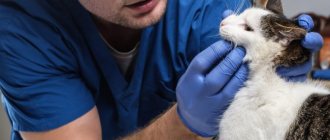
Worms in cats are a fairly common occurrence. Moreover, parasitic worms infect both those cats that do not go outside at all, and those who like to walk outside. Many cat owners wonder how their pets become infected with this disease. It's very simple: the eggs of worms are brought home by the person himself on the sole of his shoe.
All cat owners should periodically carry out antihelminthic prophylaxis, and if there are obvious signs of the disease, the necessary therapy is required. Below we will consider in detail the types of worms and the symptoms of the disease. Detailed recommendations for the treatment and prevention of helminthiasis will be given.
Types of worms
In veterinary medicine, helminthiasis is a fairly well-known disease that is often found in pets. Helminths (worms) that infect a cat’s body come in several varieties. The most common types of worms in cats:
- Round nematodes or white worms are the most common parasites. There are mature worms reaching 10 centimeters in length. The most common nematodes are hookworms. They are usually less than 2 centimeters in size and are found in the small intestine. Roundworms feed on the blood of an infected animal and can cause life-threatening anemia.
- Flat, these include trematodes or flukes, they infect the lungs and liver. When infected with this type of worm, sometimes pets do not show signs of illness at all. The worms that cause paragonimiasis migrate to the lungs and destroy lung tissue. In this case, the animal has a cough. Opisthorchiasis larvae parasitize the liver, disrupting its full functioning. They can also colonize the pancreas and gallbladder.
- Tapeworms usually reach up to 70 centimeters and consist of multiple segments. The cat's body in this case is usually used as a temporary host. Animals usually get sick from eating a sick animal. Tapeworms can be detected when examining your pet. Small segments of a parasite that looks like rice are sometimes found on the fur near the cat's anus.
Roundworms are usually small in size, but can cause serious harm to the animal, since they are found in the body in large quantities and affect not only the intestines, but also the liver and esophagus.
Types of worms dangerous to humans
Worms found in cats can also cause serious trouble for owners, as they can cause serious harm to human health. Infestation is especially dangerous for children.
- The danger of opisthorchiasis is that it affects the digestive organs: liver, pancreas, gall bladder.
- Diphyllobothriasis resides in the small intestine and is sometimes about 10 meters long.
- Echinococcosis and alveococcosis are extremely dangerous for people, as their larvae can cause serious harm to internal organs.
- Roundworms enter the body through the skin and infect the human blood and liver.
The larvae of alveococcosis can remain in a pet for years without causing much harm to it, and a person faces mortal danger in the form of: liver tumors, metastases of the lungs or brain.
Tapeworms can enter through fleas on the fur of a sick animal. Thus, it is necessary to begin treatment for worms in cats as soon as possible.
Toxocariasis
The disease is caused by the parasite Toxocara cati. It can occur in cats of all breeds and ages, but usually affects only kittens. There are described cases of human infection, but they concern children and the elderly. The body of adults who do not have problems with immunity quite actively resists infection and destroys the larvae that manage to get inside.
All nematodes, and Toxocara is no exception, have a rather complex and long life cycle. In particular, there are many possible routes of infection:
- Kittens can become infected directly through their mother's milk.
- Eating food contaminated with parasite eggs, drinking contaminated water.
- The animal can also eat a mouse, frog or beetle, which may also contain dormant eggs of parasitic nematodes.
Female parasites are extremely fertile. Every day they release thousands of eggs into the thickness of semi-digested food masses, which after a few hours end up in the external environment. But they do not immediately become dangerous for animals: first, the eggs need to mature in the external environment for several weeks. Only after this do they acquire invasiveness (the ability to become infected).
Eggs are quite stable even in outdoor conditions (provided that they are not irradiated by solar ultraviolet radiation), but indoors they can be stored for several months, or even years!
