrhea) are possible, and the animal loses weight. With massive invasion, intestinal obstruction may form. Phenomena of protein and mineral deficiency in the animal are also observed.
Trichinella
Trichinella disrupts heart rhythm.
Trichinosis, or infection of the body with roundworms - Trichinella, usually occurs in three phases:
- an asymptomatic incubation period, which usually lasts no more than one and a half months;
- phase of disease development, accompanied by characteristic clinical symptoms (fever, chills, general weakness, muscle pain and swelling);
- peak of the disease, characterized by persistent fever, myalgia of the muscles of the neck, calves and lower back, puffiness of the face and allergic skin rashes (the latter appear as a result of an allergic reaction to helminths, accompanied by an increase in the level of eosinophils in the blood).
If trichinosis reaches its peak stage, the active development of accompanying respiratory tract diseases, such as bronchitis, pleurisy or even pneumonia, begins. The cardiovascular system suffers no less.
Thus, for carriers of Trichinella, heart rhythm disturbances, tachycardia and arterial hypertension are very typical. As is the case with damage to the body by other helminths, prolonged presence of parasites in the body of the carrier can ultimately lead to appendicitis and peritonitis, anaphylactic shock, internal bleeding, the initiation of oncological processes, or even brain damage.
Disease prevention
The eggs themselves are not dangerous to the pet. Immature larvae, having penetrated the body of a potential carrier, are simply digested in the stomach without causing any harm to health. The main condition for the development of tapeworm is the maturation of the egg in the body of an intermediate host, usually fleas. Therefore, all preventive measures that will help prevent infection must be aimed at destroying these insects.
You need to train your cat to wear a collar and periodically hunt fleas with special means. For prevention, it is constantly necessary to treat animal bedding, houses and ottomans with them. All items that can be removed and washed should be washed in hot water.
It is also advisable to treat all rooms. To do this, you can use any drug, for example: solutions of karbofos, chlorophos, Actor, Perol.
To effectively treat an apartment, you need to:
- Perform general cleaning, remove dirt from all corners where flea larvae may be present.
- Remove carpets, move furniture away from the wall.
- The spray must be applied to all places where parasites may be located.
- The apartment should “infuse” for 2-3 hours, then it is ventilated.
- Carpets need to be dusted, floors need to be vacuumed, and wet cleaning needs to be done again.
If the insects remain, then with a high degree of probability the infection with worms will occur again.
To protect yourself from tapeworms, you must:
- provide animals with anti-flea collars or regularly bathe them with special shampoo for preventive purposes;
- Regularly check your pet’s coat for the presence of fleas, and if detected, carry out appropriate treatment;
- keep the house clean;
- wipe your shoes after returning from the street;
- exclude unwashed vegetables and unfrozen meat from the animal’s menu;
- ensure the hygiene of trays and bowls, including their regular treatment with antiseptics;
- remember to prevent helminthic infestations among family members;
- wipe the floor, furniture and other surfaces where cats like to be with disinfectants;
- Give your pets antihelminthics regularly: when walking outside - once every six months, when constantly at home - once every 12 months.
Wide tapeworm
In severe cases of tapeworm infection, high fever and nausea occur.
Another dangerous flat parasite for humans, the broad tapeworm, causes a rather specific type of helminthiasis. We are talking about a disease called diphyllobothriasis.
This helminthiasis is distinguished by the long incubation period of its pathogen (it takes, on average, about two months for the worm to “take root” in the body). How is diphyllobothriasis diagnosed?
As a rule, the general condition of the patient with helminthiasis of this type is only slightly impaired. In some cases, the infected person may complain of slight dizziness or malaise, which appears only occasionally.
With a more severe form of infection that occurs with complications, the symptoms of diphyllobothriasis become more pronounced. The patient experiences an increase in body temperature (usually up to 37.5 degrees), nausea and diarrhea. Unpleasant, crusty rashes appear on the skin.
Most patients also complain of pain in the upper abdomen.
