A kitten's severely swollen belly is often a symptom of a dangerous disease, the untimely treatment of which can lead to dire consequences. But the reason for this pathological condition lies in other disorders. Therefore, if the owner notices that the cat has an unnaturally enlarged belly, the pet is not eating well, is lethargic, or cannot go to the toilet on its own, it is better not to hesitate to visit the veterinarian.
Diagnostics
Once you notice a difference in your cat's natural flatulence, the next important step is to see your veterinarian. Initially, your veterinarian will want to obtain a complete medical history. Diet patterns and specific foods can help identify the immediate cause of your cat's gas. Therefore, it is important to record exactly what your cat eats, when she eats, and how much. Additionally, your veterinarian may order a hypoallergenic food trial to determine if a food allergy is to blame.
If the problem is caused by a more serious complication, such as a medical condition, your veterinarian will recommend further diagnostic tests. For example, if parasites are suspected to be the culprit, your veterinarian will order stool samples as they are very useful in identifying any worms. If your vet suspects IBD, he will order a gastric biopsy, a procedure that can be done either through abdominal surgery or an endoscope. An endoscope is much less invasive, but both procedures have certain risks that your veterinarian should consider.
Your veterinarian may recommend a few more tests. Some of these include urinalysis, complete blood count (CBC), biochemical profile and abdominal x-ray.
© shutterstock
Symptoms of Gas in Cats
Gas is certainly a typical digestive reaction, but unfortunately, it can also indicate a more serious problem. There are a few obvious signs your cat may be exhibiting, so be on the lookout if you wish:
- Excessive flatulence
- Unpleasant/strong odor
- Vomit
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Protruding belly
- Whirlwind (low rumbling from the lower abdomen)
© shutterstock
Treatment
Treatment of the underlying disease is necessary if it is identified.
There are several rules to reduce the symptoms of bloating:
- Try to feed your cat more often, in small portions, in a calm environment to prevent aerophagia. If you have several animals competing for food, feed them separately in different rooms. It is possible to use special bowls that prevent the rapid swallowing of food;
- make sure the food is fresh, dry food must be in a tightly closed bag, in a bowl for no more than a day, wet food and homemade diet are removed as soon as the cat finishes eating;
- block the cat's access to the trash can;
- Choose a cat food that is low in fiber and highly digestible, or consult a veterinary nutritionist. You may need a therapeutic diet (prescribed by a veterinarian).
Diagnosis and treatment
Therapy is aimed at eliminating the cause of bloating. Symptomatic treatment is prescribed.
If the doctor determines that flatulence is caused by poor nutrition, then he prescribes an appropriate diet. Your cat's food should consist of foods low in carbohydrates.
What to do and how to help your cat before visiting the clinic? As first aid, you can give her a cleansing enema (if you know how) and give her the following medications:
- Traumeel (to relieve spasms).
- Activated carbon, Polysorb (to remove gases).
- Lactoferon (to avoid the development of putrefactive microflora).
- Liarsin (to normalize the digestion process).
Homeopathic remedies (Nux vomica-homaccord, Engistol) have proven themselves well in the treatment of flatulence and intestinal disorders. Dill water helps, as well as infusions of cumin, chamomile, and fennel.
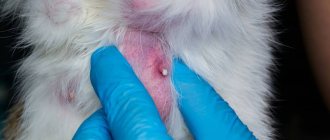
Bacterial infection of the deep layer of skin
Occurs when microbes enter deep into the dermis.
Read also: How to make a plane from foam plastic
Furuncle
First, a painful node appears, then an abscess matures in its center. After 5–7 days it opens, a purulent-necrotic core is released, and the wound is scarred. When there is more than one lesion, they speak of furunculosis.
Carbuncle
These are several boils united into a common infiltrate. The place looks like a purple-bluish tumor. Pain increases, well-being suffers, body temperature rises. After opening the formation, a deep ulcer remains, healing with a scar.