So, when moving to a new house or apartment, we strongly advise you to clean thoroughly, not sparing with chlorine-based disinfectants. If you have such an opportunity, you need to “fry” the premises using a quartz irradiator.
Ways of infecting cats with worms
Of course, cats that walk on their own can become infected anywhere and anytime. But often those pets who have never left the house in their lives become infected with a similar disease. Main sources of infection:
- Products. Raw meat and fish are especially dangerous for animals.
- The trash can is a big danger in summer, as flies can land on it. They are the main carriers of helminth eggs.
- Human clothes and shoes. A person, without knowing it, can bring worm eggs into an apartment on the soles of shoes with the remains of cat and dog feces.
Kittens have the only way of infection is from an infected cat, which can infect them both in utero and through breast milk.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Long worms in cats: main types, description and methods of treating parasites in cats
Tapeworms in cats and dogs: symptoms, signs, medications and treatment tablets
Why are most flatworms internal parasites of other animals?
Pulmonary fluke: what diseases it causes, symptoms and treatment methods
Ascaris in contrast to flatworms, special differences
What do worm larvae look like: round and tapeworms, flukes
Symptoms of animal infection
At home, it is impossible to diagnose the presence of worms yourself, since sometimes the symptoms can be vague. The condition of the animal depends on the type of parasite that infected the body. The cat must be shown to the veterinarian, he will take the necessary tests. For example, the exact type of parasite can be accurately detected in stool.
You cannot engage in self-diagnosis, since it is quite problematic to determine the type of worms yourself.
- Poor appetite. Sometimes, on the contrary, there is an increase in appetite.
- Loose stools, which at times alternate with constipation.
- Vomit. Vomiting with worms or blood occurs.
- There are worms in the stool.
- There is blood or mucus in the stool.
- Itching that irritates the anal area. Cats seem to “ride” with their tails on the floor.
- Periodic bloating.
- Cough, sometimes difficulty breathing.
- Kittens lag behind their peers in growth.
- The animal becomes lethargic, weak, devoid of playfulness, and lies down more.
- Dull, lacking shine wool.
- Losing weight of an animal.
- Yellowness appears on the mucous membranes of the eyes.
- Fluid comes out of the eyes.
- In extreme cases, limb paralysis occurs.
- Premature labor often occurs in pregnant cats.
Cause of pinworm infection
Pinworm infection in humans occurs for the following reasons:
- poor sanitary and hygienic conditions;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- pinworms in family members.
The only source of pinworm infection is humans. The infection spreads very easily through the mouth, for example through contaminated hands or food. This problem especially affects children, who often do not follow basic hygiene rules and put various objects, toys or school supplies, such as pens and pencils, in their mouths, which facilitates the penetration of pinworms into the body.
Pinworm infection through contaminated hands
This is why it is so important that adults teach children basic hand hygiene rules and set an example of proper behavior themselves.
Treatment
What to do if the owner suspects worms in his pet? At the first sign of worms in cats, you should contact your veterinarian. Since infestation indicates that there are many parasites in the pet’s body. It is not recommended to treat your pet with medications at home.
First, the veterinarian will take tests to identify the type of parasite, and then prescribe the only correct medications that will help cure the cat. For example, if you give an animal a medicine that helps eliminate tapeworms, it will not be effective against other types of parasites.
List of drugs
Usually the veterinarian prescribes:
- Pirantel. This is a mild remedy against roundworms. It does not kill the parasites inside the cat, and only immobilizes them. Thus, it does not lead to intoxication of the body and is safe. Worms can be found in your pet's feces after defecation.
- The drugs praziquantel, fenasal, and phenalidone are effective against infection with flatworms.
- If you treat roundworms with detrazine or fembendazole, you can quickly achieve the desired result.
- Praziquantel helps kill the fluke that attacks the lungs.
- Milbemax is effective against roundworms.
- Complex treatment under the supervision of a veterinarian is necessary if the animal is infected with opisthorchiasis, which affects the liver.
