( 1 votes, rating: 1.00 out of 5)
5589564
06/12/2021 owner reviews 1,
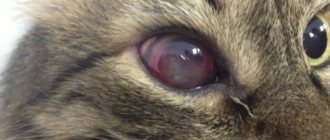
Brown spots on the eyes of cats are medically known as iris freckles, iris hyperpigmentation, melanoma, and iris melanosis. Areas of darker pigmentation appear in the iris (the colored part of the eye). The incidence of iris melanosis is quite common and usually affects middle-aged and older cats.
Iris melanosis is caused by an overgrowth of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing pigmentation. For simplicity, we will call the benign form iris melanosis and the malignant form malignant melanomas.
Dark spots can appear in cats of any eye color and can be cancerous or benign.
Benign iris melanosis can sometimes develop into malignant melanoma when the cells undergo malignant transformation. More often than cancer, iris melanoma can lead to glaucoma, a condition caused by increased pressure inside the eyeball. Glaucoma causes distorted vision and can be very painful. Malignant melanomas can metastasize to the lungs, liver, and other parts of the body.
- Appearance
- When to contact a veterinarian
- Care
Mycoplasmosis
Mycoplasma is a special type of microorganisms that occupy an intermediate position between bacteria and viruses.
In almost 90% of healthy cats this microorganism can be isolated, i.e. it is a normal inhabitant of the conjunctiva in cats. Mycoplasmosis in cats is an infectious disease that is characterized by the development of bilateral conjunctivitis with severe redness (hyperemia) of the entire conjunctiva, including the third eyelid.
Symptoms:
- Discharge from the eyes (tears, mucous or purulent discharge).
- Redness of the eyes.
- Sneezing, nasal discharge, and cough may occur.
— If both eyes of an animal are affected almost simultaneously, this indicates the infectious nature of the disease. If only one eye waters and turns red, then most likely it is conjunctivitis of non-contagious etiology. Often, mycoplasmosis in a cat disappears on its own after 7-10 days (if the underlying disease is eliminated and the immune system is strengthened). Otherwise, the disease becomes chronic.
- Joints are affected. At first the animal limps on one leg. Then it becomes noticeable that all the paws hurt. Mustache runs/jumps less. Getting up/ascending/descending becomes extremely difficult for the cat, so he sleeps almost all the time or lies down, meowing pitifully. The joints swell and do not bend.
- Body temperature rises.
Treatment
1. Treatment of the underlying infection using antibiotics and immunostimulants.
2. To treat conjunctivitis - eye drops with antibiotics.
============================================================================================================================================================================================
Types of pathological discharge from the eyes
During pathological processes, cats develop discharge that differs in color and consistency:
- Transparent. If your cat's eyes are watery but a colorless liquid exudate is coming out, this may be a sign of an allergy.
- White or light yellow. Such discharge most often occurs due to a viral or fungal infection.
- Saturated yellow or greenish (purulent) is a sign of infection with pathogenic bacteria.
- Brown or reddish discharge with a thick consistency. This color indicates that they contain red blood cells.
Symblepharon
Symblepharon is a fusion of the conjunctiva with the eyelids and cornea.
Symptoms:
Symblepharon varies in area of damage and localization: it can be partial or complete.
If it is small in size, it is sometimes an accidental finding during a general examination, but if it is of a significant size, it is already a cosmetic defect and interferes with the cat’s vision, but the symblepharon itself does not bother the cat.
With partial symblepharon, when the conjunctiva may not fuse with the cornea, the prognosis is favorable; with complete symblepharon, the prognosis is most often unfavorable.
Treatment:
1. Daily eye sanitation.
2. Separation of the conjunctiva from adjacent layers, the cornea, using local preparations with antibiotics and steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
3. In case of severe symblepharon, leading to visual impairment, the option of surgical treatment to separate the fused tissues is considered.
============================================================================================================================================================================================
When to contact a veterinarian
Any changes in the cat's eye should be evaluated by a veterinarian as soon as possible. The veterinarian will perform a complete physical examination and obtain a medical history from you, including how long the spots have been present and any associated signs.
Differential diagnosis:
Iris melanosis is not the only cause of brown spots on a cat's eye, and your veterinarian must rule out other causes before he or she makes a diagnosis.
Malignant melanoma is a cancer of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells).
