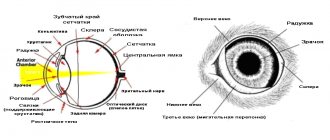
Shortness of breath in a cat or dyspnea is a disorder of the breathing process, expressed in changes in the frequency, depth and rhythm of respiratory movements. It can be both physiological and pathological in nature. In the latter case, dyspnea is a symptom of serious diseases.
Due to some differences in the physiology of dogs and cats, it is quite natural for a dog to have an open mouth with a protruding tongue during extreme heat. Thus, it regulates temperature (the body cools through the evaporation of saliva from the tongue). After all, animals do not have sweat glands on their bodies.
For a cat, an open mouth is an unnatural position, and she rarely resorts to it. In most cases, this indicates that the animal has health problems. That is why the owner should show concern in response to the appearance of this symptom in his pet. Let's take a closer look at what this phenomenon is.
Types of shortness of breath
As mentioned above, shortness of breath in a cat can be physiological or pathological.
In turn, pathological shortness of breath, based on the type of breathing disorder, can be divided into the following types:
- bradypnea - slow breathing when the functions of the respiratory center are suppressed;
- tachypnea - rapid shallow breathing. This is a characteristic symptom of fever, as well as anemia and other blood diseases.
In addition, there are several forms of shortness of breath, depending on which phase of breathing is disturbed:
- inspiratory dyspnea - the inspiratory phase is disrupted;
- expiratory shortness of breath - the expiratory phase is disturbed;
- mixed shortness of breath - both inhalation and exhalation are complicated.
How can I help at home?
The cat needs to be kept calm and not create additional stress on the respiratory system (it is vitally important not to agitate the cat, this can be very dangerous!). Under no circumstances should you try to put the cat down or give it water - this can be dangerous.
There is no need to use any drugs that stimulate breathing - in most cases this is not only pointless, but can also be harmful. It is necessary to take the animal to the doctor as quickly and carefully as possible.
Physiological dyspnea
Shortness of breath is almost always a sign of oxygen starvation of the body, which arises for various reasons.
Physiological shortness of breath does not require treatment. It represents the body’s reaction to certain unfavorable factors or extreme conditions. After their action ceases, the cat's breathing gradually becomes calm.
Causes
Physiological shortness of breath is characteristic of:
- severe stress;
- chest injury;
- heavy physical activity;
- overheating of the body.
Stressful conditions
During stressful conditions, the hormone adrenaline is automatically released into the blood, which has the ability to stimulate cardiac activity. The body's need for oxygen increases sharply. To compensate for this deficiency, the cat actively breathes with its open mouth.
Chest injury
Shortness of breath during chest injury is a normal physiological response of the body to pain. If the chest is bruised or the ribs are broken, deep breathing becomes impossible, as it can cause pain to the cat. In such situations, rapid shallow breathing through the mouth is observed.
Great physical activity
During fast running, hunting and games, cardiac activity is stimulated. Active blood circulation automatically leads to accelerated burning of oxygen. The animal stimulates gas exchange in the lungs, increasing the number of breathing movements.
But if the cat is overweight, then even a small load will be accompanied by pathological shortness of breath. After all, obesity in a cat is a disease. A heart covered with a layer of fat is unable to cope even with a moderate load. This situation needs to be corrected urgently.
Overheating of the body
During the heat, the cat overheats, which is why “dog” breathing can be observed - rapid, with an open mouth and a protruding tongue. A cat, like a dog, does not have sweat glands on its body. The sticking out tongue helps her to further cool her body.
Symptoms of physiological shortness of breath
Physiological shortness of breath may be accompanied by behavioral characteristics of the animal characteristic of a particular situation:
- active games and physical activity, overheating of the body - increased thirst;
- prolonged exposure to the sun - lethargy, an attempt to lie on a damp surface, hide in the shade;
- stress - fear, dilated pupils, anxiety, tossing.
How to help a cat
In case of physiological shortness of breath, the animal, first of all, is given complete rest, relieved of stress, protected from bright sun, and provided with a sufficient amount of drink.
Stress and psycho-emotional reasons
As a rule, stress and psycho-emotional reasons in cats do not often lead to breathing problems. But this statement is only partly true. There are several breeds of cats that are characterized by an overly emotional disposition and even some odd behavior:
- Persian cats.
- Siamese and crossbred animals based on them.
- “Good-natured giants”, Maine Coons, can be very aggressive.
Some representatives of these breeds are characterized by short-term (and sometimes not very short) outbursts of anger. In this case, the cat may lose control of itself, breathe hoarsely and quickly, and meow loudly and protractedly. Trying to calm him down costs yourself more. If this happens constantly, you need to consult a veterinarian about prescribing sedatives and medications to correct the animal’s behavior.
Pathological shortness of breath
Pathological shortness of breath is a sign of many quite dangerous ailments. If rapid breathing is not associated with external factors and appears regularly, there is no need to postpone a visit to the doctor.
Symptoms of pathological shortness of breath
The main symptoms of pathological shortness of breath are:
- difficulty inhaling, exhaling, breathing too often or too rarely;
- the animal adopts a posture of lack of air (the cat sits on half-bent legs with its head down and its mouth open);
- hoarse breathing;
- cyanosis of the mucous membranes of the lips, tongue, nose (evidence of hypoxia).
Main reasons
Pathological shortness of breath in a cat has various causes. They depend on which body system is affected. Basically, breathing problems can occur due to:
- diseases of the respiratory system;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases of the central nervous system;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system.
