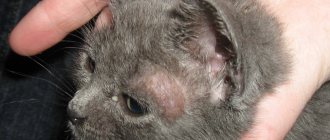
Cat owners often have to deal with various health problems with their pets. The lion's share of diseases occurs in the gastrointestinal tract; representatives of the cat family especially often suffer from digestive disorders such as diarrhea or diarrhea. In most cases, bowel dysfunction does not pose a threat to the pet’s life and does not require drug therapy. However, in some cases, frequent loose stools may signal the development of a serious illness. Especially if there is blood in the stool, the animal’s condition deteriorates sharply, an upset stomach is accompanied by vomiting, the temperature rises, etc. In this case, it is important to know what to do and how to properly treat diarrhea in cats.
Causes of flatulence in children
In the first year of life, the baby still produces insufficient digestive enzymes, gastric motility is weak, so even with minor violations of the feeding rules, flatulence occurs. This may be too frequent and/or abundant feeding, incorrect balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, etc. In addition, infants swallow a lot of air when feeding, which also causes gas formation. Source: P.L. Shcherbakov Flatulence in children // Difficult Patient, 2006, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 66-72
Other causes of gas in newborns:
- the process of adaptation of the body to life outside the womb;
- stress;
- age-inappropriate food;
- changing formula;
- overfeeding;
- introducing complementary foods too early;
- swallowing gas while crying or screaming;
- restless behavior, overexcitation, unstable emotional state;
- improper diet of the mother if the child is breastfed;
- prematurity;
- lactase deficiency;
- allergy to cow's or goat's milk protein;
- dysbiosis.
In children 2-4 years old, the reasons for increased gas formation are different:
- consumption of sweets, baked goods, white bread, foods with coarse fiber and starch;
- physical inactivity, inactive lifestyle;
- excess body weight;
- dysbacteriosis;
- congenital deficiency of digestive enzymes;
- stress, nervous tension;
- abuse of carbonated drinks;
- habit of chewing gum.
The psychological factor is very important for schoolchildren. Gases occur due to stress or psychological constipation, neuroses that affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
After 8 years the reasons are as follows:
- binge eating;
- physical inactivity;
- impaired intestinal motility, dysbacteriosis;
- neuroses;
- drug abuse;
- passion for “junk foods”, carbonated drinks;
- unbalanced nutrition, because from this age children already choose for themselves what they want to eat and what not, argue with their parents, refuse healthy food;
- intestinal infections.
Types of flatulence in older children:
- Disgestive. A consequence of a deficiency of digestive enzymes, the breakdown of undigested food remains by the intestinal microflora and, as a result, the release of large amounts of gases.
- Nutritional. Occurs when consuming gas-forming foods and drinks.
- Dynamic. It develops if the motility of the gastrointestinal tract is impaired, which leads to the accumulation of undigested food residues in the intestines.
- Dysbiotic. Explained by intestinal dysbiosis. The main reason is long-term antibiotic therapy, which suppresses the activity of microflora and stimulates the growth of colonies of foreign microorganisms. Source: N.L. Pakhomovskaya, M.M. Venediktova Flatulence: causes and ways of correction // Consillium Medicum. Pediatrics, 2022, No. 2, pp. 32-36
Types of diarrhea in cats
Depending on the causes of the eating disorder, stool takes on different colors, textures and smells. Based on the analysis of these parameters, it is possible to draw a conclusion about the presence of a particular disease and determine a course of treatment at home.
Classification of diarrhea according to consistency and the presence of foreign impurities in the stool:
- liquid diarrhea, the presence of vomiting most likely indicates food poisoning;
- the presence of mucus in stool indicates damage to the large intestine;
- blood in the stool indicates the infectious nature of diarrhea, the presence of parasites, or indicates damage to internal organs.
Depending on the color of the stool, the following types of diarrhea are distinguished:
- yellow stool – incomplete digestion of food eaten;
- black color - indicates the presence of internal bleeding (you should seek emergency veterinary help or call a veterinarian at home), may also be a consequence of taking medications containing iron or indicate an excessive meat diet;
- green color - with a high degree of probability indicates the consumption of spoiled foods that provoke rotting processes in the intestines; you can treat green diarrhea yourself;
- white color - indicates the presence of problems in the biliary tract;
- orange color - the pet is experiencing severe intoxication and needs emergency help.
Symptoms of the disease in children of different ages
For children under one year old
- Restlessness, frequent crying.
- Visually noticeable bloating.
