The appearance of bloody diarrhea in a cat is a serious reason for immediate contact with a veterinarian. The cause of this condition in a pet can be a dangerous infectious disease, helminthic infestation, poisoning, malignant tumors and other pathologies. All of them pose a danger to life, so owners must be able to provide timely and competent assistance to the animal.
Diarrhea in cats and cats: causes
Diarrhea is not an independent disease, but a manifestation of an infectious, inflammatory process, dysbacteriosis. The causes of stool disorder can be divided into 2 groups: pathological conditions and external factors.
Pathological conditions causing diarrhea:
- Foreign body in the intestine. While playing or eating, an animal may accidentally swallow a small object. The thread and casing from the sausage do not break down under the influence of gastric juice, and a congestion forms, disrupting the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Worm infestations. Parasites feed on intestinal juice, attaching themselves to the villi of its walls. An irritated gastrointestinal tract does not function well.
- Viral and bacterial infections. Pathogens disrupt the normal intestinal microflora.
- Constipation. Lack of fluid and age-related changes lead to problems with motor skills. Constipation alternates with loose stools.
- Metabolic diseases.
- Stress. Anxiety and excitement affect the innervation of the stomach, which leads to disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
The second group includes the following:
- Poor quality water. A cat is a predator; the hunter's instinct prompts him to “get” water. Pets often drink from the toilet.
- Reaction to new food. If the diarrhea gets worse, the food is likely of poor quality.
- No diet. Heavy foods: smoked meats, cutlets are difficult to digest. Fermentation processes increase intestinal motility, causing diarrhea.
- Binge eating. The animal eats a lot as a result of stress: change of environment, castration.
- Reaction to drugs.
The disease is usually accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms.
Treating diarrhea in a kitten at home
Drugs
Before contacting the clinic, if there is softening of the stool or loose stools no more than once a day, the owner can begin to independently administer the sorbent - Smecta, Enterosgel, EnteroZOO, Diagel.
Do not delay examination by a doctor as the disease can progress quickly and lead to the death of the kitten.
If there is vomiting, you should not give drugs, you need to go to the clinic as soon as possible. Since it is important to stop vomiting, otherwise the administration of drugs will be ineffective and feeding will be impossible.
If the kitten already has persistent diarrhea, the presence of blood, mucus in the stool, you should immediately contact the clinic and begin therapy and diagnosis as soon as possible.
Folk remedies
If diarrhea is caused by poor diet, you can do an enema with a decoction of oak bark, calendula and chamomile.
You can also make an enema from a decoction of dried blueberries. These berries have an astringent and anthelmintic effect. However, blueberry leaves have a laxative effect.
Diet
An important aspect of therapy is feeding. It is necessary that the diet is complete and balanced and meets the baby’s needs. The food should also be easily digestible. Dangerous and harmful foods are excluded from the diet - bones, milk and dairy products, offal.
If necessary, a specialized diet is prescribed - commercial feed with readily available protein and low fat content.
In order to prevent digestive disorders and diarrhea in kittens due to improper feeding, it is recommended:
- before weaning the kittens, start complementary feeding;
- during early weaning, start feeding a specialized mixture of cat milk replacer;
- observe the feeding regime;
- transfer to food in accordance with age;
- transfer the kitten to food in accordance with its physiological state; there are special foods for castrated kittens;
- transfer to a new food or another type of feeding must be done gradually.
Feeding should be complete and balanced. This can be commercial kitten food or individually formulated diets from homemade products.
Increased body temperature in a cat
The first thing an owner should remember about body temperature is that the nose is not an indicator of body temperature.
The only possible way to measure body temperature is thermometry. Read more
Symptoms of diarrhea in cats and kittens
Diarrhea is frequent, repeated bowel movements that last more than a day.
Be sure to read:
A cat often burps: causes, symptoms, what to do when vomiting after eating, prevention, what not to do
There are two forms of the condition:
- acute – begins suddenly, lasts 1-2 weeks;
- chronic – lasts more than 2 weeks.
In addition to the main manifestation, other symptoms are observed.
They differ depending on the form of the pathology and the causes of its occurrence:
- loose stools with a persistent pungent odor;
- increasing the frequency of toileting, changing the tray more often;
- sudden onset, a well-mannered pet defecates outside the tray;
- sudden weight loss;
- blood and mucus appear in the stool;
- dehydration;
- the animal meows during toileting;
- loss of appetite;
- weakness, sudden changes in behavior.