Cat corneal sequestration is a brown or black plaque that forms on the eye due to the death of parts of the cornea. The most common causes are long-term trauma due to eyelid abnormalities or cat flu. Unlike iris melanosis, feline corneal sequestration is painful and can affect vision. The incidence is higher in Burmese, Persian and British Shorthairs.
Diagnostic examination:
- A slit lamp examination to examine the eye under magnification.
- Fine needle biopsy to determine whether the lesion is benign or malignant.
Your veterinarian may refer your cat to an ophthalmologist to confirm the diagnosis.
Source
Obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct
Normally, tears should flow out through a special channel that runs inside the nose (nasolacrimal duct), but if this outflow path is disrupted, the tear has nowhere else to flow except outward, to the area near the eyes.
Symptoms:
- Various degrees of lacrimation and brown coloration of the fur around the eyes (formation of “tear tracks”).
This may be a breed predisposition - as congenital pathology is often found in Sphynx, Persian, British, exotic, Scottish and other short-faced cats; or as a consequence of inflammatory processes in the eye area.
Treatment:
1. If the obstruction is associated with overgrowth or blockage of the nasolacrimal duct, then surgical dilation of the canal is possible. 2. But most often, with this problem, it is enough to carry out daily hygienic care using special lotions to remove tear ducts.
===========================================================================================================================================================================================
Treatment of pigmentary keratitis in pugs:
We diagnose corneal melanosis at the earliest stages and carry out comprehensive work with melanosis of any degree.
- First of all, the root cause is treated: immunomodulators for pannus (often occurs in shepherd dogs and their mixed breeds).
- blepharoplasty for eyelid pathologies (relevant for pugs and Pekingese).
- plastic surgery of the nasal fold (relevant for Pekingese).
- replacement of tears during the dry process (relevant for Shih Tzu, pugs, Pekingese, English bulldogs, spaniels and other breeds predisposed to dry eye syndrome). When the root cause of keratitis is eliminated, the pigment growth process slows down or stops altogether, but the existing pigment can remain on the cornea in the same volume.
If you find signs of corneal melanosis in your pet, you should not delay a visit to a veterinary ophthalmologist, because any disease is better treated in the early stages.
Your Pet's ophthalmologist, microsurgeon Yastrebov O.V.
Join us on social networks
Conjunctivitis
This is an inflammation of the outer layer of the eye, which is normally pink in color.
Symptoms:
- Redness of the eye,
— Discharge (can be transparent in the form of a tear, mucous, purulent)
- Squinting of the eye, local itching.
Treatment:
1. Use of local and systemic antibiotics and antiviral, and, if necessary, local antiallergic drugs.
============================================================================================================================================================================================
What causes the defect to appear?
Limitation of visual perception in a specific area of the eyeball may indicate the presence of various diseases. Abnormalities may affect the vitreous body. It fills the space between the lens and the retina and acts as an anatomical magnifying glass. With its help the eye can focus. So why do dark spots appear? Through the vitreous body, light reaches the nerves located in the central part of the macula. When it becomes cloudy, the fibers stick together. The nerves responsible for clear image reproduction lose their functions. The luminous flux cannot reach the required place where it is usually differentiated, resulting in darkening. They vary in size and shape. The main causes of dark spots include deviations that occur:
- in the cranial nerves responsible for the convergence of the eyes;
- in the vessels, which is associated with sclerotic changes that cause opacification of the vitreous body. Phakosclerosis is characterized by dehydration, as a result of which the lens loses its elasticity;
- as a result of changes occurring in the intervertebral discs and cartilage tissues, cervical chondrosis and other pathologies develop. They, in turn, contribute to spasm of the eye vessels;
- in the endocrine system. Thus, in patients with diabetes, vision begins to deteriorate significantly. This is due to disruption of the blood vessels. This complication is called “diabetic retinopathy.”
Some people develop dark spots in the eye due to prolonged exposure to harsh weather conditions. For example, these include extremely low or high air temperatures. The risk group also includes those who constantly experience excessive physical and mental stress. Provoking factors also include bad habits, such as smoking and overeating.
The disease is diagnosed mainly after a person has passed the 40-year mark. However, most studies have shown that women are much more susceptible to pathology. This is due to highly variable hormonal levels. The body undergoes severe stress during different periods of life, especially such as pregnancy and menopause.
Protrusion (loss) of the third eyelid gland
Symptoms:
— A red or pink formation appears in the inner corner of one or both eyes.
- Discharge is usually in the form of tears or mucus in small quantities.
