When talking about common feline diseases, one cannot fail to mention cancer. Yes, unfortunately, animals, like people, have a fairly high risk of developing cancer. A tumor of the mammary gland in cats is quite common, and in four out of five cases the disease takes a malignant course. This serious illness can be completely cured only with early diagnosis. The owner should closely monitor the health of his pet and, if a small lump or lump appears in the mammary glands, be sure to contact a veterinary clinic for advice.
Causes
Today, only a number of factors are known, the presence of which leads to the development of mammary gland cancer in cats. And the exact causes of this dangerous disease are still unknown to medicine. The hormonal factor is of greatest importance. Fluctuations in hormonal levels in an animal’s body can be caused by various reasons:
- Natural fluctuations. They accompany estrous cycles (physiological changes in the body that occur during the period between two estrus cycles). In this case, the risk of cancer is reduced by early (before the first heat) sterilization of the cat.
- Artificially created vibrations. This includes the effect on the hormonal background of the animal’s body with drugs of the hormone progesterone, which is prescribed to reduce the level of aggression in cats or to prevent unwanted pregnancy in females. In this case, you can avoid the risk of oncology by refusing to prescribe such drugs (or giving them not regularly, but occasionally).
In addition, the following factors increase the likelihood of tumor processes in the mammary gland:
- Age of the cat. The disease usually does not affect kittens. Cats aged 10 years and older are most susceptible to the disease.
- There is a breed predisposition. It is believed that tumors appear more often in cats of Oriental and Siamese breeds.
- Hereditary predisposition also matters.
- The risk increases if the cat has lived for a long time in a polluted environment.
- Feeding low-quality feed, a poor, monotonous diet significantly reduces the animal’s body’s resistance, and therefore increases the risk of getting sick.
There is also a version that cancer of any location, including a breast tumor, has a viral etiology. But definitive proof of it still does not exist.
Prevention
It is important to know not only how to treat mastitis in a cat, but also how to prevent it. Below we have prepared a list of useful tips for you in this case:
| Monitoring your cat's fluid intake | If there are few kittens, then limit the amount of liquid you drink for the cat who has given birth. |
| "Manicure" for kittens. | Also, be sure to trim your kids' nails. They can scratch their mother's nipples while sucking. This will cause bacteria to enter the cat's mammary glands. |
| Diet of a pregnant and lactating cat | Be sure to discuss the diet of your pregnant and lactating cat with an experienced veterinarian. Some types of food (cottage cheese, mineral or vitamin supplements, etc.) stimulate milk production. |
| Maintain animal hygiene | Dirty bedding, floors, and tray can lead to bacterial contamination of the nipples. If necessary, wash the skin with a decoction of oak bark, a very weak solution of potassium permanganate (literally a crystal in half a liter of water). If you notice cracks, be sure to lubricate them with cream. |
| Avoid injury | Place the pet's bed away from drafts. |
| Deworming, preventative treatment against fleas and ticks | Carry out deworming in a timely manner (parasites greatly weaken the immune system). Don't forget about ticks and fleas. They not only reduce the body's defenses, but also cause itching. As a result, the cat scratches itself, thereby opening the “gate” for pathogenic bacteria. |
Stages of the disease
Mammary cancer that occurs in a cat has four stages of development. They are recognized by their clinical signs and have different courses:
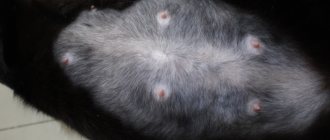
- The first stage is characterized by small, painless lumps. The lymph nodes are not yet enlarged. The disease detected at this stage can be completely cured, and the cat continues to live.
- The second stage is characterized by a more dense neoplasm, which can reach a diameter of three centimeters. The tumor at this stage is operable, animals have an approximately one-year survival rate.
- The third stage is a tumor larger than three centimeters in size, inflamed lymph nodes. The cat protects the chest, experiencing pain in the affected area.
- The fourth and final stage cannot be cured. The neoplasm is significant in size. Lymph nodes are greatly enlarged. The cat is exhausted. There are already metastases. In most cases, at this stage of the disease, surgery is powerless. Severe pain is relieved by constant use of painkillers. The prognosis of the disease is unfavorable. In especially severe cases, animal euthanasia is used.
The degree of disease in the clinic is determined by the so-called staging system, which takes into account the size of the tumor and the results of aspiration biopsy of the lymph nodes. In addition, to determine the number and localization of metastases, radiography in three projections, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are prescribed.
Types of breast tumors
Most tumors (and there are 4 pairs in total) develop from glandular epithelium and are divided into three large groups:
- Adenoma and fibroadenoma (in the case of a benign course), it is quite rare.