The easiest way to diagnose diphyllobothriasis is by assessing the condition of the patient’s oral cavity. Thus, when infected with a wide tapeworm, the mucous membrane of the host’s mouth becomes covered with bright red painful spots. A similar picture is observed in the tongue, where, in addition, atrophy of the taste buds can be noticed.
Treatment of helminthiasis
There are various anthelmintic drugs with varying degrees of intensity of therapeutic action. More often, veterinarians use general treatment, prescribing antihelminthic drugs with a broad spectrum of action. Such drugs affect the nervous system of parasites, cause their paralysis, and then death and removal from the body. Treatment can be carried out independently.
It is necessary to treat your pet at the first symptoms of helminthiasis, because before they appear, a huge number of parasites have already accumulated in the body.
To cure an animal of a certain type of helminth, it is necessary to use anthelmintic drugs that are intended specifically for this species. In order to remove worms, it is usually enough to give the cat anthelmintic once. If symptoms appear even after this, then the animal must be dewormed again. But after the first deworming, the next one must be done no earlier than 14 days. The tablet, injections and drops for cats cannot be used by humans or other animals.
If helminthiasis has overtaken a kitten, treatment must be entrusted to a veterinarian. The drug should be given in dosage according to the instructions. Moreover, the anthelmintic must be given twice. Give the second time 10-14 days after the first dose.
As a preventive measure, tablets, drops or injections against worms should be given several times a year. Most often, owners prefer to give their pet a tablet.
It is easier for a person to take a pill than for a cat. There are several ways to give the pill to an animal.
So, before giving it to the cat, the tablet must be crushed and then dissolved in water. Or put the tablet in the mouth and forcefully close it, stroke it along the throat, causing a swallowing reflex. Or grind the tablet into powder and mix with food. Anti-worm drops are no less effective. They are used in the same way as flea drops. Drops such as Prefender are an excellent means of preventing helminthiasis. Fipronil drops will help against fleas. These are modern and safe drops. A nursing cat is treated with special means.
Folk remedies
The question of how to rid a cat of worms using folk remedies is asked by many owners. In addition to medications, worms can be removed from cats using folk remedies. If the recipes accumulated by the people help, then worms can be found in feces.
It is necessary to consult with your veterinarian before using traditional recipes.
Garlic tincture enema
Worms in cats can be expelled by cleansing the intestines.
- Finely chop 6 cloves of garlic.
- Pour 250 ml. water at room temperature.
- Leave for 2 hours.
- Give an enema.
Pumpkin seed infusion
- Peel 300 grams of pumpkin seeds, while preserving the green shell.
- Grind.
- Gradually pour in 50 ml of water at room temperature.
- Add 15 grams of honey.
- Mix.
- Give the resulting infusion to the cat for 1 hour.
- After 30 minutes, do an enema using warm water.
Herbal collection
Worms in cats can be expelled with the following herbal mixture.
Take 20 grams:
- Tansy flowers.
- Peppermint.
- Buckthorn bark.
- Wormwood.
- Wild carrot seeds.
- Brew 2 tablespoons of herbal mixture with a glass of boiling water.
- Give 3 tablespoons in the morning for 3 days.
Carrot juice enemas
- Squeeze approximately 20 ml of juice from fresh carrots.
- Do it once a day for 7 days.
Onion infusion
- Cut a small onion into 4 parts.
- Pour 1 glass of boiled water, but not boiling water.
- Give to your pet in the morning for a week.
How to treat?
Treatment occurs with drug therapy. Drugs such as fenasal, bunamidine, praziquantel and a number of others are very effective in combating the parasite. There are also foreign analogues of these medicines. The appearance of fleas on an animal requires no less attention. They need to be treated together with the intestinal form of the parasite. Inspect the animal’s skin more often, comb the fur after bathing, monitor the pet’s hygiene, and do not allow the fur to become clumps. Remember, fleas carry helminth eggs and can cause re-infection of the animal. Treatment is repeated after three weeks to prevent relapse.
Purchasing medications on your own is dangerous for the health of the animal. They must be prescribed by a doctor. You can find out any information and call a veterinarian at home by phone, which is very convenient, and at any time of the day. Contacting the Ya-VET clinic and proper treatment will help your pet recover faster.