Often the problem resolves itself. But frequent bowel movements lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. Even after normalization of stool, the pet should be shown to a veterinarian.
Green feces
Fungus
Diarrhea
Vomit
Ulcer
25043 December 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Green feces: causes of appearance, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Greenish-colored feces in people of any age can be both a variant of the norm and evidence of serious changes in the body.
Feces is a waste product of the body, formed in the large intestine, consisting of 80% water and 20% dry matter. The dry residue includes undigested food (40%), almost completely non-viable intestinal microflora (30%), secretions from the glands of the intestinal wall (mucus) and dead cells of the intestinal mucosa (30%).
The composition and nature of feces are determined by nutrition, the state of the digestive system, intestinal microflora, and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The normal intestinal microflora includes a large number of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, Escherichia coli, and bacteroides. They are useful because they perform a protective function and inhibit the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. Enterobacteriaceae, enterococci, clostridia, staphylococci, streptococci, and fungi of the genus Candida are present in smaller quantities in the intestines. If they multiply uncontrolled, they can cause unpleasant symptoms.
Varieties of green feces
Green feces are found in normal and pathological conditions. With the pathological nature of the stool, the patient’s general well-being changes, the frequency of bowel movements, the consistency of the stool, its smell, and impurities of mucus, pus, and blood may appear.
Possible causes of green stool
The most common cause of green stool without changing its other characteristics is the consumption of green plant foods - spinach, sorrel, lettuce, etc., as well as products containing green food coloring. In this case, the color of the stool will normalize on its own within one to two days after stopping the use of the listed products.
Another variant of the norm is meconium - the first stool of a newborn. It is viscous, sticky, dark green in color, and consists of dead cells of the intestinal wall, mucus, amniotic fluid, and bile.
The intestines of a newborn baby are gradually populated by microorganisms. At the same time, the composition of the microflora of a breastfed baby, despite the predominance of lacto- and bifidobacteria, is more variable than that of a bottle-fed baby.
Some bacteria can affect the color of stool and turn it green. If you feel well, have an appetite and there are no other symptoms, these phenomena are considered normal.
A persistent disturbance in the composition of the intestinal microflora (dysbacteriosis) is considered a pathological condition that affects the color of stool.
When taking tablets and capsules of iron, excess iron is eliminated naturally, and the stool becomes dark, greenish, or even black.
Feces completely restore their characteristics after completing the course of medication.
Possible causes of green stool include infectious and inflammatory diseases of the stomach, small and large intestines.
What diseases cause stool to turn green?
Lactase deficiency
– a congenital or acquired condition in which the activity of the lactase enzyme and the ability to digest lactose are absent or reduced. Congenital lactase deficiency begins to appear in early childhood and persists throughout life; transient deficiency develops against the background of immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) of the newborn (occurs at 3-6 weeks of life and decreases as the child grows and develops). Secondary lactase deficiency is a consequence of a previous disease, accompanied by damage to the cells of the intestinal wall.
The main symptoms of lactase deficiency are severe bloating, intestinal colic, and loose, foamy stools after drinking breast milk or whole cow's milk.
With insufficient processing of lactose in the gastrointestinal tract, fermentation and decay processes begin, which cannot but affect the composition of the microflora. If there is a pronounced imbalance of microorganisms, green stool may appear.
A violation of the ratio of normal and pathogenic intestinal microflora is called
dysbiosis
. This condition can occur against the background of a sudden change in diet, with insufficient consumption of plant foods and dairy products, due to inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract, stomach and duodenal ulcers, infectious lesions of the small or large intestine, after taking a course of antibacterial drugs, against the background of decreased immunity .
Symptoms of dysbiosis include constipation or unstable stools, impaired processing and absorption of beneficial nutrients, bloating and abdominal pain.
Intestinal infections that are characterized by the appearance of green stool include dysentery, giardiasis, salmonellosis, and rotavirus.
Dysentery
are caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella, which are excreted in the feces of a sick person or carrier. Shigella enters the body through dirty hands, and after 2–3 days the development of the disease begins. Bacteria multiply in the large intestine, irritating and damaging its wall.
Symptoms of dysentery are a false, painful urge to defecate, as well as frequent, scanty, loose, dark green stools mixed with blood, mucus, and pus.
The patient's general health deteriorates, he is worried about weakness, and his body temperature rises. At the same time, due to small stools, the risk of dehydration remains low, but perforation of the intestinal wall is possible.