Acne (blackheads)
- inflammation of the sebaceous gland ducts due to blockage. Pustules form on the face, chest, and shoulders. Their contents dry out to crusts, after which, when rejected, scars or bluish spots remain.
Hidradenitis
Purulent inflammation of the sweat glands. The process often recurs. Favorite localizations are armpits, inguinal folds, under the mammary glands. Deep painful nodes appear, bluish-red on the outside. They are opened with the separation of liquid pus.
Read also: Botox for hair [what is it]
Erysipelas
Occurs in people who are individually predisposed. Foci of inflammation are clearly limited. The affected area is swollen, hot, bright red, with bursting blisters. The disease is accompanied by fever, intoxication, and severe pain.
Deep pyoderma can be complicated by inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and nodes, abscess, and sepsis.
How to rid a cat of flatulence
Treatment of chronic indigestion is a long process based on “experiments” with the diet, followed by tests to track trends.
If your cat has been suffering for years, consult a doctor if there are single manifestations:
Enterosgel, activated carbon or Atoxil as an absorbent.
Smecta, Almagel or analogues, to eliminate intestinal irritation.
Espumisan or an analogue drug that gently removes gases from the intestines.
Veterinary Baikal or other preparations with probiotics to repopulate the intestinal microflora.
A diet of boiled rice in water or low-fat broth until flatulence is completely eliminated.
How can herpes be dangerous?
Herpes can cause many complications. Some of them are life-threatening.
- Bacterial complications. Most often, bacteria simply attach to the virus and the blisters fill with pus. If the blisters have already burst, then the ulcers become covered with pus, the pain in the lip becomes unbearable and a crust does not form.
- Herpetic stomatitis is a lesion of the oral mucosa. The disease begins with a sharp increase in temperature, salivation and sharp pain when chewing food. There are many blisters in the mouth, similar to herpes on the lips.
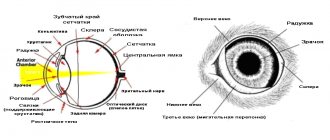
- Herpetic eye damage begins with pain in the eyes and lacrimation. A person cannot open his eyes due to severe pain. A dangerous condition that can result in blindness.
- Herpes of the esophagus. Occurs when herpes spreads from the lips. There are difficulties when swallowing, severe pain, refusal to eat and weight loss.
- Herpetic pneumonia and herpetic hepatitis occur in people with immunodeficiency and occur together with bacterial and fungal processes.
- Herpetic damage to the nervous system occurs in the form of meningoencephalitis and is the most severe form of herpes. It begins with a sharp headache, nausea and vomiting, high fever, movement disorders and convulsions. The disease is unfavorable.
Photo: To avoid complications, you need to start treating herpes in a timely manner.
The main causes of spasms in children
The diseases and causes that can lead to this problem are quite extensive. It is worth noting that in children, spasms and pain are most often observed in the gastrointestinal tract and accompany various organic and functional diseases of the stomach and intestines. The difference between organic and functional diseases lies in the presence of structural or biochemical changes in organs and tissues. Organic diseases have them, but functional ones do not. Functional pathology is caused by changes in the regulation of these organs, which can also cause symptoms similar to organic ones. In young children, spasms are more often observed against the background of functional pathology. With age, the incidence of organic pathology increases. The most common causes of excessive contraction and abdominal pain in children are:
- Intestinal colic.
- Functional diarrhea and constipation.
- Acetonemic syndrome.
- Biliary dyskinesia, inflammation of the gallbladder.
- Gastritis, peptic ulcer.
- Diseases accompanied by malabsorption syndrome. Malabsorption is a malabsorption of substances in the small intestine.
- Inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Chronic colitis, intestinal infections, parasitic infestations.
There are also many other diseases that are accompanied by excessive contraction of muscle cells and pain. We list only the most common of them. Often spasms are accompanied by inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract (cystitis, pyelonephritis). In this case, they occur in the urinary tract. Often, during the formation of the menstrual cycle, teenage girls may experience severe cramps and pain in the lower abdomen. This problem is called dysmenorrhea. Vascular spasms often develop when the temperature rises in children, which is characterized by the appearance of “white fever”. In this article we will briefly talk about the main causes of spasms in children, as well as the diseases that lead to them. Let us explain the basic principles of use and the mechanism of action of drugs used for this pathology.