Basic rules for taking medications
- Medicines should be given to the cat in the morning before meals.
- It is necessary to strictly observe the dosage of the drug.
- Sometimes, as prescribed by the veterinarian, before giving the cat medicine it is necessary to cleanse the intestines.
- Medicines in tablet form should be crushed and placed on the root of the tongue. Thus, the pet will be forced to swallow it.
- It is quite effective to add medications to food.
- If an animal behaves aggressively, it must first be restrained so that it does not injure itself.
After 14 days, the cat needs to be given the medicine prescribed by the veterinarian again.
Features of growth and development of flatworms
Infection of an animal with flatworms is called cestodosis . Prevention of worms was invented for a reason; a cat can die if the reproduction of such adapted parasites is not suppressed in the early stages. Those small, white, moving worms that you found in the tray are young individuals whose goal is to find a carrier, grow and give birth.
When a worm finds a favorable environment, it molts and becomes something like a tadpole. The oral apparatus of the parasite is well developed already at this stage. To gain strength and grow, the worm gnaws into the cat's intestines for a while . Externally, nothing is noticeable about the animal if the parasites have just begun to attack the body. The worms are actively growing, eating more and the cat begins to become exhausted.
Folk remedies
The question of how to rid a cat of worms using folk remedies is asked by many owners. In addition to medications, worms can be removed from cats using folk remedies. If the recipes accumulated by the people help, then worms can be found in feces.
It is necessary to consult with your veterinarian before using traditional recipes.
Garlic tincture enema
Worms in cats can be expelled by cleansing the intestines.
- Finely chop 6 cloves of garlic.
- Pour 250 ml. water at room temperature.
- Leave for 2 hours.
- Give an enema.
Pumpkin seed infusion
- Peel 300 grams of pumpkin seeds, while preserving the green shell.
- Grind.
- Gradually pour in 50 ml of water at room temperature.
- Add 15 grams of honey.
- Mix.
- Give the resulting infusion to the cat for 1 hour.
- After 30 minutes, do an enema using warm water.
Herbal collection
Worms in cats can be expelled with the following herbal mixture.
Take 20 grams:
- Tansy flowers.
- Peppermint.
- Buckthorn bark.
- Wormwood.
- Wild carrot seeds.
- Brew 2 tablespoons of herbal mixture with a glass of boiling water.
- Give 3 tablespoons in the morning for 3 days.
Carrot juice enemas
- Squeeze approximately 20 ml of juice from fresh carrots.
- Do it once a day for 7 days.
Onion infusion
- Cut a small onion into 4 parts.
- Pour 1 glass of boiled water, but not boiling water.
- Give to your pet in the morning for a week.
How can you get rid of helminths?
To combat helminths, anthelmintic drugs are used; Consult your doctor about the most effective treatment option. Please note that if routine anthelmintic treatment is missed, kittens may become re-infected. This may result in your kitten vomiting adult roundworms even though he has previously received treatment. Therefore, observing the frequency of use of drugs against helminths and carrying out constant treatments in accordance with the instructions for use and the recommendations of the veterinarian help protect against infection.
Prevention
As you know, it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it later. If you follow some rules, you can protect not only the cat, but also yourself from these troubles, which are sometimes very difficult to deal with.
- If you do not give your cat raw meat or fish, you can avoid such a problem as worms in your cat. Raw foods must first be boiled and then fed to your pet.
- To prevent cats from getting worms, they need to be treated with anthelmintic medications once every 3 months.
- In order to avoid this problem, you need to keep your cat's litter box clean and disinfect it regularly.
- If you regularly treat your animal with a flea solution, your cat may not develop worms at all.
- Outdoor shoes should be stored in a special closet, away from the pet.
- It is necessary to do regular cleaning of the door mat.
- Do not pet the cat immediately after going outside; you need to wash your hands first.
- A bell on the animal's neck will prevent it from catching a mouse or bird, which could become a source of disease.