- Stool disorders - diarrhea or constipation, which is especially typical for lactase deficiency.
- Belching, hiccups.
- Lack of appetite - breast refusal.
- A few minutes after feeding, the baby tries to pull his legs towards his chest.
For children of older age groups
- Rumbling in the stomach, pain, feeling of fullness.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Increased volume of gases that may escape uncontrollably.
- Bloating, which is visually noticeable in a child during flatulence.
- Feeling of a full stomach, lack of appetite.
- Dyspnea.
- Constipation and diarrhea, alternating with each other.
A characteristic feature of the disease is the disappearance or significant weakening of symptoms after the release of gases.
Why does my child have a stomach ache?
Abdominal pain is a common symptom in children and can have many possible causes. Some common causes include constipation, viral infection, gastrointestinal and urinary tract infections. Most abdominal pain in children is mild and transient and is caused by minor illnesses (eg, gastroenteritis, viral infection). Mild, intermittent pain in the central abdomen is usually not serious. In young children, it can be difficult to immediately determine the cause of mild abdominal pain. In some cases, the cause of pain may be the psychological state of the child.
There are more serious causes of abdominal pain, but they are less common. These include severe infections and problems requiring surgery, such as appendicitis.
Treatment of children of different age groups
Treatment methods for the disease depend on age. Diet, medication, and lifestyle changes may be indicated.
What help can be provided for intestinal flatulence in an infant?
First aid for flatulence in children involves alleviating the condition. A decoction of chamomile and “No-spa” (drotaverine hydrochloride) will help relieve intestinal spasms and ease colic. You can stimulate the passage of gases with the help of Espumisan.
Important! Children under three years of age should not be given medications that have not been approved by the supervising pediatrician.
can be placed on the baby's stomach . Massage is also used to relieve discomfort: circular movements without pressure in a clockwise direction. The child's condition can be alleviated by placing him on his back and bending his legs several times, each time bending them towards his stomach and straightening them. Source: A.N. Surkov, V.V. Chernikov Symptom of flatulence in young children: causes and ways of correction // Pediatric pharmacology, 2013, v. 10, no. 1, pp. 78-82
If these measures do not help, a special gas outlet catheter can be used.
A nursing mother should be careful when consuming gas-forming foods - legumes, cocoa, coffee, chocolate, sauerkraut, baked goods, muffins, grapes, fresh vegetables and fruits.
After each feeding, you need to hold the baby upright so that excess air comes out with a burp.
You can use any medications only as prescribed by a doctor. This could be Espumisan, enterosorbents, eubiotics.
Treatment of older children
In some cases, digestive enzymes are prescribed in tablets. Changes are made to the diet, from which harmful foods are excluded: carbonated drinks, chips, legumes, potatoes, raw vegetables and fruits, chocolate, cocoa. It is important that the child does not overeat. To relieve spasms, improve motility and increase the tone of the intestinal walls, the doctor may prescribe a special drug, for example Iberogast.
It is imperative to observe what the child eats to determine what food causes bloating. Food should be steamed or boiled, and its temperature when served should be moderate. It is recommended to drink more - still water, herbal decoctions. You need to eat 4-6 times a day in small portions and chew your food thoroughly.
Authorized products:
- low fat cheeses;
- dairy products;
- lean fish;
- porridge without milk;
- rabbit meat, poultry;
- pumpkin, beets;
- egg dishes (not fried).
The child should move more, walk, play with peers. It is important to protect him from stress.
kitten has diarrhea
Diarrhea in a kitten, due to indigestion, can be treated at home. It is important to know and understand how to do this correctly. The kitten has diarrhea, what should the owner do:* Remember what your pet ate. Perhaps they gave me new food. The wrong food means the kitten has diarrhea. Temporarily remove fish, fermented milk and, above all, milk from your diet. Buy veterinary food that is used to treat diarrhea.
* Do not introduce other foods into your diet. Enter later when it passes. Give in microdoses and one product for 4-5 days. Only after you are convinced that it is OK, add volume.
* Do not leave leftover food on the table. The kitten is able to jump onto the table and eat its belly there. Overeating contributes to the appearance of diarrhea in a kitten.
* While treatment is taking place, reduce the amount of food you eat. Fresh water for drinking is available in an accessible place. The pet may refuse to eat, but will want to drink water.
* Try to pay more attention to the baby, try to play. If he doesn't show interest, leave him alone... let him sleep. Don’t pick him up for no reason; create conditions for relaxation. Arrange a place to relax where you will feel safe.
