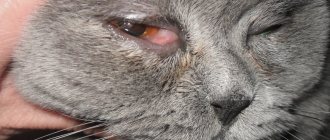
An important indicator that can signal serious troubles associated with a cat’s health is the darkening of the color of its urine. Having barely noticed this problem, the owner must immediately contact a veterinarian to receive qualified help. At the same time, it is necessary to control not only the color of urine, but also the smell and transparency. These indicators can become symptoms of a large number of serious diseases associated with the liver, urinary tract diseases or dehydration. Why do cats have dark urine, and what should the owner do to protect the animal from unpleasant consequences? The answers are further in the article.
How to determine the color of urine in cats
The urine of a healthy cat has an unsaturated yellowish or amber color. Urobilin gives urine a straw-colored hue, which must be removed from the blood, since a high concentration of this bile pigment in the body leads to a negative effect on the cat’s nervous system.
If the urine is too rich or dark in color, this indicates problems in the animal’s body that need to be addressed urgently. The difficulty is that assessing the color of urine in cats can sometimes be difficult. The reason for this is the habit of most individuals to go to the toilet on a tray with filler. In order to be able to systematically control the tone of your cat’s discharge, you should train him to go to an empty litter box. After your pet relieves itself, you need to pour the liquid into a transparent container and place it against the background of a white sheet of paper. With this method, color deviations can be easily determined. A piece of clean white cloth placed directly on top of the cat litter can also help assess urine status.
It is worth noting that clear urine in a cat can also be a warning sign. In most cases, this is an indicator that the animal drank a lot of water and the body did not have time to secrete the required amount of urobilin, so the discharge does not have a yellowish tint. But in some situations, the absence of a characteristic color of urine indicates pathologies of the endocrine glands, diseases of the adrenal glands, or diabetes mellitus. There is a high probability of having one of these diseases in those cats that are constantly lethargic and have no appetite for a long time. If the owner notices these symptoms in his pet, he must contact a veterinarian to prescribe appropriate treatment.
Diet for cats with kidney disease
When the kidneys are sick, the pet suffers from dehydration. During treatment, be sure to provide him with water - give him wet food, low-sodium broth, tuna juice.
Particular attention should be paid to a diet low in protein and phosphorus. Ask your veterinarian how to feed your pet correctly. The diet should contain a reduced amount of phosphorus and protein, enriched with omega-3 fatty acids.
If you give dry cat food, it is not advisable if you have kidney disease. Give preference to high quality wet food. For example, Dr. has proven himself well. Clauder's Diet Kidney diet for kidney disease. If your pet has stones, for treatment, buy food for cats with kidney disease, which reduces the risk of stones.
Causes of urine color change
Dark urine can appear in a pet as a result of both ordinary physiological reasons and serious diseases. In any case, they need to be identified in order to provide the correct treatment if necessary.
The main reasons for changes in the color of urine:
- infections in the genitourinary system;
- sand and stones in the genitourinary system;
- dehydration of the body;
- reproductive system;
- estrus;
- other serious illnesses requiring medical care, and in some cases, operations.
Introduction to the problem
The color of urine is an important indicator of a cat's health. Normally it is light, may have a yellow tint or is almost transparent. Darkening may indicate serious problems with your pet's health. Having noticed this, you cannot expect the problem to disappear on its own. You need to seek help immediately.
It is best if you arrive at your appointment already with a portion of urine. Then the doctor can evaluate its color, smell and take a part for laboratory analysis. Dark urine in a cat may indicate serious diseases associated with the liver, diseases of the genitourinary system, or dehydration.
Options for changing urine color
By the shade of urine you can roughly determine what problem caused its darkening. But you should not start treatment on your own based on these data. It is better to contact a specialist who will determine the causes of this phenomenon and advise the correct methods of therapy.
Possible options for changing the shade of urine:
- Bright yellow urine is a sign of mild dehydration. It is observed in cats who have not drunk for a long time in hot weather, or in the first week after surgery and sterilization as a result of a long-term diet. Such dehydration eliminates the danger to the body, provided that the animal receives a sufficient amount of water.