Prevention of the disease is important. If your pet is healthy, then the owner’s risk of contracting helminths will be significantly reduced, and a healthy animal will delight you with its playfulness and beautiful appearance.
We recommend reading: What should you consider when choosing and using anthelmintics for cats?
Danger to humans
Prevention of infection with cestodes is important to protect not only domestic animals, but also the person himself. It is for this reason that it is necessary to combat mice and rats, as well as blood-sucking ectoparasites. How dangerous are cat “cestodes” for their owners? Here everything depends solely on the type of worms, as well as on the human condition.
In particular, there are isolated reports about the possibility of “picking up” parasites from the genus Taenia. The risk of infection is relatively low, and diseases caused by these cestodes are not very common in our country, but still the probability is different from zero.
The eggs of all cysticerci develop successfully when they enter the human body . To remove cysts or larvae that have not yet had time to “pupate” in the internal organs, it is necessary to resort to serious chemotherapy or (more often) surgical intervention.
Finally, long-term use of antihelminthic drugs in prophylactic doses will be required. This is necessary to completely prevent the possibility of re-infection.
What about the common Dipylidium caninum? It is reported that there is also a possibility of infection with it. But this happens more often in the case of small children who accidentally eat an infected flea. But in this case, parents do not need to panic: in the human body this parasite feels “out of place”, almost does not grow, and is easily destroyed by praziquantel.
Complications due to the activity of worms
Warning symptoms should not be underestimated. Unfortunately, an untreated problem can cause many complications, the most common of which are:
- problems with concentration, which leads to problems with learning and remembering;
- sleep disorders;
- inflammation of the female genital organs;
- colitis;
- appendicitis;
- dermatitis (caused by constant scratching around the anus);
- weight loss.
Why are nematodes dangerous for cats?
Nematodes in cats living in the blood and tissues of the body are not just disgusting, but also dangerous. Helminths feed on lymph, blood and organ tissue, depleting the host’s body. All types of worms release substances into the body that cause intoxication.
Dead parasites decompose, which also leads to poisoning. Serious allergic reactions are possible. Using fixation devices, helminths injure tissue, which can lead to necrosis and even rupture of an organ or blood vessel.
Dangerous signs of worms - constipation and a bloated stomach - indicate intestinal obstruction, which can lead to the death of the pet (the worms have multiplied so much that they have clogged the intestinal lumen, making it impossible for the natural exit of processed nutritional masses).
Nematodes in cats
Toxocaroses
Helminth infections in cats are diseases caused by helminths - parasitic worms that live in various internal organs and tissues of animals and humans. Cats are usually parasitized by helminths from the classes of trematodes (Thematoda) - flukes, cestodes (Cestoda) - tapeworms and roundworms (Nematoda).
The causative agent is the roundworm Tohosaga mystax from the suborder Ascaridata. The nematode is light yellow in color, the head end is equipped with three lips and wide lateral wings. The length of the male is 5-10 cm, the caudate end is curved, at its apex there is a cone-shaped appendage and two equal spicules. The length of the female is 9-12 cm, the tail is straight. Toxocara eggs are round, 0.068-0.075 mm in diameter, covered with a cellular membrane.
Nematodes in cats. Helminths have a strong pathogenic effect on the body of cats. Kittens are especially affected, and adult animals often die. Along with this, there are diseases common to animals and humans.
The development cycle proceeds directly according to the roundworm type with migration of larvae through the blood of the definitive host. Intrauterine infection is possible.
Cats become infected through nutrition. Pathogens, parasitizing in the small intestines, migrate and penetrate various organs, become encysted and do not lose their invasive properties for a long time.
A sign of this disease may be developed pneumonia with a cough, which is caused by the passage of larvae through the lungs. And in kittens, the intestinal form is more common, which is accompanied by diarrhea and constipation, as well as perversion of appetite, bloating, colic, and emaciation.