- Carcinoma or adenocarcinoma (in the case of a malignant course) of the mammary gland in a cat, it is much more common. Most of it comes from the epithelium of the ducts and alveoli of the mammary glands. Inflammatory carcinoma of the mammary glands is especially dangerous. It is accompanied by an inflammatory process and therefore has a particularly unfavorable prognosis.
- Mixed tumors affect both ductal and epithelial tissues of the mammary glands. They are characterized by a more favorable course.
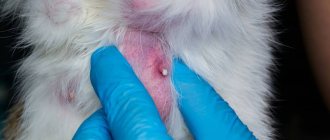
Breast carcinoma is a mobile nodular formation. In later stages, it often breaks open and may ulcerate or bleed. The mammary glands are most often affected on one side, less often on both sides. The disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the groin and axillary areas.
It is not always possible to determine the type of tumor (benign or malignant), especially if it has burst. In this case, the treatment regimen is based on the method of treating a potentially malignant neoplasm.
Varieties
Considering the nature of the disease, a tumor in a cat can be of the following types:
- Benign. It does not pose a threat to the life of the animal and responds well to treatment. This type includes adenomas and cysts. Often one mammary gland is affected. The formation does not bleed or metastasize and does not require special treatment. But if the tumor is large, the doctor will advise removing it, as there is a risk of degeneration into oncology.
- Malignant. Dangerous to the health and life of domestic cats and dogs. Oncological forms are considered sarcoma, adenocarcinoma, solid, lattice, mucinous and tubulopapillary cancer. The formation spreads metastases, grows into neighboring tissues and destroys them.
Characteristic symptoms
The main symptoms appear when the disease has already entered the advanced stage. At this stage, the animal’s general well-being worsens and its appearance changes. The tumor may appear as single or multiple nodes. The inguinal and axillary lymph nodes are inflamed. The lesion may involve several lobes of the mammary gland. Sometimes its true size can only be assessed after shaving the fur over a fairly large area of the body. The main clinical signs at this stage are:
- the neoplasm is significant in size;
- there is quite severe inflammation of the surrounding tissues;
- the cat is in quite a lot of pain;
- body temperature may rise;
- the animal loses weight sharply, there is no appetite;
- Bleeding and discharge of pus from the opened tumor are possible.
If a cat's mammary gland is swollen and painful, this is not always associated with cancer. Very often, some non-tumor conditions of the mammary glands have similar signs. Basically, these are hyperplasias (tissue growths) of various etiologies and some other conditions:
- hyperplasia of the gland ducts;
- breast cysts;
- lobular hyperplasia;
- fibroadenomatous hyperplasia;
- false pregnancy;
- true pregnancy;
- consequences of the administration of progesterone hormone drugs.
Establishing diagnosis
As already mentioned, with breast cancer, early diagnosis of the disease is very important, so the owner is required to deliver the animal to a good veterinary facility on time. Only a doctor can make a high-quality diagnosis. He has at his disposal all types of instrumental examinations (ultrasound, radiography, magnetic resonance and computed tomography). In addition, a biopsy or fine needle aspiration (penetration) of the lesion for cytological examination helps to make an accurate diagnosis.
A lot depends on how carefully the biopsy material is taken. Additional trauma to the tumor can lead to a sharp increase in the number of metastases, which will make the patient's condition more severe. The inguinal and axillary lymph nodes must be examined, since they are also often affected by the disease.
In this case, a detailed blood test, including its biochemical formula, is no less informative. It will allow you to determine the degree of the inflammatory process, as well as the presence of concomitant infections, which cannot be ignored when prescribing a treatment regimen.
Treatment methods
In most cases, treatment for breast cancer is radical. Surgery to remove the tumor is proposed. It usually takes place in several stages:
- removal of a mammary tumor, which is performed in cats with a significant area of healthy tissue;
- removal of nearby lymph nodes to prevent further metastasis;
- chemotherapy - as the final stage of treatment, designed to stop the tumor process and eliminate the possibility of relapses.
Removal of the affected area with a significant area of healthy tissue
The smaller the tumor size, the higher the chances of success of the operation. It is believed that the prognosis of the disease is favorable if the diameter does not exceed 3 cm. The degree of surgical intervention may vary depending on the size of the affected area:
- If the cat's tumor is small in size, only the affected gland is removed.
- If neighboring glands are captured, then during one intervention the entire row of glands is removed.
- If it is bilateral (two-sided), removal of the breast tumor is carried out in two stages with an interval of two weeks. But, if the lower or upper layers of the skin are involved in the tumor process, the entire affected area is removed at once.
It is difficult to say how long a cat will live after a mastectomy. The operation is classified as difficult, so a 100% guarantee of success is usually not given. There is also no certainty that the disease will not return in the form of a relapse.