There are many other diseases that are accompanied by excessive contraction of muscle cells and pain.
Prevention
Prevention of a bloated abdomen in a cat, as well as any other serious pet disease, comes down to following the rules for keeping cats in an apartment:
- It is necessary to regularly treat worms: kittens - once a month, adult cats - once every 3 months throughout their lives.
- Follow the principles of proper animal nutrition. If you are not sure about the chosen feeding tactics, make an appointment with a veterinary nutritionist: the doctor will be able to select not only ready-made food, but also a balanced homemade diet.
- It is advisable not to allow pets to walk outside to avoid infection with the feline infectious peritonitis virus, for which there is currently no vaccination.
- It is necessary to install special “anti-cat” nets on the windows, which prevent not only falling out of the window, but also getting stuck in windows open for ventilation.
Disease prevention
The best method of dealing with any disease is its prevention. Preventive measures against dropsy are available to any cat breeder, the main thing is not to forget about it:
- Compliance with the diet (when preparing a diet, you can contact a veterinarian).
- Walks in the open air.
- Fortification (you can select good vitamins with the help of a veterinarian).
- Avoidance of stressful situations (cats under stress have reduced immunity).
- Preventive vaccinations, as well as treatment for worms, fleas and other parasites.
- Preventative examinations at the veterinarian.
Ascites (abdominal dropsy) is an accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity, but this phenomenon cannot be called an independent disease. Typically, ascites occurs against the background of another disease as a symptom. This disease is the cause of dropsy. Therefore, treatment must be comprehensive. Veterinarians prescribe groups of drugs aimed at combating symptoms, and the underlying disease is treated separately.
Bloating in kittens
When purchasing a kitten, always inspect its tummy. In a healthy animal it should be soft and small. A temporary increase may occur after a recent feeding or shortly before going to the toilet. If a healthy baby's tummy becomes the size of a balloon or a pear, be sure to worm your pet and take him to the vet. Anti-parasite tablets are given at intervals of 2 weeks. At the first ingestion, all adult individuals die, and at the second, the remaining eggs, which have evolved into adult worms, die.
What to do if your cat has a big belly and a thin back
The owner of the animal needs to carefully monitor the health of his pet and promptly pay attention to changes in his figure. It is important to be able to distinguish an increase in abdominal volume from simple obesity.
When fat deposits can be found in the chest area, you simply need to reconsider the animal’s diet. But if the cat has a large belly and a thin back, ribs and pelvic bones noticeably protrude, then this may be an alarming sign.
Unsterilized cats should first of all exclude the possibility of pregnancy and pyometra. In the second case, only timely operation will help. With the development of viral peritonitis or leukemia, the quality of life of the animal can be improved with timely diagnosis.
Since an enlarged abdomen is one of the symptoms of deadly cat diseases, the sooner an accurate diagnosis is made, the greater the pet’s chance of recovery.
Diagnostics in a veterinary clinic
The diagnostic task is to differentiate ascites from other diseases with similar symptoms, for example, from exudative peritonitis. Thus, with peritonitis, an increase in temperature, pain when pressing on the abdomen, and a significant number of leukocytes and proteins are observed.
And finally, the most obvious sign of peritonitis is the transience of the disease. With ascites, as mentioned above, the disease has a long development.
Necessary diagnostic methods for suspected ascites include:
- taking anamnesis;
- analysis of clinical symptoms;
- palpation of the abdominal cavity;
- urine and blood tests;
- X-ray of the peritoneum, sternum;
- Ultrasound of the chest and abdominal cavity;
- fluid examination;
- endoscopy;
- biopsy.
Differential diagnosis helps to identify the underlying pathology that caused ascites. Without determining the provoking factor, it is impossible to prescribe adequate treatment, since the amount of fluid will increase with each relapse.