- Pink-red urine can indicate a number of common problems in cats, including urinary tract infections, bladder or kidney stones, and cystitis. If pink discharge is found in a castrated cat, then this is a sign of the presence of kidney stones and cystitis at the same time. In this case, sand and stones go into the bladder, causing it to be injured, ulcers and erosions form, which provoke the development of infection. The constant presence of blood in a cat’s urine requires immediate treatment, because delaying medical help can lead to the death of the animal. In some cases, red urine may indicate injury due to bruising of internal organs.
- Brown urine often indicates high levels of bacteria. Low blood clotting can also cause this problem. In any case, the animal loses weight, appetite and interest in everything around it. When such urine appears in cats, it is possible to develop blood parasitic infections and leptospirosis - very serious diseases. Mature cats that are ready to mate may also have brown urine. In this case, there is no need to worry about the animal, since dark urine is obtained from mixing urine with menstrual flow.
- Bloody urine indicates severe cases of glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis.
- Greenish or green-yellow urine indicates liver damage, which leads to parenchymal jaundice. The result of such a disease can be a neuropathic attack and death.
Most often, darkening of a cat’s urine indicates problems with the genitourinary system. These are very serious illnesses that require immediate medical attention.
Kidney functions
The main job of the kidneys is to remove toxins from the body. It also forms urine, which contains:
- excess liquids, mineral salts, organic substances;
- uric acid;
- urea;
- ammonia, other metabolic products.
Urine flows down the ureters into the bladder, then comes out during emptying.
Other features
- Maintaining water, electrolyte, acid-base balance;
- regulation of blood pressure;
- removal of excess calcium;
- production of the active form of hormone D;
- synthesis of the hormone erythropoietin, which is responsible for the creation of red blood cells in the bone marrow.
Prevention
It is better to prevent any disease than to later spend much more time and money fighting a serious illness. For animals, the issue is especially acute, because any problems with their health completely depend on the owners, who, in most cases, ignore unpleasant symptoms in the first stages. As a result, pets have severe complications that even experienced specialists cannot cure. Therefore, the first action that an owner should take if he notices that a cat has dark urine is to show the animal to a veterinarian to rule out dangerous health problems and prescribe the correct treatment individually for a particular individual. Moreover, serious illnesses are accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms that are difficult to ignore.
Observation of the cat owner is the best preventative measure for minimizing the risk of death, or carrying out complex treatment, which includes surgery.
4.Treatment
Not so frequent cases of conditionally normal darkening of urine under the influence of controlled situational factors (and restoration of color in a natural way) are discussed above. As for pathological causes, then, of course, therapeutic prescriptions will be determined by the entire complex of diagnostic data and individual anamnestic information. It is unrealistic to identify all possible schemes or at least directions of treatment in this case.
However, again and again we draw attention to the fact that the timeliness of seeing a doctor is not just important - this factor can have a critical, life-saving significance.
Recommendations for the owner
While the doctors are investigating and finding out why the cat has dark urine, you need to calm down and organize appropriate conditions for the patient for treatment and recovery. First of all, you need to maintain a drinking regime and avoid dehydration. When a disease is detected, a specialist prescribes a strict diet. It completely excludes raw meat and fish.
At the same time, it is desirable to ensure maximum rest for the patient. It is better to limit movement within one room. But here nature comes to the rescue. If an animal feels unwell, it sleeps more often.
Let's go to the clinic
The animal should not be fed 8 hours before visiting the veterinarian. This is important because all analyzes will be more informative and accurate. Prepare the tray by morning. To do this, remove all the filler from it and wash it thoroughly. Lay the mesh on top. If the cat is used to scooping up the litter with its paws, then place a piece of sterile gauze.
Using a sterile syringe, collect 40 to 80 ml of urine. Within two hours, the jar must be delivered to the clinic for laboratory testing. In addition to examination and urine analysis, the veterinarian performs an ultrasound. If necessary, a general and biochemical blood test is prescribed. If a cat's urine is dark brown, then it is often impossible to wait for the results of all tests. Therefore, based on the initial examination, a course of treatment begins, which will be adjusted as other laboratory findings are received.
You might be interested in:
"Leave me alone, but don't leave me alone." If your loved one leaves home, how can you help him?