Treatment:
1. Surgical, preference is given to repositioning the gland rather than removing it, since this gland accounts for 30 to 50% of the total amount of tears produced.
============================================================================================================================================================================================
Entropion of the eyelids
This is an incorrect position of the upper and/or lower eyelids, in which the free edge of the eyelid is shifted inward towards the eyeball.
Symptoms:
— Eyelashes and hair on the eyelids, when turned in, greatly irritate the eye.
— The cat squints its eyes a lot.
- There is severe lacrimation or purulent discharge. Constant irritation can lead to corneal injury.
Treatment:
1. Surgical. With spastic volvulus, therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease, but in some cases, after eliminating the cause that caused the spastic volvulus, it is still necessary to resort to surgical correction.
============================================================================================================================================================================================
Diagnostics
If the owner notices brown discharge around the cat's eyes, he needs to take the pet to a veterinary clinic. In most cases, examination and history is sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Sometimes it is necessary to conduct additional tests to help rule out head and eye injuries, as well as diseases of internal organs and infectious diseases. To do this you may need to do:
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision;
- X-ray of the skull;
- blood and stool tests.
Corneal ulcer
This is an inflammation of the cornea, accompanied by its defect.
Symptoms:
- Squinting (blepharospasm)
- Watery or purulent discharge, pain.
— You may notice a roughness, indentation, or whitish spot on the surface of the cornea.
Treatment:
Depending on the severity of the process:
1. Medication (antibiotics, keratoprotectors, etc.)
2. Surgical.
============================================================================================================================================================================================
Diseases associated with the appearance of yellow spots on the white of the eye
If the cause of the spots is a general disease of the body, then nausea, chills, increased fatigue, loss of appetite, etc. may be added to the listed symptoms.
Yellow spots may be evidence of the following disorders in the body:
A:
- Jaundice - occurs when there is a violation of the metabolism of bilirubin (bile pigment, one of the most important components of bile)
- Hepatitis (a viral disease caused by a pathogen with pronounced hepatotropic properties
- Liver cirrhosis (pathological condition of the liver, which is a consequence of impaired blood circulation in the hepatic vascular system and dysfunction of the bile ducts)
- Anemia or anemia (a pathological condition characterized by a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin and, in the vast majority of cases, the number of red blood cells per unit volume of blood
- Liver cancer
- Gallstones are formed in the body under the influence of a number of unfavorable factors and can take on different shapes, structures, and sizes.
Uveitis
Inflammation of the iris and ciliary body - structures located inside the eye.
Symptoms:
- Squinting, redness and clouding of the eye.
- Constriction of the pupil.
— Precipitates on the corneal endothelium (small white dots on the inner surface of the cornea)
— Exudate (effusion) in the anterior chamber of the eye
- Decrease in intraocular pressure.
Treatment:
1. Local corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, mydriatics and systemic drugs.
===========================================================================================================================================================================================
Glaucoma
This is an increase in intraocular pressure due to a decrease in the outflow of intraocular fluid. This pathology leads to a narrowing of the visual fields, and ultimately to complete loss of vision. Glaucoma can be primary or secondary (against the background of the underlying disease). In cats, glaucoma most often occurs after the age of 6 years and is secondary.
Symptoms:
- Redness of the eye
- Watery eyes, squinting (blepharospasm)
- Pupil dilation and signs of concomitant disease (uveitis, tumors) may be observed.
— In the case of an acute attack of glaucoma, the eye becomes cloudy, tortuous vessels on the surface of the eye are clearly visible and severe pain, the eye may increase in size.
Treatment:
1. Drugs to lower intraocular pressure.
============================================================================================================================================================================================
Preventive measures
To prevent brown discharge from appearing again in a cat, the owner of the animal should pay attention to the prevention of ophthalmological diseases. What exactly needs to be done:
- accustom your pet to good quality food;
- In the room where the cat lives, it is advisable not to use deodorants or smoke;
- adhere to the vaccination schedule;
- carry out antiparasitic treatment in a timely manner;
- protect the cat from contact with sick animals;
- support the cat’s immunity with vitamin and mineral complexes;
- Wipe your pet's eyes daily with hygiene lotion.
The health of the pet is in the hands of the owner. And if a cat has brown or reddish discharge in the corners of its eyes, it is better not to waste time, but to contact a veterinary clinic. If left untreated, purulent inflammation can lead to vision loss.