Treating bloating at home
At home, treatment of bloating is possible only in cases where there is simple intestinal flatulence caused by aerophagia or feeding of low-quality food.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that lead to increased gas formation. Among the medications the cat is given - children's espumezan, smecta, lactobacterin.
If, after these measures have been taken, your cat’s abdominal bloating persists, you should immediately contact your veterinary clinic. The veterinary clinic will conduct a thorough clinical examination and, if necessary, prescribe additional tests. And in accordance with the diagnosis, appropriate treatment will be carried out.
Source
Probability of death
The likelihood of death depends on the situation. The exact indicator is determined only by diagnostic results.
Remember that complications are possible even with non-hazardous factors. The bloating puts pressure on the chest, preventing normal breathing. There is also a high risk of gastric volvulus, intestinal rupture, tissue necrosis and sepsis. To avoid unpleasant consequences, contact your veterinarian if you have any alarming symptoms.
Manifestations of flatulence
With flatulence, people usually complain of bloating (a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the abdomen), as well as aching pain in the abdominal area. The pain can also be acute (so-called “gas colic”). The pain usually goes away or decreases after the gas has passed.
There are two possible manifestations of flatulence.
At first, the passage of gases is difficult. In this case, there is an increase in the abdomen as a result of bloating of the intestines. The main complaint is discomfort or pain in the abdominal area.
With the second option, the gases escape, but this process itself causes concern. This happens often, violently and is not always controllable. This condition can significantly complicate our lives. There may be no pain; patient complaints are usually formulated as “rumbling” or “transfusion” in the abdomen. Flatulence may also be accompanied by:
- belching;
- bowel problems (constipation or diarrhea);
- nausea;
- bad breath;
- decreased appetite;
- shortness of breath (breathing disturbance due to flatulence is called dyspeptic asthma
. The swollen intestines compress the diaphragm, preventing a normal inhalation).
Sometimes, with flatulence, manifestations from the cardiovascular system are observed: a burning sensation in the heart area, headache, irregular heartbeat, etc.).
Possible causes of bloating
Next, we will consider the possible causes of a hard abdomen in a cat, conditionally dividing them into non-dangerous and dangerous (i.e., life-threatening for the pet).
Non-hazardous conditions
- Obesity is the scourge of modern domestic cats. Locked within four walls, cats do not hunt and move little, making obesity almost inevitable. Abundant deposits of subcutaneous fat in the abdominal area of a cat can form not only folds, but also a voluminous large belly.
- Pregnancy is a normal physiological process during which the pet's abdominal cavity increases significantly. Of course, this condition occurs only in females. Pregnancy often comes as a surprise to cat owners, especially if the pet ran outside the day before or you picked it up recently. Pregnancy in cats lasts about two months. If the cat has a large belly, but you are sure that she is not pregnant, it is still necessary to do an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity to exclude an “interesting” position.
- Flatulence, or bloating, can be classified as both non-dangerous and (in advanced cases) and dangerous conditions. Most often, this condition occurs when the pet is suddenly overfed (this often happens if we take a hungry cat from the street), when feeding spoiled food or giving food that is unsuitable for the cat (for example, a large portion of milk for a cat that is not used to drinking it).
Dangerous conditions
- Viral diseases that can lead to bloating. For example, infectious peritonitis is a dangerous, contagious and difficult to treat disease.
- Neoplasms , such as lymphoma, often produce effusion into the abdominal cavity and, as a result, a distended abdomen. Despite the fact that such conditions are most often incurable, timely diagnosis and chemotherapy can extend the pet’s life by several years.
- Heart disease can lead to something called congestive heart failure, which can cause fluid to accumulate in both the chest and abdomen.
- Coprostasis , or constipation, is a common problem in domestic cats. When the condition is neglected, the abdomen of cats and kittens enlarges, thickens, becomes inflated and hard. Unfortunately, enemas do not always help in such conditions, and surgery may be required.