Giardiasis
Caused by the protozoan Giardia. The transmission mechanism is fecal-oral, infection is possible through direct contact with a sick person or through contaminated water and food. It takes up to four weeks from the moment of infection to the manifestation of symptoms. Children and adults with low acidity of gastric juice are more likely to get sick.
Protozoa cause symptoms of inflammation of the small intestine: nausea, bloating, pain in the upper and middle thirds, around the navel, frequent (up to 5 times a day) liquid, copious, foamy, foul-smelling green stools.
Extraintestinal manifestations are also possible - skin rashes, severe allergic reactions.
Giardia
Salmonellosis
caused by bacteria of the genus Salmonella. They enter the human body through poorly cooked eggs, dairy products and meat. The period from infection to the onset of disease manifestation lasts up to two days. Symptoms of salmonellosis include spasmodic pain in the upper abdomen and near the navel, nausea, vomiting (up to 3 times a day), as well as frequent (up to 15 times a day) copious, liquid, foamy, foul-smelling stools the color of swamp mud.
The disease is dangerous due to severe intoxication, dehydration, possible entry of salmonella into the blood and disruption of the functions of many organs and systems (sepsis).
Rotavirus
spreads through food, water, airborne droplets, and household contact. It is perfectly preserved in the external environment and is resistant to most disinfectants. For the development of the disease, just a few viral particles enter the mouth. It begins with symptoms of an acute respiratory viral infection - increased body temperature, redness and soreness of the throat. Then comes frequent, profuse vomiting and frequent (5–15 times a day) loose stools, which can be of different shades, including yellow-green. Against this background, dehydration quickly develops.
Which doctors should I contact?
If there are signs of an intestinal infection, especially in a child, it is best to call an ambulance team, which, if necessary, will take the patient to an infectious diseases hospital.
In other cases, you should contact , , , .
Diagnostics and examinations for the appearance of green stool
To establish the causes of green stool, the doctor conducts a thorough survey and examination of the patient, clarifies the diet and nature of the diet, and clarifies concomitant diseases and conditions.
For a more complete understanding of the picture, a number of laboratory and instrumental research methods may be required:
- general blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula;
If your cat has water diarrhea
The causes of stool abnormalities are judged, among other things, by the consistency and color of the stool. Watery discharge usually occurs suddenly and goes away on its own. The acute form of the pathology is often caused by poor-quality food or drink. Some cats do not tolerate milk well.
The pet is given boiled water and food is reduced. Food is completely excluded from the table. If after 2 days the condition does not improve, blood is observed in the stool, and the animal begins vomiting, then a veterinary examination is necessary.
Clinical picture
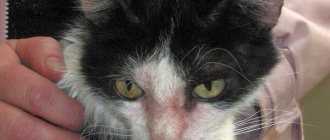
To know what to do if your cat has diarrhea with blood and mucus, you need to understand where the bleeding occurred in the gastrointestinal tract.
If the inflammation is localized in the stomach and small intestine, the liquid stool turns black and lacks mucus, and vomiting and gas formation are also possible. When the large intestine is damaged, the diarrhea contains streaks of scarlet blood with mucus. The cat does not have vomiting or flatulence.
Owners need to pay attention to these signs to help the attending physician understand the causes of bloody diarrhea in a cat.
Symptoms that require immediate medical attention
You should not try to do anything on your own if your cat’s diarrhea with blood is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a sharp decrease in body temperature below acceptable values;
- temperature rise above 41 °C;
- frequent vomiting mixed with blood and bile;
- severe tension in the abdominal wall;
- fetid, putrid odor emanating from feces;
- nervous phenomena.
In these cases, it is necessary to treat bloody diarrhea in cats only in a clinical setting.
If your cat has diarrhea with blood and/or mucus
Bloody or mucous discharge is a severe symptom. Mucus is a substance secreted by cells containing antibodies.
The cell reaction is protective and indicates the entry of pathogenic substances into the body. Mucous stool without blood is often observed after deworming. Anthelmintic drugs contain substances that not only kill parasites, but also activate the body's protective functions.
Be sure to read:
The kitten has bad breath: reasons, what to do, when it is an alarming symptom, prevention
Blood appears when the walls of the small or large intestine are damaged.
Causes:
- changes in diet, food intolerance;
- intestinal parasites (giardia);
- toxoplasmosis is a disease caused by single-celled parasites Toxoplasma gondii;
- injury or abscess of the digestive organs;
- idiopathic megacolon;
- intoxication;
- oncology.