* As soon as the kitten has diarrhea
withhold food and offer water. If he doesn’t drink, then drink from a syringe - this will help avoid dehydration. Once about 12 hours have passed, start feeding in tiny doses. When the kitten's diarrhea subsides, also feed in tiny doses. Eating too much may cause the diarrhea to return. It is better to underfeed than to overfeed.
* The tummy is swollen - the gases are tormenting. Try giving activated carbon or smecta.
* Do not treat with antibiotics unless diarrhea is a concern.
* For the patient, create an atmosphere of silence, do not disturb - provide a place to rest.
* It is advisable to submit stool for testing. Tests will show the reason.
* On the first day of diarrhea, let the kitten fast. Only water for a day. A day has passed - a gentle diet - give me rice, the same chicken. You will switch to your usual diet when your condition stabilizes.
* While he is recovering, give up the factory feed. Feed with boiled yolk, lean boiled meat, rice porridge, diluted with meat broth. If he doesn’t eat it, crumble the boiled chicken breast.
*When kittens have diarrhea, the main problem is dehydration. It’s not diarrhea that’s scary, but the loss of fluid in the body—potassium and sodium salts are lost, which leads to disruption of water-salt metabolism, and diarrhea only gets worse.
* Look at your pet - the eyes are dull, the nose is dry and the mucous membranes of the mouth are dry. These signs indicate that there is not enough fluid in the body. Try to determine the degree of dehydration. Pull back the skin on the withers and release. By the speed of skin straightening, you will understand how dehydrated the body is. Straightens in 2 seconds - dehydrated. The pulled skin stuck together - extremely severe dehydration.
* We save the pet - in this situation, Ringer's or Ringer-Locke solution is urgently administered. Inject into the withers. Ideally, a dropper in a veterinary clinic. Sometimes it is possible to limit yourself to Regidron. Dilute two teaspoons in a glass of boiled water and feed your pet, replacing the water.
* It hasn’t improved in eight hours - then intravenous infusions cannot be avoided. Damaged intestinal walls are no longer able to absorb water, and this is a serious case and fluid from dehydration should only be administered intravenously.
treating diarrhea in a kitten at home
- Atoxil, Enterosgel - stops diarrhea in a kitten.
- Loperamide - used after defecation.
- Levomecithin - it’s a pity that the bitter one is difficult to drink.
- Smecta stabilizes intestinal motility, as well as for the normal functioning of the mucous membranes.
- Dicynon - intramuscularly if there is blood in the stool. Stops bleeding.
- Phthalazole is good for eliminating diarrhea. Crush 1⁄4 tablets, pour the powder into a drinking cup and pour 2-5 ml of warm boiled water. Shake, draw into a syringe and slowly pour into the animal’s mouth. Give twice a day.
- Activated carbon - grind and give with food. Or dilute it with water, draw this suspension into a syringe and give it to your pet. Do this every 6 hours until the signs of intoxication go away.
Treatment of diarrhea in kittens with folk remedies
- Boil rice - boil, drain and give to your pet.
- Congee is also good. Draw into a syringe and drink. The decoction will envelop the stomach and thus prevent the toxins from doing harmful things, and will also remove the toxins out.
- Crushed oak bark strengthens the stomach. Bring 60 ml of water to a boil, add 1 teaspoon of bark and place in a steam bath for about 15 minutes. Cool, divide into 4 shares and pour 1 share into the animal’s mouth through a syringe.
- Sage and wormwood are pharmaceutical anti-inflammatory agents. Take half a teaspoon, cover with 80 ml of boiling water and simmer on low heat for 15 minutes. Strain and drink in small portions
food for diarrhea in a kitten
When a kitten has diarrhea, nutrition is of utmost importance. Feed your pet properly with light food.
Let's consider the rules of feeding a kitten who suffers from diarrhea.
* fasting diet for 12 hours - only water. After this, boiled rice + boiled chicken or beef. Refused - through a syringe, rice water or meat broth.
* make it a rule - food is low-calorie, gentle and not greasy
how to recover:
* boiled egg
* meat or chicken broth
* rice porridge + minced chicken or beef.
* kefir
Conclusion: the owner is responsible for the health of the pet. Don't forget to monitor your pet's diet! Get your vaccinations on time! Remember - health means life is in the hands of the owner!