- Kidney failure caused by diseases such as chronic kidney disease. In advanced cases, it can also lead to hydrops of the abdominal cavity, manifested by bloating in cats and kittens.
- Liver diseases , such as lipidosis and cirrhosis, cause blood to pool in the abdomen and result in ascites (dropsy), causing the cat's belly to become distended.
- Injuries , most often associated with a fall from a height, can lead to damage to the spleen, large vessels and other organs, causing internal bleeding and rapid enlargement of the abdomen.
- Pyometra , or purulent inflammation of the uterus, is very common in adult unsterilized cats, especially after the use of hormonal drugs to stop heat. It is for this reason that all cats are recommended to be sterilized.
- Worm infestation is much more common than domestic cat owners might imagine. In advanced cases, parasites can clog the intestinal wall, cause perforation of its wall, peritonitis and, as a result, the cat will have a painful, hard stomach.
Flatulence as a sign of “pancreatic” problems
Everyone is undoubtedly familiar with flatulence. But, in some cases, the symptom does not carry anything other than psychological discomfort. In others, it signals digestive disorders. So how can we distinguish what is acceptable from what is pathological? And what is the connection between flatulence and the “health” of the pancreas?
"Gas" standards
Calculating the volume of excreted intestinal gases in domestic conditions is a virtually impossible task. But, normally, this figure reaches 2.5 liters per day.
The thing is that the digestive system is in direct contact with the air of the environment. And therefore, part of the gas enters the intestines when swallowing, when eating.
“Gas” is also added by intestinal bacteria, which form it during their life processes.
At the same time, the normally predominant saccharolytic microbiota (lacto-, bifidobacteria, streptococci and others) for the most part uses carbohydrates that are not absorbed in the small intestine “for food”, and “waste” in this case becomes lactic and acetic acids, carbon dioxide, water and hydrogen.
Carbon dioxide is further converted by other bacteria, and hydrogen is absorbed into the blood and excreted through the lungs.
However, if the amount of undigested carbohydrates increases significantly (for example, with excess consumption of sweets, lactase deficiency or deficiency of pancreatic amylase), the concentration of hydrogen, acids and, accordingly, released gases with a sour odor also increases.
Some representatives of the intestinal microbiota do not use carbohydrates as food, but sulfur-containing compounds, in particular proteins. With the formation of hydrogen sulfide, ammonia and cadaverine.
In this case, “gases” acquire a pronounced putrid or rotten odor. And the cause of this problem is often a deficiency of proteolytic (breaking down proteins into amino acids) pancreatic enzymes.
When flatulence is no longer “safe”
As already noted, the formation and release of intestinal gases is a normal and inevitable phenomenon. However, only in the case when their volume and characteristics do not cause either psychological or physical discomfort.
If flatulence bothers you regularly or is present “background”, accompanied by abdominal pain and/or changes in frequency (diarrhea or constipation) and character (for example, “fatty” stools), as well as general weakness and fatigue, you should exclude, at a minimum, enzymatic insufficiency of the pancreas, as one of the most common causes of flatulence.
It is also worth noting the fact that clear clinical signs of pancreatic insufficiency appear when enzyme deficiency reaches approximately 90% of normal. And up to this level, the symptoms are often “mild”, inconsistent and associated with the nature of the diet.
How to check
Changes in the coprogram may indicate pathology:
- neutral fats,
- muscle fibers with striations,
- increase in the amount of extracellular
- or the appearance of intracellular starch,
- presence of iodophilic flora
However, they can only serve as indirect signs of “pancreatic” problems, since they also accompany a number of other digestive disorders.
A more “specialized” study of the functional state of the gland is a stool analysis for pancreatic elastase. Because this proteolytic enzyme passes through the entire digestive tract almost unchanged.
A decrease in elastase in feces is the most reliable sign of pancreatic insufficiency. This applies not only to elastase itself, but also to other enzymes of the gland, even at the earliest stages of the pathology.
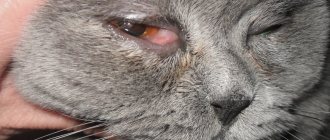
Why do cold sores appear on the lips?