If blood or mucus is detected, seek medical attention.
Diagnostics
Before treating bloody diarrhea in a cat, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of its occurrence.
To do this, a veterinarian conducts the following studies:
- collection of anamnestic data;
- examination, including palpation, percussion and auscultation;
- general and clinical blood test;
- examination of feces for the presence of eggs, segments or larvae of helminths;
- instrumental methods (if necessary).
Instrumental methods include:
- radiography;
- endoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- Ultrasound.
If a veterinarian suspects a malignant tumor causing diarrhea in a cat, he may prescribe a blood test to detect the leukemia virus or immunodeficiency virus, conduct a biopsy followed by tissue histology.
If your cat has diarrhea and vomiting
Loose stools with vomiting are called gastroenteritis - a disorder or inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. Vomiting indicates irritation in the stomach or small intestine. Diarrhea – due to irritation anywhere in the intestinal tract.
Factors causing these manifestations:
- Changes in diet. An abnormal reaction is caused by dairy products and grains.
- Toxins. A cat can bite off a houseplant or chocolate. Toxic substances can get in with household chemical residues.
- Diseases caused by parasites, bacteria or fungi.
- Parasitic infestations: hookworms, tapeworms, roundworms, Giardia.
- Heatstroke.
- Lesions of the pancreas, liver.
- Cancer.
Pets are less able to cope with any changes. If sharp restrictions in the diet and the creation of comfortable conditions do not help, the cat is taken for examination.
If your cat has yellow diarrhea
The color of excrement is affected by bilirubin, which is part of bile. It is secreted by the liver and from there it enters the intestines. In the colon it is oxidized to stercobilin, which gives dark color to stool.
Disturbances in the oxidative process may be associated with dysbiosis caused by poor nutrition. Overfeeding an animal or heavy food puts stress on the liver, impairing its function. The gland secretes excess amounts of bilirubin.
The body eliminates excess in undigested form. Liver dysfunction can be caused by pathologies: hepatitis, pancreatitis.
If your cat has white diarrhea
A light shade indicates serious problems with the gallbladder or liver. A diseased gland secretes an insufficient amount of bile. The danger is that bile helps digest semi-saturated fats. Their deficiency leads to the development of various diseases.
Diseases causing disturbances in bile secretion:
- hepatitis;
- cholangitis;
- cirrhosis;
- atony of the gallbladder.
The doctor identifies the pathology and prescribes treatment.
Treating a cat for diarrhea at home
“Home” therapy can only be carried out under certain conditions:
- absence of blood, mucus in feces, does not acquire green or other uncharacteristic tint;
- the pet has a relatively normal appetite;
- Vomiting and aggressiveness are not observed.
Be sure to read:
A cat is vomiting yellow liquid: normal or pathological, first aid, what to do, best medications, diet
The animal is given absorbents: Smecta, activated carbon. To prevent dehydration, split drinks are prescribed: boiled water / rehydron solution. Antidiarrheals and antibiotics are prescribed by the doctor.
Medicines and dosage for diarrhea in cats
Drug therapy is prescribed by a veterinarian.
| name of the drug | pharmachologic effect | dosage |
| Lignitin (tablets) | absorbent, antidiarrheal | table/2 kg weight, 7-10 days |
| Loperamide (tablets) | antidiarrheal | 0.5 mg/0.4 kg body weight, every 8 hours |
| Enterofuril (suspension) | broad spectrum antimicrobial | 1 ml/2.5 kg, no more than 5 days |
| Furazolidone | synthetic antibiotic | the diagram is signed by a veterinarian |
| Phthalazole | Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial | the dosage is determined by the doctor |
| EnteroZoo (paste) | detoxification | 2 tsp / 2 kg |
To restore the microflora, they follow a diet and give bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
Prices for appointments in our clinics
| Name of veterinary services | Unit | Price, rub |
| ⭐ Initial appointment | 1 animal | 400 |
| ⭐ Repeated appointment | 1 animal | 250 |
| Initial appointment with a specialist | 1 animal | 1100 |
| Consultation without an animal | — | 550 |
| Consultation with a doctor based on test results | 1 PC. | 400 |
| Weighing animals | 1 animal | For free |
| Additional fixation for aggressive animal behavior | 1 animal | 700 |
All our Veterinary Clinics:
For any suggestions regarding the site: [email protected]
|