Respiratory system diseases
They can be divided into two types:
- Upper respiratory tract diseases. Shortness of breath occurs when the airways are blocked by mucous secretions due to sinusitis, rhinitis, and allergic reactions. The cause may also be nasal polyps or foreign bodies stuck in the respiratory canals.
- Diseases of the lower respiratory tract. Severe forms of pneumonia lead to filling of the alveolar spaces with purulent exudate. In this case, shortness of breath is accompanied by severe intoxication and high fever. Asthma attacks are characterized by their frequency and are caused by exposure to allergens - asthmatic pathogens in the allergic mood of the body.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
The most common cardiovascular disease is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in cats. The walls of the myocardium thicken, simultaneously reducing the size of the heart chambers. In this regard, blood flow is disrupted, which causes the development of hypoxia. Due to the mild symptoms, the disease is often diagnosed only at a late, life-threatening stage.
Noting lethargy, blueness of the mucous membranes, and increased drowsiness of the animal, an attentive owner should be wary. Particular concern should be caused by the fact that a cat of normal build breathes with an open mouth after running or playing. This is a clear indication of poor heart function. The animal must be shown to a veterinarian as soon as possible.
Diseases of the central nervous system
Shortness of breath may be a symptom of a cat's brain tumor affecting the respiratory center. Such pathologies are usually accompanied by coordination problems, dizziness, and vomiting. Such conditions are characterized by slow breathing - bradypnea.
Disease of the hematopoietic system
Severe anemia in cats—a critically low hemoglobin content in the blood—leads to shortness of breath. This disease is characterized by drowsiness, lethargy, cold extremities, metallic odor of saliva, and muscle weakness.
Diagnosis of the disease
A pet with pathological shortness of breath should definitely be shown to a doctor. The diseases of which it is a symptom are usually classified as severe and cannot be cured with home remedies.
After interviewing the owner and auscultating (listening) to the animal’s breathing and heart sounds, the doctor prescribes a set of diagnostic measures, the main ones being chest x-ray, laboratory blood tests, and echocardiogram. If a brain pathology is suspected, an MRI or CT scan of the head should be done.
Treatment options
Since shortness of breath is not an independent disease, but a symptom, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the cause of dyspnea. The doctor selects his tactics based on the diagnostic results.
In case of actively progressing respiratory failure, preliminary therapy should be carried out to improve the general condition of the pet. He is placed in an oxygen chamber, and in severe cases artificial ventilation is started.
The main treatment measures are as follows:
- In case of pathologies of the upper or lower respiratory tract, the following are prescribed according to indications: bronchodilators, anti-inflammatory drugs, broad-spectrum antibiotics. If the reason is the presence of a foreign body in the respiratory tract, then the animal is prepared for surgery to remove it. An asthma attack can be controlled with special medications (glucocorticosteroids, bronchodilators).
- For pathologies of the cardiovascular system, treatment is prescribed based on the results of the examination. Cardiomyopathy requires the use of beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics.
- Pathologies of the central nervous system. If a diagnosis is made of a brain tumor, then the cat begins to be prepared for surgery, and in the meantime a course of chemotherapy or radiotherapy is administered.
- Anemia must be treated with iron supplements and vitamin supplements. In severe cases, a complete blood transfusion is prescribed.
When heavy breathing is normal
It is incorrect to say that if a cat is breathing heavily, then some illness is to blame. So, our pets usually breathe heavily in the following cases:
- Fatigue
after active games or a long run;
Aggression
in relation to another unfriendly cat that is nearby;
Fear
(an animal may be frightened, for example, by the noise of a new vacuum cleaner, the roar of a gunshot, a trip in a car, etc.);
Estrus period and sexual heat
;
Pregnancy and lambing
(and even after giving birth, the cat can breathe heavily while feeding the kittens);
Staying in a stuffy and hot room
;
- Emotional experiences during sleep
(cats often breathe heavily if they see an unpleasant dream).
General preventive recommendations
Since there can be many causes of respiratory problems in cats, preventive measures boil down to maintaining the good physical condition of the animal. If the body has high resistance, the cat gets sick much less often and becomes more resilient. In addition, the cat is less likely to develop any hereditary diseases.
It is necessary to ensure that the animal does not overheat in the summer, do not overload it beyond measure, and do not overfeed it. It is very good if, from childhood, the kitten is surrounded by a calm, friendly environment.
The cat is breathing heavily: how to provide first aid?
The animal should be observed. If abdominal breathing is associated with physiological reasons, it will pass within half an hour. You need to come to terms with abdominal breathing associated with pregnancy or lactation; this is a normal phenomenon. If your pet gets sick in a car, you need to stop and wait until the animal comes to its senses.
Special remedies have been developed against motion sickness. Veterinarians recommend giving 1 ml of Vetspokoin suspension or a drop of Stop-Stress per 1 kg of weight a couple of hours before the trip.
If heavy breathing is caused by hot weather, then the pet is moved to a cool place or the air conditioner is turned on, but so that the cold air does not fall on the cat. Otherwise, shortness of breath will occur due to bronchitis or rhinitis.
In all other cases, the animal must be shown to a veterinarian. Above we have given a fairly comprehensive list of problems, most of which only a doctor can identify and help the animal.
Be sure to read:
A kitten's eyes are festering: normal or pathological, reasons, what to do at home, medications