Those who suffer from herpes have noticed that exacerbations begin along with ARVI. Herpes occurs when immunity decreases, the protective forces of which are used to suppress ARVI. Colds on the lips also appear when the body’s defenses are weakened: with chronic fatigue, lack of sleep, frequent stress, poor diet, alcohol abuse and active smoking, in women at the beginning of pregnancy and in the first 5-7 days after childbirth.
Photo: Colds on the lips can only appear if the immune system is weakened
What to do to eliminate the pathology?
If the kitten's sides are swollen due to a severe internal illness, the doctor will hospitalize the pet and, if necessary, perform surgery. In other cases, you can deal with the problem at home. For constipation, you can give your pet the drug Duphalac and use microenemas. Vaseline oil will help improve digestion; its dosage is 0.1 ml per 100 g of weight. It is recommended to give the product 2-3 times a day.
If the cat's swollen sides are a sign of helminthic infestation, in this situation antihelminthics will help normalize the condition. Doctors at the Zoovet clinic point out that not every drug is intended for kittens aged 2-3 months. Therefore, the veterinarian must select the medicine, taking into account the baby’s age, the degree of invasion and other individual characteristics.
After giving birth, the cat's abdomen will return to its normal position without special treatment. The problem of overeating is easy to eliminate. Often, increased appetite is associated with a lack of vitamins and other elements in the body. Therefore, it is better to feed your cat with ready-made food, where all the ingredients are balanced and selected for a certain age.
Source
What should the owner do
Under no circumstances should you play Aibolit or give your pet medications without consulting a veterinarian. Only a specialist can prescribe medications and set their dosage, based on the severity of the pathology, general condition and age of the animal.
Uncontrolled use of medications can lead to potassium being excreted from the body along with urine. This will worsen the cat’s well-being and lead to complications, even to the point where the animal dies. Human diuretics are especially dangerous in this regard.
Increasing their dosage independently can lead to disturbances in the level of electrolytes and leaching of fluid from the microcirculation network. This is fraught with the possible development of encephalopathy.
At the first opportunity, you should take the animal to the clinic so that the doctor can examine it and prescribe appropriate treatment.
A cat with abdominal hydrops is prescribed a therapeutic diet that involves limiting the consumption of water and any other liquid. The food of a sick pet should be nutritious, balanced in vitamins, minerals and carbohydrates and consist mainly of proteins.
The diet includes meat, poultry, sea fish, cottage cheese, kefir. You can add salt to food, but the amount of salt should be minimal.
What to do?
Bloating is an abnormal enlargement of the abdominal cavity. The term usually refers to abdominal enlargement rather than simple fullness. In a cat, bloating can be a consequence of poor nutrition or a symptom of a large number of diseases, including fatal ones. The most common causes of this phenomenon are discussed below.
Coprostasis
Constipation, or coprostasis, is a blockage of the large intestine with feces. The causes of coprostasis may be the following:
- A sharp transition from mother's milk to other foods.
- Binge eating.
- Eating bones, especially heat-treated ones.
- Low protein content in the diet.
- Accumulation of hair in the gastrointestinal tract (when licking itself, the cat swallows some hair).
- Dehydration from not drinking enough.
and:
- A large number of worms.
- Prostate enlargement (in males).
- Abscess or cyst in the intestinal tract.
- Obesity.
- Problems with intestinal motility.
The norm is considered to be stool once a day. When feeding natural food, periodic absence of stool for 3 days is acceptable.
Symptoms:
- Oblong lumps can be felt in the abdomen.
- Vomiting (often with constipation from wool).
Treatment:
- Warm water enema.
- Vaseline oil - 1 ml per kg of body weight at intervals of 8-10 hours orally (it is important to avoid getting into the lungs).
- Magnesium sulfate – 20 ml of concentrated water solution, orally.
Helminthiasis
It is almost impossible to protect a cat from worms. A pet can pick them up through contact with outdoor shoes, from an eaten insect, from raw or undercooked fish or meat. They affect internal organs. Symptoms:
- Bloating.