Resuscitation. Can she help? What you need to know about resuscitation and the condition of a person in the terminal stage of illness in order to make the right decision at the end of the life of a loved one.
Spiritual testament: how to convey your experience to loved ones. About the practice of writing letters in which a person can summarize his life, give parting words and share lessons with those who will remain after his departure.
The grief of waiting is completely natural. A translation of a Norwegian article that the experience of impending separation from a loved one, when he is still alive but seriously ill, is a normal state of mind.
Urine microalbumin, mg/l: normal 0–30 Protein, mg/dl: normal - negative.
Urine containing a large amount of protein foams heavily, and the foam persists for a long time. Normally, during high physical activity, hypothermia, allergic reactions and some other conditions, a larger amount of albumin may be present in the urine (functional hyperalbuminuria). In addition, proteins produced by tubular epithelial cells can also be detected in the urine. The cause of persistent hyperalbuminuria requires clarification (especially with concomitant persistent hyposthenuria), since this condition usually serves as one of the first markers of the development of severe nephropathies (diabetic nephropathy, primary chronic glomerulo- and tubulointerstitial pathies). Globulinuria (proteinuria) is always a pathology and can be associated with both infectious and non-infectious diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Features of physiology
Cats have a specific physiology. For many millennia, these animals survived in desert landscapes with very little water. Because of this, cats began to drink less than other animals (such as dogs). The cats made up for the lack of water with liquid that they got from food. This feature remains unchanged today: cats still drink little, so they need food with a high fluid content.
Due to their physiology, cats' kidneys produce very concentrated urine. The specific gravity, or density, of urine shows the amount of substances dissolved in it. The gravity of cat urine is usually above 1.040. A reading below 1.020 indicates problems with the kidneys. For comparison, distilled water has a reading of 1.000, while human urine ranges from 1.002 to 1.030.
Manifestations of bile stagnation
- Skin itching. The symptom worsens in the evening and after contact of the skin with warm water. This provokes the appearance of scratches and pustular rashes on the skin. The patient becomes anxious, irritable, and suffers from insomnia.
- Feeling of fullness and pain in the hypochondrium on the right side. The latter can “give” to the right shoulder blade, arm, collarbone, and lumbar region.
- Changes in skin and mucous color. This usually manifests itself as yellowing of the sclera of the eyes, then the yellowness spreads to other parts of the body. Hyperpigmentation, a darkening of the skin, may also occur.
- Abnormal stool. Cholestasis is characterized by discolored yellow, gray or white stool. Due to the abundance of fats, it becomes liquid and has a foul odor. Later, indigestion and constipation occur.
- Skin formations. You can see xanthomas (thickened areas of rough skin on the body that are brown or yellow) on the chest, back, and elbows. Symmetrical yellow formations on the eyelids are called xanthelasmas. They appear when the amount of cholesterol in the blood increases for three or more months and may disappear after it normalizes.
- Dyspeptic disorders. There is a bitter taste in the mouth, nausea and vomiting are noted. Appetite is often reduced or absent, causing the patient to lose weight.
- Darkening of urine. The released liquid changes from straw-yellow to the color of “dark beer.”
- Signs of hypovitaminosis (due to impaired absorption of fats, the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins - A, D, E, K) is impaired. With prolonged cholestasis, vitamin K is not sufficiently absorbed from the intestine, and increased bleeding occurs. Vitamin D deficiency is accompanied by brittle bones and pain in the limbs and back. With poor absorption of vitamin A, distance vision deteriorates, and a person sees worse in the dark. Vitamin E deficiency reduces libido.
Urobilinogen, mg/dl: normal - Traces
A colorless substance, a product of bilirubin reduction, formed in the intestines, including. and under the influence of bacteria. Urobilinogen is formed from direct bilirubin that enters the intestine as part of bile and is partially absorbed back into the blood. Oxidation of urobilinogen in urine leads to the formation of urobilin. This reaction causes urine to darken during storage. With hemolytic jaundice, toxic and inflammatory liver lesions, enteritis and constipation, the level of urobilinogen increases significantly. When the bile duct is blocked (obstructive jaundice), urobilinogen is usually absent in the urine.