Disease prevention
The child should eat in a calm environment. While eating, you should not turn on the TV, because it is distracting and encourages the swallowing of air with food. Meals should be spaced throughout the day and always be at the same time. You can’t eat hastily and on the go. It is recommended to place the baby on his stomach for 5 minutes before feeding. After eating, place it in an upright position for a few minutes.
Sources:
- P.L. Shcherbakov. Flatulence in children // Difficult Patient, 2006, vol. 4, no. 9, pp. 66-72.
- N.L. Pakhomovskaya, M.M. Venediktova. Flatulence: causes and ways of correction // Consillium Medicum. Pediatrics, 2022, No. 2, pp. 32-36.
- A.N. Surkov, V.V. Chernikov. Symptom of flatulence in young children: causes and ways of correction // Pediatric pharmacology, 2013, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 78-82.
Grek Elena Anatolyevna Clinic
Author of the article
Grek Elena Anatolyevna
Doctor of the highest qualification category
Specialty: gastroenterologist
Experience: 24 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
What can be done to relieve a child's pain?
There are many things parents can do to relieve their child's stomach pain. Often something as simple as gently rubbing the belly with your hand or distracting the child's attention can help relieve the condition. You can also offer the child a drink of water or sit the baby on the potty or toilet. If this does not help, the child can be given paracetamol in the dosage recommended for the appropriate age and weight. Children should not be given aspirin because it can cause a rare but serious condition called Reye's syndrome.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with a gastroenterologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (comprehensive) | 2900 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space (and retroperitoneal lymph nodes) | 1400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder | 1400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (comprehensive) | 2900 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the liver | 1600 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1600 rub. |
| Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection (HELPIL test) | 1200 rub. |
| Colonoscopy | 5050 rub. |
| Biopsy during endoscopic examination (1 biopsy) | 1000 rub. |
| Body composition assessment - bioimpedance analysis | 2150 rub. |
| Body composition assessment - repeated (bioimpedance analysis) | 1750 rub. |
| Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EFGDS) | 3050 rub. |
Differential diagnosis: conditions causing abdominal pain.
| Age | Main reasons |
| Newborns | Infantile colic, enterocolitis (eg, cow's milk protein-induced), pyloric stenosis |
| Infants and children <2 years of age | Viral diseases, infantile colic, intussusception, mesenteric adenitis, reflux esophagitis, Hirschsprung's disease. |
| 2-5 years | Viral diseases, intussusception, appendicitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, mesenteric adenitis, hemolytic-uremic syndrome, testicular or ovarian torsion, pneumonia, bacterial peritonitis |
| > 5 years | Viral diseases, appendicitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, mesenteric adenitis, testicular or ovarian torsion, epididymitis, pneumonia, inflammatory bowel disease, cholelithiasis, pancrolithiasis, psychosomatic pain |
| Teenagers | Rupture of an ovarian cyst, testicular or ovarian torsion, epididymitis associated with the menstrual cycle, sexually transmitted infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, urolithiasis, functional pain in stomach. |
| All children | Abdominal trauma, gastroenteritis, constipation, urinary tract infection, pyelonephritis, sepsis, diabetic ketoacidosis, intestinal obstruction (eg, abdominal adhesions), hepatitis, hernia, malignancy |
What to do if the cause of the child’s abdominal pain has not been found?
Often in children suffering from abdominal pain, the cause of their condition is not discovered. Some children may have repeated episodes without a clear cause, and this can be confusing for parents. This condition is sometimes called functional abdominal pain, and is quite common (affecting 10-15% of children). Some children may also have recurring stomach pain when they are worried (about themselves, friends, family or school). If your child experiences recurring episodes of pain, it is important that he is seen by his regular healthcare provider, who can help diagnose and treat the pain.
If there is any doubt about the child’s condition, the doctor will suggest hospitalization to observe how the child’s condition develops. If it turns out that he needs emergency help, the child can be quickly operated on. If nothing serious is revealed and the pain goes away, the child will be sent home, under the supervision of a pediatrician and parents.
Call a doctor at home Make an appointment with a doctor or call +7 (812) 331-17-74
If you give a child paracetamol, will this prevent the doctor from making a correct diagnosis?
There is a perception among parents and doctors that giving a child a painkiller such as paracetamol may prevent the doctor from making a correct diagnosis. However, data from numerous studies have shown that this is not the case. Prescribing paracetamol to a child will not prevent the doctor from diagnosing the child's condition and will not mask the serious cause of the abdominal pain. In fact, a simple pain reliever such as paracetamol may be a good measure to use before deciding whether to take your child to the doctor.