Removal of lymph nodes
Fine-needle aspiration of regional (associated with the organs in question) lymph nodes makes it possible to determine the degree of their involvement in the pathological process. Usually, surgery is prescribed to remove the affected lymph nodes (inguinal and axillary). Sometimes ovariohysterectomy (removal of the uterus and ovaries) is performed simultaneously, which facilitates postoperative therapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the final stage of treatment. During it, quite strong drugs are used (Doxorubicin, Cyclophosphamide), which help to completely stop the tumor process. But, at the same time, they have quite significant side effects and cause severe intoxication of the body. Therefore, chemotherapy is carried out under careful monitoring of the animal’s condition.
If a cat has contraindications to mastectomy (old age or poor health), chemotherapy becomes the only way to stop the pathological process and even slightly reduce the size of the tumor.
Chemotherapy is also used when the tumor is small and the attending physician decides to do without surgery.
Help with tumor diseases
If your pet has a mammary tumor and purulent discharge is observed, consultation with a veterinarian is necessary. In most cases, the exposed tumor is urgently removed. But, if this path is dangerous, they resort to conservative treatment. Applications of Levomekol ointment are usually prescribed. Before smearing, treat the wound with chlorhexidine. In addition, antibiotic therapy is carried out (Tsiprovet, Fosprenil). The wound is covered with a loose bandage, with free access of air. A loose blanket is put on top.
If a cat has a tumor, it needs to be given maximum attention and care. You can take care of her without fear for your health - the disease is not contagious.
Therapy
Treatment for hard mammary glands in a nursing cat depends only on what causes these lumps. For diseases such as mastopathy and cancer, a qualified veterinarian prescribes conservative therapy or surgical treatment. In the first case, the animal takes medications aimed at stabilizing hormonal levels and vitamins. In the second case, surgical intervention is performed, during which the mammary gland and nipple are removed. Subsequently, they are sent for laboratory testing.
In some cases, there are indications that do not allow surgery. The reason for refusal may be a weak heart. Then there is another way - chemotherapy. This method is also quite serious; it is prescribed when the purr has a strong liver and kidneys. Chemotherapy for cats is carried out using the following drugs:
All final decisions are made after a detailed study of all influencing factors. The opinion of experts depends on:
- stage and type of cancer;
- tumor localization;
- general health of the animal;
- material capabilities of the owners.
Radiation therapy has become an analogue of radiation therapy. This procedure is used not only to eliminate cancer cells, but also to neutralize their consequences. Ionized radiation, entering the body, prevents cancer relapses. Based on the type of beam, this therapy is divided into x-ray therapy and gamma therapy.
Postoperative period: animal care
A caring owner should know what to do in the postoperative period. His main task is to accurately follow all medical recommendations:
- The most important condition is to create all the conditions for the animal to recover as quickly as possible. He needs rest for successful rehabilitation.
- The diet is compiled together with the attending physician. Only recommended foods or feeds are allowed and given in moderation. There should be no deviations from the dietary regime.
- Timely treatment of seams and surrounding tissues is important.
- Postoperative drug therapy will help create protection against infections to eliminate the possibility of complications.
- Protective bandages and blankets should be used to prevent the animal from injuring the operated area.
At the slightest hint of postoperative complications (the stitches have ruptured and pus appears, or the temperature has risen), you must immediately take the animal to the clinic.
Preventive measures
A preventive measure that provides almost one hundred percent protection against this disease is sterilization of the cat in childhood, even before the onset of the first heat, and castration of the cat before the age of 1 year.
Regular prevention consists of the following:
- when playing with a cat or male cat, it is necessary to conduct an incidental examination of the mammary glands;
- the animal is subjected to an annual preventive examination at a veterinary institution after reaching 10 years of age;
- hormonal medications that regulate the cat’s sexual activity and delay the onset of pregnancy should be abandoned;
- It is equally important to follow the principles of proper and nutritious nutrition for your pet;
- and, finally, it is necessary to promptly treat inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system of pets.
Breast tumors are a very serious disease. Any person caring for their pet is interested in the question: how long do cats with this disease live? If detected early, their lifespan may not be limited by the disease. In other cases, their average lifespan ranges from 2 to 20 months (if you count from detection).
You should never despair and lose hope for the recovery of your family friend. We must do everything possible and believe, according to the principle: as long as you believe, you live.
Diagnostic measures
For a full examination of your pet, an ultrasound scan of the problematic glandular tissue is performed.
When a cat’s mammary glands are swollen, you should urgently contact a veterinary clinic, where they will conduct a comprehensive examination and tell you what to do and how to overcome the problem. To make a diagnosis, the following manipulations are performed:
- chest x-rays;
- biopsy;
- ultrasound examination;
- analysis of milk from a damaged mammary gland;
- laboratory testing of urine and blood;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.