- Constipation alternating with diarrhea.
- Worms in feces indicate a large number of them in the body.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting with worms.
Treatment consists of using anthelmintic drugs for external and internal use.
Panleukopenia
Feline distemper, or panleukopenia, is caused by one of the parvoviruses. Summer and late autumn are the most favorable times for the spread of the virus. Its carriers can be blood-sucking insects, ticks and healthy animals.
2–12 days after the virus enters the gastrointestinal tract, it affects the intestinal mucosa, lymphoid tissue and bone marrow.
In animals older than 3 months, the disease causes the following symptoms:
- Body temperature 40–41 degrees.
- Weight loss.
- Refusal to drink despite being thirsty.
- Vomit.
- Diarrhea.
- Bloating.
- Severe abdominal pain.
About a week after the onset of symptoms, the cat has a 50% chance of recovery generally. If the temperature drops to 37–38 degrees, the likelihood of death increases. If a kitten from 1 to 3 months is infected with parvovirus, the probability of death is close to 100%.
When diagnosing panleukopenia, other diseases with similar symptoms should be excluded:
- Poisoning.
- Non-contagious gastroenteritis.
- Lymphosarcoma.
- Toxoplasmosis.
When treating panleukopenia, depending on the nature of the course, the following are used:
- Drugs against the virus.
- Drugs that activate the immune system.
- Drugs that support the functions of the cardiovascular system.
- Antiemetic drugs.
- Broad spectrum antibiotics.
- Drugs that restore electrolyte balance.
- Painkillers and antispasmodics.
During the recovery period, the following diet is necessary:
- Fresh lactic acid products.
- Rice water with the addition of boiled egg white.
- Puree soups from cereals, vegetables with the gradual inclusion of boiled minced meat.
Immunity after illness lasts 3–4 years. Prevention consists of vaccination and hygiene.
Peritonitis
Inflammation of the peritoneum during a general severe condition of the body is called peritonitis. The cause is usually the penetration of infection into the abdominal cavity from the organs. This disease is often caused by a coronavirus. There are 2 forms of coronavirus peritonitis – wet and dry.
Peritonitis
The wet form leads to death 1–1.5 months after the onset of symptoms:
- The abdomen is enlarged and soft.
- Fever.
- Lethargy.
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight loss.
The dry form leads to death a year after the onset of the disease. The symptoms are the same as with the wet form, with the exception of an enlarged abdomen. There is no treatment for coronavirus peritonitis; sick animals must be euthanized.
Coronavirus usually enters a cat's digestive tract from the feces of an infected animal. Not all carriers of the virus get sick. Stress can provoke disease in healthy carriers. Most often, kittens from 1 to 4 months get sick. Predisposition to the disease is inherited.
Prevention:
- Avoiding stress.
- Avoiding crowding of animals.
- Maintaining hygiene rules.
Abdominal dropsy, or ascites, is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity without an inflammatory process. The reason for this may be:
- Heart failure.
- Liver failure.
- Disturbances of water-salt and protein metabolism.
- Abdominal wall lesions.
Symptoms:
- Bloated belly
- Reducing bowel sounds.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Difficulty in cardiac activity.
- Inactivity.
- Yellowness of mucous membranes.
Treatment:
- Diuretics.
- Cardiotonic drugs.
- Pumping out liquid.
- Limiting water and salt.
- Protein diet.
In case of acute urinary retention, the bladder may rupture, its contents may enter the abdominal cavity and peritonitis may occur. Urinary retention is not always easy to notice, as many litters instantly absorb urine. If your pet assumes a characteristic posture for urination very often, it means it is not happening. In this case, one of the following treatment options is urgently required:
- Bladder catheterization - insertion of a tube for the free flow of urine.
- Cretrostomy - making an incision for the free flow of urine.
Both treatments are performed under general anesthesia.