In kittens, underdevelopment, rickets, and sometimes epileptic convulsions are also noted. Adult animals rarely get sick and are usually asymptomatic, i.e. without noticeable clinical signs.
To treat toxocariasis, piperazine salts are usually used (0.2-0.4 g per 1 kg of animal weight) three times, i.e. for three days in a row, given along with food. Nilverm (15-20 mg per 1 kg) is also recommended - a single dose.
An accurate diagnosis of toxocariasis can only be made when parasite eggs are detected in feces.
To prevent the incidence of toxocariasis, you should regularly remove cat feces, as well as periodically examine animals for the presence of helminth eggs in feces, and, if necessary, deworm the animals. It is also necessary to destroy synanthropic rodents, as possible carriers of the invasion.
Trichinellosis
The causative agent is Trichinella spiralis from the family Trichinellidae. It parasitizes cats, foxes, arctic foxes, martens, dogs, lynx, rats and many wild animals. Sexually mature helminths parasitize the intestines of animals.
Reinfection of cats occurs when they eat contaminated, non-neutralized meat waste infected with Trichinella larvae, when they eat dead animals or the carcasses of killed animals.
The diagnosis during the life of animals is made on the basis of an immunological (ICP) study of cats, as well as an assessment of clinical and epidemiological data; posthumously - based on the results of compression trichinoscopy or digestion of calf muscles in artificial gastric juice.
Find out more: Symptoms of toxoplasmosis in cats. Treatment and prevention
Nematodosis: Toxascariasis
Toxascariasis is a disease of cats caused by nematodes that live and reproduce in the intestines of their owners. The causative agent of toxascariasis is large nematode helminths up to 10 cm long. The eggs of this parasite are round, with a smooth outer shell - this is how they differ from Toxocara eggs.
Nematodes in cats. Nematode eggs, once in the external environment, complete their development and larvae are fully formed in them, which become invasive already on the 8-9th day. Once in the intestine of the animal, the larvae penetrate its walls, and then, on about the 9th day, they again enter the intestinal lumen, where after 3-4 weeks they become sexually mature.
Toxascariasis, like their owners, is quite widespread. Their eggs are resistant to environmental factors and therefore can survive in the soil for a long time, so infection can occur at any time of the year. Infection of healthy animals occurs with food and water or through rodents.
The diagnosis of toxocariasis is established on the basis of scatological studies. All preventive measures, as well as treatment, are the same as for toxocariasis.
Externally, the signs of toxocariasis are less pronounced than with toxocariasis. Although during infection there is inflammation of the intestines, loss of appetite, sometimes diarrhea, and general emaciation of animals.
Ankylostomosis
Hookworm disease is a nematode infection of dogs, cats and other carnivores caused by roundworms of the family Ancylostomatidae. Helminths parasitize in the small intestine. The disease is characterized by digestive disorders in the animal and skin lesions during the migration of larvae.
The causative agent is Ancylostoma caninum, a thin nematode up to 21 mm long. It is characteristic that the large oral capsule contains two chitinous plates, with 3 hook-shaped teeth protruding at the edges. The eggs are gray, oval, 0.06-0.08 x 0.04-0.05 mm in size, contain blastomeres.
Animals can become infected in two ways: when they ingest larvae with food and when the larvae themselves actively invade through the skin. If in the first case the larvae, having entered the intestines with food, quickly develop and reach sexual maturity in 14-16 days, then in the second they migrate with the blood to the heart, then to the lungs, bronchioles, bronchi and trachea.
Then they are swallowed with mucus and grow to the sexually mature stage in 18-22 days, i.e. 4-6 days longer than in the first case.
Hookworms are hematophagous (feed on blood). They have glands in the oral cavity, the secretions of which hemolyze the blood, which promotes its influx and hemorrhages. The disease is diagnosed by examining feces using the Fulleborn method. Eggs are differentiated from uncinarium eggs by their size. After the death of the animal, the intestines are opened to detect nematodes.