In the article I will list the main reasons why a cat has a swollen belly (constipation, gas, disease, etc.). I'll tell you how to help your pet and when you should contact a veterinarian.
Bloat can happen for many reasons, and some of them can be life-threatening for your pet.
A kitten's belly may become bloated due to certain foods. Often, flatulence (accumulation of gases in the intestines) results from feeding your pet milk and dairy products (especially for adult animals).
The cause of bloating may be the high content of carbohydrates in the menu: wheat, corn, etc.
Constipation is an accumulation of stool that becomes dry and hard and cannot be passed out on its own. This leads to intoxication of the body, and gases begin to accumulate in the intestines, which cause bloating.
Constipation occurs for many reasons:
- incorrectly composed diet;
- intestinal obstruction;
- accumulation of wool in the stomach;
- congenital anomalies;
- obesity and inactivity.
We suggest you read: Symptoms of worms in cats, how to recognize them by signs, treatment. Constipation can cause bloating in a cat.
Parasites actively multiply in the pet’s intestines and cause intoxication. Along with bloating, the cat also experiences other symptoms: vomiting, bowel irregularities, and the presence of worms in the feces. Moreover, the cat may be thin, but with a bloated intestine.
The animal eats a lot
Cats that eat very greedily and eat a lot often suffer from flatulence. At the same time, they swallow food without chewing it, which leads to large amounts of air entering the intestines and stomach. As a result, the intestines can swell to incredible sizes. Usually the animals themselves who live in shelters or nurseries eat so greedily.
Overeating leads to bloating in animals
Enlarged intestines can be a symptom of serious diseases of the internal organs:
- Pyometra. With this disease, pus accumulates in the cat's uterus, which is accompanied by an enlargement of the abdominal cavity. Associated symptoms: depression, fever (not always present), discharge from the loop.
- Peritonitis. An enlarged abdomen or ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity) accompanies the wet form of coronavirus infection (FIP).
- Tumors. The volume of the abdomen may increase significantly due to a malignant tumor in the abdominal cavity.
Bloating can occur with intestinal obstruction. This condition is life-threatening and requires immediate surgery. Some diseases can cause bloating
Now let's talk about what to do to eliminate a bloated belly in your pet. The method of eliminating bloating depends on the root cause of this condition:
- If flatulence was caused by poor nutrition, it is necessary to exclude all gas-forming products (primarily milk) from the pet’s diet. You can also give your pet Espumisan, Lactobacterin or Acipol.
- In case of constipation, it is necessary to exclude obstruction. If it is not there, the pet is first given Vaseline oil, and if it does not give an effect, then you can use laxatives (Lactusan, Duphalac, etc.).
- If the bloating was caused by helminths, you should give your pet a drug against these parasites. The following drugs are most effective: Milbemax, Kanikvantel, Prazitel, Drontal. In case of severe infestation, the medicine is given twice, with a break of 10 days.
- If the bloating was caused by overeating or the cat greedily swallowing air while eating, you can first fill the dry food with warm water. It is also recommended to provide your pet with constant access to food (in this case, a strictly daily amount is poured into the bowl per day).
In the event that an enlarged abdomen is the result of diseases of the internal organs, it is necessary to show the pet to a veterinarian.
Treatment of a cat should depend on the diagnosis
If your pet exhibits symptoms such as vomiting, pain, and drooling along with a bloated belly, you should consult a veterinarian.
The doctor will prescribe the necessary tests and examinations (blood tests, ultrasound, x-rays, etc.), after which he will prescribe the appropriate treatment:
- A pathological condition such as pyometra requires immediate surgical intervention. During the operation, the doctor carefully removes the uterus along with the pus that has accumulated in it.
- If the abdomen has become enlarged due to infectious peritonitis, the doctor will prescribe supportive treatment: antibiotics and corticosteroids. Also, with the wet form of FIP, the fluid that accumulates in the abdomen is periodically pumped out.
- If a cat has an obstruction, the doctor will prescribe an immediate operation, during which the root cause of this condition (foreign body, tumor, etc.) will be eliminated.